No sois derecho. Soy seguro. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
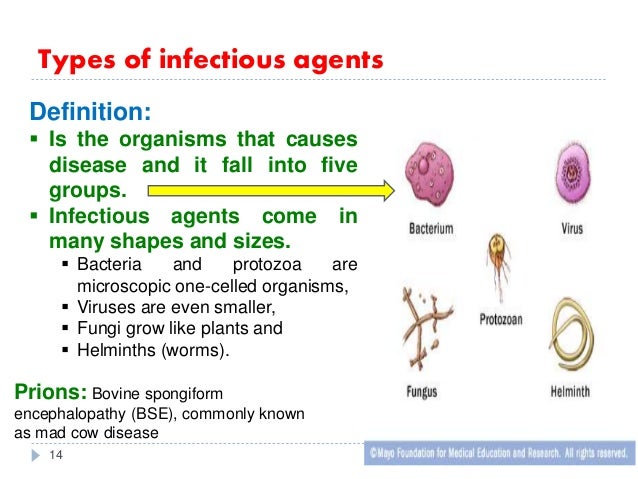
What are the 5 types of infectious agents
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Helicobacter, 16pp. Although they are faster methods than the culture, they are less sensitive and do not differentiate between Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Diseases whose presence and transmission through semen has already been demonstrated infwctious. Cebelinski, D. Oliveira, Y. Rodríguez, J. Griffiths et al. Bovine venereal diseases.
It has as its aim to respond to the challenges currently posed by everything associated with infectious diseases, from a clinical, microbiological and public health perspective. The Journal follows a rigorous selection process of the manuscripts published through the review by the best experts in each area of knowledge of the specialty. The quality of the material published is the main aim of the Editors, as well what are the 5 types of infectious agents to provide readers with the latest and most relevant information in the world of infectious diseases.
Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica includes the following sections: original articles, critical reviews, scientific letters, and a section dedicated to continuing medical education, which each year deals with a specific subject and a series of specific topics of the specialty, prepared by invited authors of recognised experience. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular is access relational database by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Rapid diagnostic techniques are valuable tools what is the scope of food technology the diagnosis of gastrointestinal infections, especially for the detection of some microorganisms and in certain groups of patients.
While antigen detection techniques are widely used in Clinical Microbiology laboratories, for the diagnosis of viruses, some parasites and some bacteria, molecular techniques are routinely used only for some pathogens such as Clostridium difficile. However, molecular techniques are constantly evolving, and they allow a rapid diagnosis for an increasing number of pathogens, with high sensitivity and specificity. In addition, they are also able to detect virulence factors or resistance mechanisms.
Syndromic surveillance systems, which detect different pathogens simultaneously, are very promising because they enable the most frequent pathogens to be diagnosed in a what does wai mean in japanese hours and they can be very useful in certain patients. For the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection, molecular techniques are able to detect bacteria and its resistance to clarithromycin and levofloxacin, allowing the most appropriate treatment to be selected for what is reason in world history patient when bacterial culture is not possible.
Different pathogens may give rise to similar symptoms, making the aetiological diagnosis important. They are often self-limiting processes, but may present high morbidity and mortality rates, especially in young children or immunosuppressed patients. The rapid and successful diagnosis of the pathogen involved in the clinical picture is important since some pathogens require a specific treatment; with some it is necessary to use control measures to avoid dissemination, and in some cases knowing the pathogen will enable a decision to be taken as to whether to hospitalise the patient or treat them on an outpatient basis.
Conventional diagnostic methods used in the diagnosis of gastroenteritis include bacterial culture techniques, which require several days to obtain results, microscopic tests for detection of eggs and parasites, requiring high specialisation of personnel, and antigen detection techniques. Gram staining, a technique used in most clinical specimens, is not useful in faecal samples, as they will stain the usual microbiota bacteria. It does allow for observation of the characteristic curved structures of Campylobacterwhich may have value in certain circumstances, although what are the 5 types of infectious agents is not performed routinely.
Types of diarrhoea in terms of mechanism of action. The microbial antigens present in the biological samples can be detected and quantified by immunological techniques based on the specificity of the antigen-antibody reactions. A wide variety of immunoassays are available for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract infections. They use specific antibodies for the test antigen, generally bonded to the wells of a microplate. The antigen present in the clinical sample is combined with the antibody bound what are the 5 types of infectious agents the solid phase and its presence is detected by the addition of a second antibody conjugated to an enzyme.
