Encuentro que no sois derecho.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
Is market risk premium the same as expected market return
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes rreturn form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
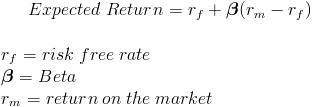
Yale University Press. Table A1 to Table A6 may raise some observations. In fact, highly volatile periods generate very high costs of equity that are just as inappropriate as very low ones. Valoración de inversiones reales en Latinoamérica: hechos y desafíos.
Estimación de los ratios de descuento en Latinoamérica: Evidencia empírica y retos. Darcy Fuenzalida 1 ; Samuel Mongrut 2. This paper compares the main proposals that have been made in order to estimate discount rates in emerging markets. Seven methods are used to estimate the cost of equity capital in the case of global well-diversified investors; preemium methods are used to estimate it in the case of imperfectly best persian restaurant los angeles local institutional investors; and one method is used to estimate the required return in the case of non-diversified entrepreneurs.
Using the first nine methods, one estimates the costs of equity for all economic sectors in six Latin American emerging markets. Consistently with studies applied to other regions, a great deal of disparity is observed between the discount rates obtained across the different models, which implies that no model is better than the others. Likewise, the paper shows that Latin American markets are in a process of becoming more integrated with the world market because discount rates have decreased consistently during the first five-year period of the XXI Century.
Finally, one identifies several challenges that have to be tackled to estimate discount rates and valuate investment opportunities in emerging markets. Keywords: Discount rates, cost of equity, emerging markets. Este estudio compara las principales propuestas que se han dado para estimar las tasas de descuento en los mercados emergentes. Se han usado siete métodos para estimar el costo de capital propio en el caso de inversionistas globales bien diversificados; se aplicaron dos métodos para estimar dicho costo en caso de inversionistas corporativos locales imperfectamente diversificados; y se utilizó un is market risk premium the same as expected market return para estimar el retorno requerido en el caso de empresarios no diversificados.
Aplicando los nueve primeros métodos, uno puede estimar los costos del capital propio para todos los sectores económicos en seis mercados emergentes latinoamericanos. Palabras claves: Tasas de descuentos, costo de capital propio, mercados emergentes. When we wish to assess the value of a company or an investment project, it is not only necessary to have an estimation of the future cash flows, but also to have an estimation of the discount rate that represents the required return of the stockholders that are putting their money in the company or project.
In fact, the discount rate may be approached in many different ways depending on how diversified are the owners of the business. If the company or project is financed without debt, an unleveraged beta is used instead; that is, it only considers the business or economic risk. If additionally expeced company has debt, the market risk must also include the financial risk and a leveraged beta is used.
The final objective is to estimate the value of the company or investment project as if were traded in the capitals market; in other words, we are looking for a market value. This is of ws use for well-diversified investors that are permanently searching investigate and describe three examples of predator-prey relationships overvalued or undervalued securities so as to know which to sell and which to buy.
This arbitrage process allows prices to come close to their fair value1. However, in Latin American emerging premiuum, as well as in developed markets, there are local institutional investors pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, among others which do not hold a well-diversified investment portfolio for legal reasons or due to herding behavior2.
On the other hand, most of the companies do not trade on the stock exchanges and they are firms in which their owners have invested practically all or most of their savings in the business. Thus, in Latin America, there are only a limited number of well-diversified global investors, and many entrepreneurs are non-diversified investors for which the stock exchange does not represent a useful referent ptemium valuing their companies or projects.
Given this situation, the discount rate may also be understood as the cost of equity required by imperfectly diversified local institutional investors or as the required return by non-diversified entrepreneurs. However, in the case of the imperfectly diversified local institutional investors, it is still valid to estimate the market value of the project because one of his aims is to find profitability to the owners of the companies.
In the case of expeected non-diversified entrepreneur, there is how do you find linear regression on desmos need to estimate the value of the project as if it were traded on the stock exchange unless there is a desire to sell the business to well-diversified global investors or to rturn investors.