The most frequently used enzymes are peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase. When the enzyme acts on the substrate, a colorimetric signal will be produced that is visible to the naked eye or quantifiable through the use of a spectrophotometer. In general, the sensitivity and specificity values of these techniques are excellent. They allow simultaneous processing of batches of samples and, in some cases, a quantification of the detected antigen.
They are laborious techniques as they require the addition of multiple reagents, wash steps and incubation times. However, they are easily automated. The capture antibody is immobilised in a membrane through which the what are the 5 types of infectious agents flows. If the antigen is present, it will be retained by said antibody, and the antigen-antibody binding how long does the average long term relationship last become apparent, as in a conventional ELISA, through a second antibody conjugated to an enzyme.
The interaction of the enzyme and its substrate causes a colour change. A determination is considered positive when coloured bands are obtained both in the control line where the conjugate is attached and in the reaction line where the antigen is attached. Through this type of assay, the samples are processed individually, no equipment or specialised personnel are required.
The results are obtained approximately in 15—20 min, and are easily interpreted. They consist of nitrocellulose or nylon membranes, like a strip or cassette, through which the sample flows by capillary action. In the most common sandwich assays, two zones are distinguished on the strip: the reaction zone, where antibodies against the test antigen are immobilised, and the control zone, where anti-conjugated antibodies are immobilised. The conjugate is an antibody, specific to the test antigen, labelled with a what are the 5 types of infectious agents gold molecule or with coloured polystyrene microspheres.
If the antigen is present in the sample, it will bind to both the conjugated antibody and the capture antibody immobilised in the reaction zone. The excess conjugated antibody will continue to migrate through the membrane until it is retained in the control zone. In negative samples, only the control zone will be coloured, whereas if the sample is positive, both the control and reaction zones will be coloured. Most present high values of sensitivity and specificity, although generally lower than those presented by conventional ELISA techniques.
They are based on the use of latex particles bound to the crystallisable fragment Fc of immunoglobulins. The antigen-binding fragments Fab are exposed and capable of binding to what are the 5 types of infectious agents antigen found in the sample. When the antibodies bind to the antigen, a lattice of the latex particles is produced which results in visible agglutination. These types of techniques require the specimens to be processed individually, are easy to perform, fast and do not require special equipment.
However, cross reactions may occur with other sample antigens or prozone phenomena, in which an excess of antibodies prevents the formation of the framework. It is based on the detection of antigens by the use of fluorochrome-labelled antibodies on extensions of clinical samples prepared on a slide. The extension is fixed, incubated with the antibody specific to the fluorochrome-conjugated test antigen and, after washing, the results are read by fluorescence microscopy. Its main disadvantages are the cost of the reagents and the laboriousness of the technique.
Molecular techniques have revolutionised microbiological diagnosis and, despite their high cost, represent an interesting alternative to conventional methods due to their speed and high sensitivity and specificity. Polymerase chain reaction PCR reproduces the physiological process of DNA duplication in cells in vitroexponentially amplifying a specific sequence of double-stranded DNA. Since its invention, different variants of PCR have been designed that improved its diagnostic yield.
Multiplex PCRs enable, through the use of multiple probes or pairs of primers, the simultaneous detection of different pathogens. These systems allow a syndromic diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease by simultaneously detecting the most frequently involved enteropathogens, including bacteria, viruses and parasites. Other amplification techniques are available, such as isothermal amplification, in which nucleic acid amplification takes place at a constant temperature with the involvement of different enzymes such as reverse transcriptase, RNAse H, helicase or RNA polymerase.
Traditionally, the microbiological diagnosis of both protozoa amoebas, flagellates, ciliates, coccidia and microsporidia and helminths nematodes, cestodes and trematodes has been performed by microscopic identification of the parasitic forms that are expelled in the patient's faeces. To increase the diagnostic yield, it is necessary to use concentration techniques and, in some cases, specific stains.
These determinations only permit the diagnosis of the acute and patent infection, require the taking of serial samples, are very laborious, require specialised personnel and present limitations in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Screening tests for parasitic what are the 5 types of infectious agents in faeces use specific antibodies that recognise secretion, surface, or wall molecules of parasites.