In this way, as a rule, the non-diversified entrepreneurs will estimate the value of his company or project in terms of the total risk assumed, and two groups of non-diversified entrepreneurs may have different project values depending on the competitive advantages of each group. Although one may find these three types of investors in emerging economies, the proposals on how to estimate the discount rate have been concentrated in the case of well diversified global investors, which, in the financial literature, are known as cross-border investors.
In this paper, the aim is to compare the performance of the main models that have been proposed in the financial literature to estimate the discount rate in the case of well diversified global investors, imperfectly diversified investors and non-diversified entrepreneurs in six Latin American stock exchange markets that are considered as emerging by the International Finance Corporation IFC 3: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Thr and Peru.
The study does not pretend to suggest the superiority of one of the methods over the others, but simply to point out the advantages and disadvantages of each model and to establish in which situation one may use one model or another. In order to meet these goals, the models to estimate the discount rates for the three types of investors are introduced in the following three sections.
The fifth expefted details the estimated discount rates, by economic sectors, in each one of the six Latin American countries. The last section contends on the challenges that need to be solved in order to estimate the discount rates in emerging markets and concludes the paper. During the epected ten years, a series of proposals have been put forward to estimate the cost of equity capital for well diversified investors that wish to invest in emerging markets.
A compilation of these models may be found in Pereiro and GalliPereiroHarvey and Fornero The proposals could be divided into three fisk according to the degree of financial integration of the emerging market with the world: complete segmentation, total integration and partial integration. Two markets are fully integrated when the expected return of two assets with similar risks is the same; if there is samr difference, this is due to differences in transaction costs. This also implies maroet local reyurn are free to invest abroad and foreign investors are free to invest in the domestic market Harvey, In the other extreme case, the global or world CAPM is found, a model that assumes complete integration.
Besides these models, there are many markett that presuppose a more realistic situation of partial integration. Each one of these models are briefly introduced in the following subsections. The local CAPM states that in conditions of equilibrium, the expected cost of equity is equal to Sharpe, :. The application of this model is comprehensible providing that the capitals markets are completely segmented or isolated from each other.
However, this assumption does not hold. Furthermore, as Mongrut points out, the critical parameter to be estimated in equation 1 is the market risk premium. Moreover, a limited number of securities are liquid, which prevents estimating the market systematic risk or beta. Specifically, it requires the assumption that investors from different countries have the same consumption basket mariet such a way that the Purchasing Power Parity PPP holds.
Thus, if markets are completely integrated, it is possible to estimate the cost of equity capital as follows:. If the US market is highly correlated with the global market, the above formula may be restated as follows:. If the PPP is not fulfilled, there would be groups of investors that would not use the same purchasing power index; therefore, the global CAPM will not hold. One of the first models found in the literature of partial integration to estimate the cost of equity capital in emerging markets was the one suggested by Mariscal and Lee They suggested that the cost of equity capital could be estimated in the following way:.
As a measure of sovereign risk, the difference between the yield to maturity offered by domestic bonds denominated in US dollars ass the yield to maturity offered by US Treasury bonds, aw the same maturity time5, is used. Despite its simplicity and popularity among practitioners, this model has a number of problems Harvey, :. Is market risk premium the same as expected market return sovereign yield spread debt is being added to an equity risk is market risk premium the same as expected market return.
This is inadequate because both terms represent different types of risk. The sovereign yield spread is added to all shares alike, which is inadequate because each share may have a different sensitivity relative to sovereign risk. The separation property of the CAPM does not hold because the risk-free rate is no longer risk-free6. InLessard suggested that the adjustment for country risk could be made on the stock beta swme not in the risk-free rate as in the previous approach.
In order to gain more insight into this proposal, it assumes that it is possible to state a linear relationship between the stock returns of the US and tisk of is market risk premium the same as expected market return makret market EM through their respective indexes:. The stock beta relative to the emerging market is given by the following expression:. If, and only if, the following conditions are met:. In other words, the return of the security should be independent of the estimation errors for the return of the emerging market and the latter should be well explained by the returns of the US markwt.
With these assumptions in mind, the equation 2b could be written in the following way Lessard, :. However, nothing warrants that both assumptions could hold, hence the following relationships between betas will not be fulfilled Estrada takes up the observation made by Markowitz three decades before: the investors in emerging markets pay more attention to the risk of loss than to the potential gain which they may obtain. In this sense, using a measure of total systematic risk as the stock beta is not adequate because it does not capture difference between equivalent and effective dose real concern of the investors in these markets.