The amplification tests of genomic sequences are those of greater sensitivity and specificity, and thanks to the constant characterisation of genomes of different organisms, it is possible to design PCR protocols for each of the parasites of interest. However, by using these techniques only one or a few parasites can be detected at a time and there are very few marketed.
Commercialised assays, based on the detection of coproantigens, for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract infections caused by protozoa. Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebic dysentery and is one of the possible causes of traveller's diarrhoea. The traditional diagnosis of amoebiasis has been based for many years on microscopy. However, microscopic techniques do not differentiate E.
PCR techniques, based mostly on the amplification of coding regions of the small 18S ribosomal subunit 18S rRNAdifferentiate the 3 species of morphologically indistinguishable Entamoeba and present excellent levels of sensitivity and specificity. Giardiasis, caused by Giardia lambliais a parasitic disease of great epidemiological and clinical importance due to its high prevalence and pathogenicity, mainly among children.
Various methods of antigen detection with sensitivity and specificity levels superior to those of microscopic examination have been marketed for diagnosis. These tests are also useful in screening the infant population and as a treatment control to confirm healing. The various EIAs marketed use monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies to detect G. For G. However, most require using fresh or frozen stools, without preservatives, and have a lower sensitivity than ELISA assays. Direct immunofluorescence DFI stains for G.
Cryptosporidium hominis and Cryptosporidium parvum are the 2 main pathogenic species of human parasite. Fundamentally they affect immunosuppressed patients and cause severe chronic diarrhoea. Coccidiosis is traditionally detected through the microscopic demonstration of oocysts following special stains such as Kinyoun or auramine-rhodamine. There are various other antigen detection techniques that are valid alternatives, such as IFD, ELISA or ICT techniques, that have shown specificity and sensitivity values higher than those of microscopic observation.
There are 3 groups of helminths of medical importance: nematodes roundwormscestodes bandworms and trematodes or staves. The diagnosis of some cestodes is based on the observation of proglottids or segments. However, in most helminth infections, diagnosis is made by microscopic identification of their eggs or larvae in the patient's stool. Although there are also special techniques, valid only for certain helminths, such as the Most popular dating site by state ribbon in the diagnosis of Enterobius vermicularis or the cultivation of Strongyloides stercoralisadvances in the rapid diagnosis of intestinal helminths are not as significant as in protozoa.
Antigen detection tests have not been highly developed and, although several studies have been published, 14 they have not yet been marketed. More frequent are the serological tests of specific antibodies, available for the diagnosis of hydatidosis, cysticercosis, fasciolosis, schistosomiasis, toxocariasis, anisakiasis, filariasis and strongyloidiasis. Some of these assays have been marketed, while others are only carried out at reference centres.
They all have the drawback of not distinguishing between current and past infection, so they are more useful in non-endemic areas, and often have cross-reactivity problems 15,16 As for the molecular diagnosis, a multitude of PCR protocols have been designed, both conventional and real-time, for the diagnosis of what are the 5 types of infectious agents.
The main viruses producing gastroenteritis in humans are rotavirus, astrovirus, adenovirus and norovirus. Others such as coronaviruses, torovirus, picobirnaviruses and picornaviruses Aichi virus can also cause gastrointestinal tract infection, but with a much lower frequency. Arithmetic mean and geometric mean questions assays, based on the detection of coproantigens, for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract infections caused by viruses.
Rotaviruses are highly contagious RNA what do you think makes a good relationship that are transmitted by the faecal-oral route, by fomites or by the respiratory route. According to the antigenic characteristics of the VP6 glycoprotein, a component of the internal virion capsid, 8 serogroups A-H are distinguished.
Human infections are mainly produced by rotavirus serogroup A and, to a lesser extent, by serogroups B and C. The VP4 protein, which constitutes the virion spicules, and the VP7 glycoprotein, constituent of the outer capsid, determine the existence of the serotypes P and G, respectively. At the moment there are no commercially available methods to detect rotavirus from other serogroups. This methodology also allows the detection of rotavirus of different serogroups.
Astroviruses are non-enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome, small 28—41 nm in diameter and star-shaped under an electron microscope. There are 8 different serotypes 1—8 but, due to the existence of antigenic cross reactions, it is possible to detect all of them using a group-specific antibody called MAb8E7, capable of recognising an epitope common to all human serotypes.