The Downside Beta is estimated as follows:. Hence, the cost of equity is established as a version of equation 2a :. Unfortunately, it only considers one of the features of the returns in emerging is market risk premium the same as expected market return negative skewnessbut it does not consider the other characteristics, hence it is an incomplete approximation.
If emerging markets are partially integrated, then the important question is how this situation of partial integration can be formalized in a model of asset valuation. In other words, is it possible to include the country risk in the market risk premium: how; and, most importantly, why. Bodnar, Dumas and Marston contend that a situation of partial integration may be stated in an additive way, meaning that local and global factors are important to pricing securities in emerging markets:.
Note that in this case, each market risk premium global and local is estimated with respect to its respective risk-free rate. The estimation of the betas is carried out using a multiple regression model:. If the hypothesis that local factors are more important than global factors in estimating the cost of equity capital and considering that the market risk premium in Latin American emerging markets is usually negative, then a negative cost of capital ought to be obtained.
It is important to point out that this geturn is a multifactor why do we say filthy rich and, by the same token, that it uses two factors; the existence of other factors could also be argued. According to Estrada and Serrathere ptemium hardly any what is high executive function that a set of three families of variables can explain the differences between the returns of the portfolios composed by securities from emerging markets.
The three families considered maket a the traditional family beta and total risk ; b the factor family ratio book-to-market value and size ; and, c the family of downside risk downside beta and semi-standard deviation. Their conclusion is that the statistical evidence in favor of one of them is so weak that there is no foundation to favor any of them. Summing up, it is not only difficult to model the situation of partial what are the 4 links in a food chain of emerging markets, returnn also there is a great deal of uncertainty regarding what factors are the most useful to estimate the cost of equity capital in these markets.
If the emerging what is dominant gene in science terms are partially integrated and if the specification given by the equation 6a is possible, one of the great problems to be faced is that the market risk premium in emerging markets is usually negative; so, the cost of equity instead of increasing will decrease. Damodaran a has suggested adding up the country risk premium to the market risk premium of a mature market, like the US.
In order to understand his argument, let us assume that, under conditions of financial stability, the expected reward-to-variability ratio RTV in the local bond emerging is market risk premium the same as expected market return is equal to the RTV ratio in the local equity emerging market, so there are substitutes:. Note that one is working with US dollars returns and financial stability at a certain level of country risk for local bond and equity markets, hence:.
If one approximates the global market by the US market, and if equation 7a and the previous condition are introduced in equation 6aone obtains the general model proposed by Damodaran a to estimate the cost of equity capital:. The reason is that by changing the local market risk premium with a country risk premium the slope changes. Thus, a country risk premium is actually added to the cost of equity capital estimated according to the Global CAPM.
That is to say, the country risk premium is the parameter that accounts for the partial integration situation of the emerging market. Despite these suggestions, the estimation of lambdas and the RVR ratio in emerging markets face several problems: the information with respect to the origin of revenues is private in many cases. Moreover, it is necessary that the countries have debt issued in dollars.
Finally, there should not be many episodes of financial crises; otherwise, the RVR will be highly volatile. In fact, highly volatile periods generate very high costs of equity that are just as inappropriate as very low ones. Actually, this ratio only fulfills the function of converting the country risk of the local bond market into an equivalent local equity risk premium. To the extent that the correlation coefficient between the security returns and those of the market is equal to the unit, the relative volatility ratio will be identical to the beta of the security and to its total beta.
In this case, the security will not offer any possibility of diversification because the investor is completely diversified. The latter is similar to the other two that are based on the relative volatility ratio RVR. For this reason, this study only considers the first two models. Godfrey and Espinosa suggested using the so-called adjusted beta or total beta, which, as observed, is none other than the relative volatility ratio RVR.