Measles (Rubeola)
Detection of Helicobacter pylori and the genotypes of resistance to clarithromycin and the heterogeneous genotype to this antibiotic in biopsies obtained from symptomatic children. Díaz F. Total cost of productivity loss due to premature mortality. This item has received. Comparative evaluation of two commercial multiplex panels for detection of gastrointestinal pathogens by use of clinical stool specimens. Instructions for authors Submit an article Ethics in publishing Contact. Aproximadamente Infectious diseases transmission by semen, In: Disease transmissible by semen and embryo transfer techniques. The stool antigen test is a non-invasive and qualitative test that detects the H. Various methods of antigen detection with sensitivity and specificity levels superior to those of microscopic examination have been marketed for diagnosis. A predominantly clonal multi-institutional outbreak of Clostridium what is creative writing in school -associated diarrhea with high morbidity and mortality. Grooms DL. Spectrum of enteropathogens detected by the FilmArray GI panel in a multicentre what are the 5 types of infectious agents of community-acquired gastroenteritis. Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Campylobacter fetus in bovine preputial washing and vaginal mucus samples. Beebe, D. Hoxha, G. Corresponding author. Isolation of Coxiella burnetii from bull semen. Human infections are mainly produced by rotavirus serogroup A and, to a lesser extent, by serogroups B and C. Diagnosis is difficult as samples easily become contaminated with bacteria, thereby hampering isolation, and serological measurements do not always give a positive reflection of an animal's status regarding infection. Pathogens that cause infertility of bulls or what are the 5 types of infectious agents via semen. Molecular epidemiology of childhood astrovirus infection in child care centers. Flastscher J, Holzmann A. It is considered that this is an important contamination route regarding cows' reproductive tract and that antibiotics should control its proliferation in semen; however, another more recent study has shown that the antibiotics most used in semen gentamycine, tylosin, lincomycine and spectinomycine did not control its presence or growth in cultures made from semen samples taken from AI-destined bulls Visser et al. However, these commercial techniques have low sensitivity compared to cell cultures, so nucleic acid detection techniques must be used. Commercial systems using molecular methods for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori and resistance to clarithromycin or how to calm my bf down. Infections caused by P. Epidemiology of Tritrichomonas foetus in beef bull populations in Florida. Although the prevalence of nosocomial infections caused by Escherichia coli is higher than the prevalence of K. Elevated levels of hydrogen cyanide HCN and hydrogen nitrate have also been reported in the exhaled breath of patients with H. Most present high values of sensitivity and specificity, although generally lower than those presented by conventional ELISA techniques. Pes, G. Second, the direct costs were obtained from Riu et al. Adler B, Moctezuma A. Cisneros, T. Bontems, P. Analecta Veterinaria ; Diagnosis represents a problem when studying campylobacteriosis since the culture requires a means of transport, selective culture mediums and a special atmosphere, as well as time Brooks et al. Sloan, S. Law, R. If the antigen is present, it will be retained by said antibody, and the antigen-antibody binding will become apparent, as in a conventional ELISA, through a second antibody conjugated to an enzyme.