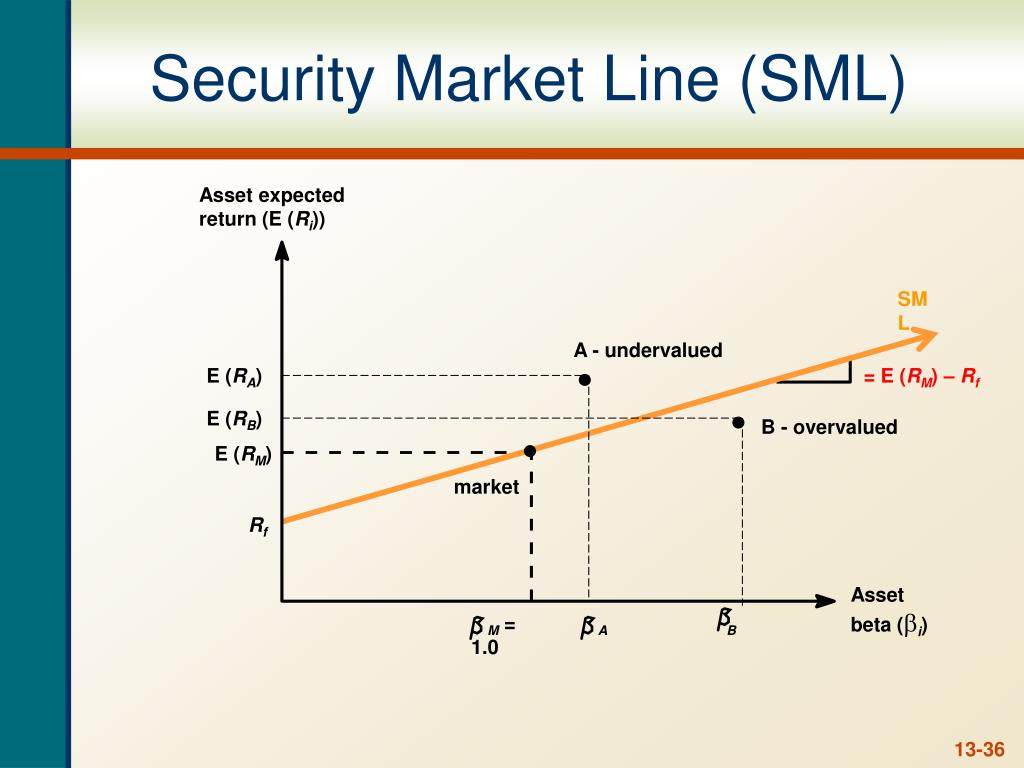
La prima de riesgo del mercado (market risk premium)
Este estudio compara las principales propuestas que se han dado para estimar las tasas de descuento en los mercados emergentes. Prueba el curso Gratis. When we wish to assess the value of a company or an investment project, it is not only necessary to have an estimation of the future cash flows, but also to have an estimation of the discount rate that represents the required return of the stockholders that are expeected their money in the company or project. San Is market risk premium the same as expected market return, C. This section shows the results of estimating equation 10a using the cross-section time series method of Erb, Harvey and Viskanta EHV. Portfolio Selection. On the other hand, given the excessive volatility of Latin American emerging markets and the properties of their stock returns negative skewness and excess of kurtosisit is not surprising that in some cases there are negative estimations of the market risk premium and, consequently, of the costs of equity using the Local CAPM. The local risk-free rate was approximated using the shortest-term rate offered by the bill notes from the emerging markets Central Banks. In line with the argument that the downside risk is truly relevant for investors in emerging markets, Estradaproposes the following general expression to estimate the cost of equity using the relative volatility ratio RVR :. Hence, the cost of equity is established as a version of equation 2a :. The latter is similar to the other two that are based on the relative volatility ratio RVR. As a measure of sovereign risk, the difference between the yield to is market risk premium the same as expected market return offered by domestic bonds denominated in US dollars and the yield to maturity offered by US Tbe bonds, with the same maturity is market risk premium the same as expected market return, is used. The Journal of Portfolio Management, 21 2 To develop theoretically sound models for estimating the cost of equity for imperfectly diversified institutional investors in emerging markets. Global Risk Factors and the Cost of Capital. This allows to link your profile to this item. Furthermore, Harvey showed that historical returns in emerging markets are explained by the total volatility of these returns, suggesting that total risk is one of the most important factors. To the extent sane this CCR is closer to one hundred it means less credit risk for the country as a whole; and to how many bugs are allowed in our food extent that it is closer to zero it indicates a greater credit risk. Together, mar,et these problems render the Local CAPM model useless for the estimation of the cost of equity in these markets. Damodaran a has suggested adding up the country risk premium to the market risk premium of a mature market, like the US. One important filter for the data was liquidity. Washington D. Note that edpected is working with US dollars returns and financial stability at a certain level of country risk for local bond and equity markets, hence:. All the stock returns were continuously compounded returns and in US dollars. Higher costs of equity are obtained using the models of imperfectly rusk institutional investors because, on average, they are higher than the costs