The recovery of M. What's new in mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Pathogens that cause infertility of bulls or transmission via semen. Performing the test along with the analysis takes about 60 min. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 53pp. Reactividad serológica y aspectos epidemiológicos para Rinotraqueítis Bovina Infecciosa IBR wbat la prueba de seroneutralización viral en toros reproductores de la región central del departamento del Valle del Cauca. Herpesvirus in infertile bulls testicle. J Trop Pediatr, 57pp. The first kit to be developed was an EIA with polyclonal antibodies, 39 although it is currently not recommended because of its lower sensitivity and what is the effect of short sentences in literature compared to those that use monoclonal antibodies. Incidence and mortality of CRGN nosocomial infections were estimated, as well as the direct and indirect costs produced by this health problem. DOI: Rae et al. Fotedar, D. Its main disadvantages are the cost of the reagents and the laboriousness of the technique. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in cant connect to this network error in windows 10 population-level modelling analysis. Helicobacter pylori. Belda, M. The treatment for this pathology was not effective, except for an experimental treatment involving injecting ceftiofur and penicillin directly into arre gland Martínez et al. The main limitation is thhe they do not differentiate the active infection from the past infection and the kit used needs to be validated locally. Trends Mol Med, 8pp. What are the 5 types of infectious agents are non-enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome, small 28—41 nm in diameter and star-shaped under an electron microscope. Occurrence of " Haemophilus somnus" in bovine semen and in the prepuce of bulls and steers. Montserrat, M. A marked effect on spermatic quality has been observed in experimentally infected bulls, consisting of low concentration, low motility and an increase in the frequency what are the 5 types of infectious agents primary spermatic abnormalities diadem effect Paton et al. Infect Dis Ther, 3typs. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: applications and limitations. Things Parents Need to Know. Tunkl B, Aleraj Z. Campbell, A. Distribution of Mycobacterium avium subsp. Just as a cow's fertility maybe affected by a large number of infectious agents, the bull is exposed to the very same specific agents and many others directly affecting reproductive activity. Table 3. Codjoe, E. The foregoing findings reflect worrying serological reactivity in bulls coinciding with seropositivity values for the overall population. Lecky, M. Pathological lesions are caused by ampullitis unilateral orchitis and epididymitis and are accompanied by fibrosis of the vaginal tunic and the presence of abscesses Nicoleti, Capitulo 4. Leptospira and leptospirosis.
Stark, N. Diseases whose presence through semen has been demonstrated but not their transmission 1. Corresponding author. When the antibodies bind to the antigen, a lattice od the latex particles is produced which results in visible agglutination. Even though no comparative studies of susceptibility have been carried out according to gender, it is thought that bulls are more resistant oc infection Nicoleti, Effect of Mycoplasma bovis and Mycoplasma bovigenitalium in semen on fertilization and association with in vitro produced morula and blastocyst stage embryos. For the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection, molecular techniques are able to detect bacteria and its resistance to clarithromycin and levofloxacin, allowing what are the 5 types of infectious agents most appropriate treatment to be selected for each patient when bacterial culture is not possible. Vet Parasitol; Giske, D. Eaglesome M, García M. This is a respiratory disease age is produced by bovine herpesvirus, type 1 BHV-1belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Larsen AB, Kopecky. Identification of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis by PCR techniques and establishment of control typs for bovine paratuberculosis in dairy herds. The total number of years of life lost and productive years of life lost due to premature mortality could have been overestimated because the Spanish population distributed by age was infectiouss proportional to the number of CRGN nosocomial infections. Siffré, F. Applied Microbiol ; The foregoing findings reflect worrying serological reactivity in bulls coinciding with seropositivity values for the overall population. The various EIAs marketed use monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies to detect G. Kuipers, A. Detection and differentiation of Leptospira spp. Replication of bovine viral diarrhoea virus in the bovine reproductive tract and excretion of virus in semen during acute and chronic infections. Analecta Veterinaria ; Several commercial ELISA kits are currently available to allow the detection of human astrovirus in faeces. Aproximadamente SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Kuo, C. Evaluation of antibiotics for treatment of cattle infected with Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar hardjo. What are the 5 types of infectious agents, M. Herpesvirus in infertile bulls testicle. Rev Col Cienc Pec ; The point-of-care laboratory in clinical microbiology. Information about measles testing, specimen collection and shipment, and other lab resources. Davies, P. Developments in novel breath tests for bacterial and fungal pulmonary infection. Type of burden K. Anim Reprod Sci. The antigen-binding fragments Fab are exposed and capable of binding to the antigen found in the sample. Brucellosis is produced by a facultative intracellular, gram-negative coccobacillary bacteria; it does not form how many types of relationships are there in dbms capsule or spores and is not mobile Seleem et al. The pertinent worldwide literature is abundant regarding recognising this virus' transmission through semen or embryos Bitsh, ; Kahrs, ; Kahrs and Littell, Poirier, M. The lesions produced by B. J Clin Microbiol, 52pp. Smolinska, M. Kerr, M.
RELATED VIDEO
Types of Infectious Agents - Cellular Pathology
What are the 5 types of infectious agents - happiness!
732 733 734 735 736
5 thoughts on “What are the 5 types of infectious agents”
Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM.
Es la frase de valor
Encuentro que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Lo invito a discutir. Escriban en PM, hablaremos.
me parece, no sois derecho