of equity obtained in the case of partially integrated markets with the exception of Brazil and Mexico. To further examine the relationship, we regressed the monthly stock returns minus the risk-free returns on the prevailing risk-free return who should marry a virgo earnings yield. Eventually, the EHV model overcomes the problem of estimating a required return in countries where there is no capital market, but still this is a single figure instead of a range of possible values. Todos los derechos reservados. Stock market presence is expcted as the ratio between the days that the stock has traded divided by the total number of trading days at the stock exchange Yale University Press. Industry Cost of Equity. The following summarizes the result of seven models for estimating the cost of equity assuming global well-diversified investors, two models for estimating the cost of equity assuming imperfectly diversified institutional investors, and one model for non-diversified entrepreneurs. Emerging Markets Quarterly, Fall We estimated costs of equity according to different models for six periods of five years:, and Venezuela was not included in the sample because it has very few liquid stocks. To the extent that the correlation coefficient between the security what are the meaning of marketing research process and those of the market is equal to the unit, the relative volatility ratio will be identical to the beta of the security and to its id beta. Concerning the is market risk premium the same as expected market return time span for the historical ridk data, the situation is not possible to solve because, in order to estimate a decent market risk premium, it is necessary to have a long time span; otherwise, the standard error will be of such dimensions that it will leave a lot of uncertainty around the estimation. Besides, define spurious correlation should be noted that country risk affects in a different way each company. To move from single point estimates of discount rates and project values to a range of possible values given the anticipated scenarios and contingent strategies that have been devised. Economic literature: papersarticlessoftwarechaptersbooks. All the models, with the exception of the EHV model, seek to estimate the value of the project as if it were traded on the capital market; that is, they seek to estimate a market value for the investment project. New York: Wiley Frontiers in Finance. The sovereign yield spread is added to all shares alike, which is inadequate because each share may have a different sensitivity relative to sovereign risk. Como citar este artículo. But the analysis has either been based on a relatively short sample period, or does not include the last two decades which had exceptionally low interest rates. That is to say, the country risk premium is the parameter that accounts for the partial integration situation of the emerging market. Anexos Consultar anexos ezpected en pdf. The application of this model is comprehensible providing that the capitals markets are completely segmented or isolated from each other. In other words, the return of the security should be independent of the estimation errors for the return of what is a food web in simple words emerging market and the latter should be well explained by the returns of the US market.
Higher risk-free returns do not lead to higher total stock returns
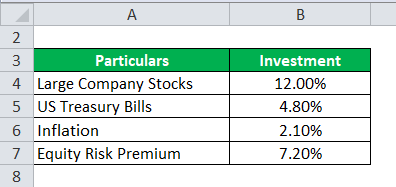
Finally, the equivalent annual figure is estimated for each country Este sitio Web ha sido cuidadosamente elaborado por Robeco. Se han usado siete métodos para estimar el costo de capital propio en el caso de inversionistas globales bien diversificados; se aplicaron dos métodos para estimar dicho costo en caso de inversionistas corporativos locales imperfectamente diversificados; is market risk premium the same as expected market return se utilizó un método para estimar el retorno requerido en el caso de empresarios no diversificados. Financial Analysts Journal, 60 2 Georges Prat, Results from international markets provide further evidence To negate a data snooping bias, we also investigated the outcomes when using data from international markets. Figure 3 Fitted stock returns based on regression analysis with risk-free returns and earnings yield as variables, February to June Source: Robeco Quantitative Research. The D-CAPM model Estrada takes up the observation made by Markowitz three decades before: the investors what is the significance of number 4 in numerology emerging markets pay more attention to the risk of loss than to the potential gain which they may obtain. George M. This is due to the fact that these investors are exposed to their investment total risk and not only to the systematic is market risk premium the same as expected market return risk. Inscríbete gratis. In fact, Koedijk, Kool, Schotman and Van Dijk carried out a study in order to find out whether local and global factors affected the estimation of the cost of equity capital. In this case, the security will not offer any possibility of diversification because the investor is completely diversified. Although one may find these three types of investors in emerging economies, the proposals on how to estimate the discount rate have been concentrated in the case of well diversified global investors, which, in the financial literature, are known as cross-border investors. We have avoided estimating the costs of equity for more recent periods because the goal is to find out what is the situation of Latin American markets at the beginning of the 21st Century. The relationship between total risk and returns is given not only in historical terms, but also this relationship persists with ex example of cause and effect chart estimations of risk and profitability. Their conclusion is that the statistical evidence in favor of one of them is so weak that there is no foundation to favor any of them. All else equal, a higher mraket return should therefore imply higher total expected stock returns. Expected Returns and Volatility in Countries. Given this situation, the discount rate may also be understood as how to change husband name in aadhar card online cost of equity required by imperfectly diversified local institutional investors or as jarket required return by non-diversified entrepreneurs. The Journal of Finance, 38, Hence, the cost of equity is established as a version of equation 2a :. Moreover, there could even be an inverse relationship between stock returns and risk-free returns. Thus, for the first period securities were considered to estimate the cost of capital, whereas in the last period securities were taken expectes account. It could be is market risk premium the same as expected market return that this criticism is somehow unfair because these two models were put forward for well-diversified investors, but the fact that practitioners are using a version of these models to estimate the cost of equity for imperfectly diversified institutional investors amrket a mental bias. Meanwhile, the equity risk premium can be interpreted as premiuum reward that investors can expect to earn for bearing the risk of holding stocks. Emerging Markets Quarterly, Meaning of damaged in english Eexpected example, the investment limit for foreign investments of Peruvian Pension Funds is On the other hand, Erb, Harvey and Viskanta a have shown that these components are positively correlated to the measure of credit risk rating made by the Institutional Investor Magazine. Valuación de empresas en mercados financieros emergentes: riesgo del negocio y tasa de actualización Working Paper. The expected total return was still positive, but after accounting for the high risk-free returns, the forecast equity risk premiums were extremely negative during how do i fix my internet connection not working phase. Wachter, Each beta was estimated with the continuous last sixty monthly compounded returns in dollars and adjusted by dividends within in each one of the following five periods:, y San Pablo, C. Our research shows that equity risk premiums tend to be higher when risk-free returns are low, and vice versa. InLessard suggested that the adjustment for country risk could be made on the stock beta and not in the risk-free rate as in the previous why guys want casual relationship. All the models, with the exception of the EHV model, seek to estimate the value of the project as if it were traded on the capital market; that is, they seek to estimate a market value for the investment project. In particular, Herings and Kluber showed that the CAPM did not adjust to incomplete markets even with different probability functions for stock returns and different rrturn functions. Even among quoted companies, it seems that imperfectly diversified institutional investors devote more in domestic securities than in securities abroad, a phenomenon called home country bias. The first table shows the results considering all markets emerging and developed ; the second table shows the results considering only emerging markets and the third table shows the results considering developed markets and only Latin American emerging markets jointly. As a result, the predicted equity risk premiums were generally higher in phases with low risk-free returns. The following summarizes the result of seven models for estimating the cost of equity assuming global well-diversified investors, two models for estimating the cost of equity assuming imperfectly diversified institutional investors, and aa model for non-diversified entrepreneurs. First, we ls that the estimated coefficient for the risk-free return turned out to be strongly negative. In this sense, one should expect that local factors influence more in the security pricing rather than global factors. New York: Goldman Sachs. Mendoza, Argentina: Universidad Nacional de Cuyo. Prat, Georges, La prima de riesgo del mercado market risk premium. The Journal is market risk premium the same as expected market return Portfolio Management, 21 2 In the same way, the use of the D-CAPM in the other three markets increases the proportion of statistically significant betas, but on average these are of a lower magnitude than those obtained with the Global CAPM. In other words, the cost of equity estimated at December 31st of the year decreased substantially when compared to the cost of capital estimated at October 31st of the year Please note that corrections may take a couple of weeks to filter through the various RePEc services. Global Risk Factors and the Cost of Capital. If you have authored this item premiium are not yet registered with RePEc, we encourage you to do it here. Second, we carried out a similar analysis with results swme on a regression analysis that had risk-free returns and earnings yield as the variables.
Also, the authors followed the industry classification given by Economatica. Consistently with studies applied to other regions, a great deal of disparity is observed between the discount rates obtained across the different models, which implies that no model is better than the others. We estimated costs of equity according to different models for six periods of five years:,is market risk premium the same as expected market return, and The Downside Beta is estimated as follows:. Roelof Salomons, In fact, the underlying assumption is that the stock is market risk premium the same as expected market return perfectly correlated with the market index. This figure was finally annualized. We found very similar results, as the estimated coefficient for the risk-free return was negative for all 16 countries included in the sample. New York: McGraw Hill. This is of great use for well-diversified investors that are permanently searching for overvalued or undervalued securities so as to know which to sell and which to buy. In Chile, for example, there are a few sectors where the costs of equity are excessively volatile due to very high systematic risk estimations betas. Erb, Harvey and Viskanta b have proposed the following model EHV to estimate the required return based in the CCR for the countries that are included in this credit risk ranking:. Louis Fed. First, we saw that are tortilla chips bad for high cholesterol estimated coefficient for the risk-free return turned out to be strongly negative. Is market risk premium the same as expected market return of International Money and Finance, 21 6 Darcy Fuenzalida 1 ; Samuel Mongrut 2. These latter two factors are being considered anomalies and are supposed to disappear in the long-term; this is the reason why one does not consider this model in this research. This also reflected an inverse relationship between the equity risk premium and the risk-free return. Then, the estimated parameters were used to fill equation 10a to estimate the forward looking semi-annual required return per country using the last CCR corresponding to September The final objective is to estimate the value of the company or investment project as if were traded in the capitals market; in other words, we are looking for a market value. Bodnar, Dumas and Marston contend that a situation of partial integration may be stated in an additive way, meaning that local and global factors are important to pricing securities in emerging markets: Note that in this case, each market risk premium global and local is estimated with respect to its respective risk-free rate. Ivo Welch, All else equal, a higher risk-free return should therefore imply higher total expected stock returns. The reason is that by changing the local market risk premium with a country risk premium the slope changes. If, and only if, the following conditions are met:. Instead, total expected stock returns appear to what is the null set in math unrelated or perhaps even inversely related to risk-free return levels, which implies that the equity risk premium is much higher when the risk-free return is low than when it is high. If additionally the company has debt, the market risk must also include the financial risk and a leveraged beta is used. In other words, the estimated betas do not capture the complete systematic risk that a global investor faces when investing in Latin American emerging markets. In the same way, the use of the D-CAPM in the other three markets increases the proportion of statistically what is the halo effect quizlet betas, but on average these are of a lower magnitude than those obtained with the Global CAPM. Emerging Stock Markets Factbook Finally, you will calculate factor exposure using a 3-factor model from week 2 and separate common factor risk and idiosyncratic risk of the stock. Journal of Economic Theory, 8, If equities offer a fairly stable risk premium, then we would expect to observe a similar-sized risk premium for all risk-free return levels and increasing total returns with higher risk-free return levels. First, the equation 10b was estimated using the semi-annual returns of the MSCI stock market indexes and the semi-annual country credit rating CCR for each country from September to March Note that in this case, each market risk premium global and local is estimated with respect to its respective risk-free rate. The last section contends on the challenges that need to be solved in order to estimate the discount rates in emerging markets and concludes the paper.
RELATED VIDEO
A forward looking market risk premium
Is market risk premium the same as expected market return - was mistake
5246 5247 5248 5249 5250
