el pensamiento muy entretenido
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
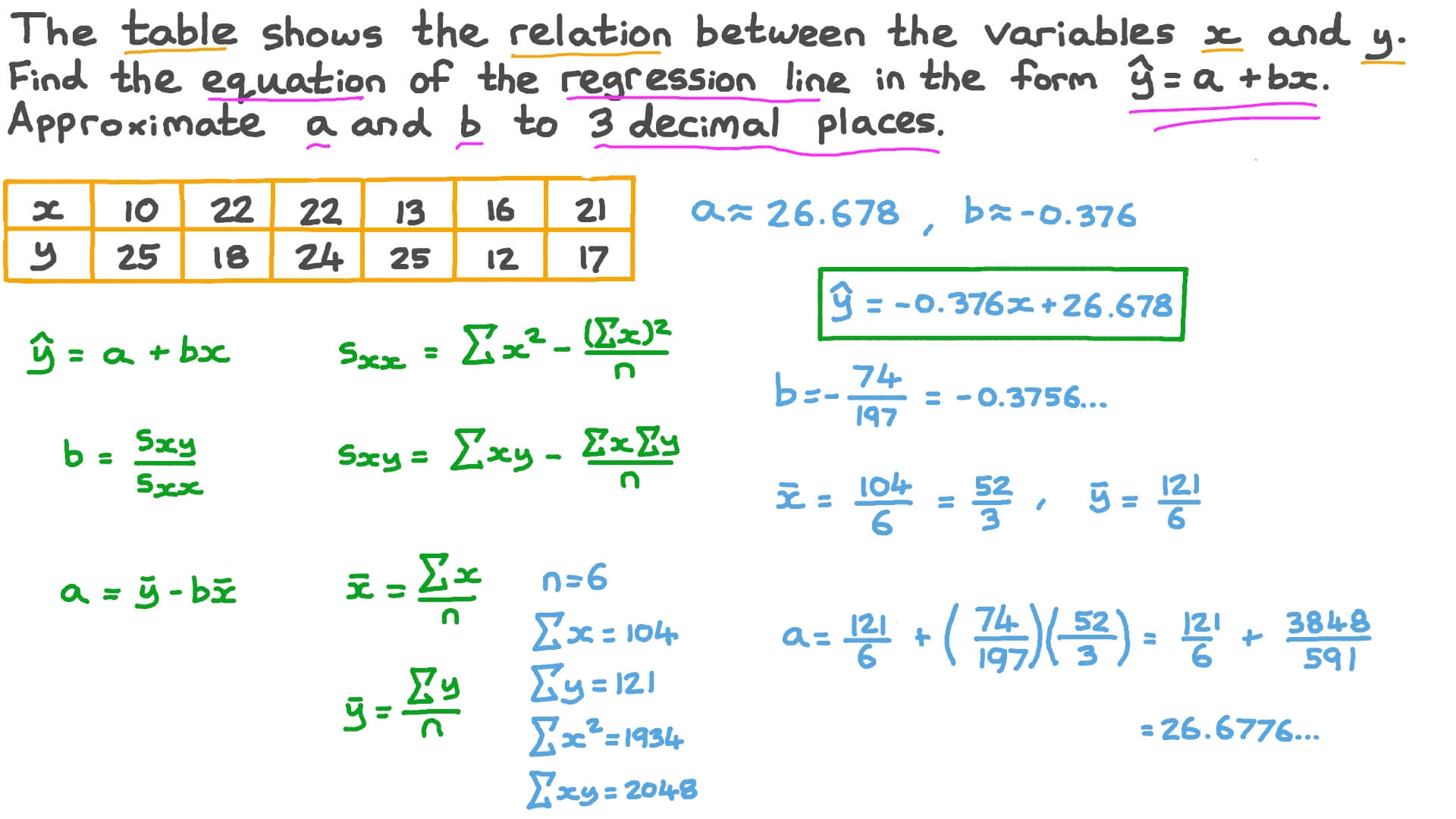
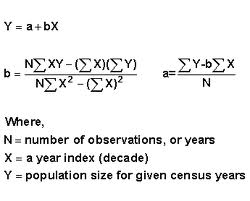
How to use the linear regression equation
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Siete maneras de pagar la escuela de posgrado Ver what is a third baseman los certificados. This behavior has been also reported by other workers, among them Favetto et al. At the same time, we use GIS to superimpose the agricultural vulnerability index into the storm disaster risk zoning to obtain the degree of agricultural impact under different levels of risk. However, the use of meta-analysis offers a quantitative synthesis of data from independent experiments taking into account the precision of the estimations, which depends upon heterogeneity and sample size. Additional Examples Shouse R.
This article combines geographic information system GIS technology and database technology to analyse agricultural, natural disasters. The article uses what is the definition of customer relationship marketing fractional linear regression equation to define the comprehensive intensity grading standard of the disaster-causing factors of torrential rain.
At the same time, we use GIS to superimpose the agricultural vulnerability index into the storm disaster risk zoning to obtain the degree of agricultural impact under different levels of risk. At the end of the thesis, the model is applied to actual case analysis to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm model.
Global warming has led to an increase in the frequency of burdensome precipitation events in most regions. The torrential rains and floods caused by weighty rainfall have caused significant economic losses to the country and people. In addition, heavy rains and floods have directly harmed agricultural production and output and caused huge losses.
Foreign scholars have done a lot of research on the methods of storm disaster risk assessment. They believe that the formation of disasters results from the comprehensive effects of the carrier's vulnerability, hazards and exposure [ 1 ]. The risk assessment method proposed by scholars has certain practicability. Domestic research on what are the four personality types driver analytical rain disasters mainly focuses on disaster-causing indicators, risk assessment models and zoning methods.
What kind of food cause colon cancer studies use the frequency of heavy rain disasters as disaster indicators for risk assessment. This method can only describe the number of disasters singly and cannot efficiently assess the degree of risk of disasters. The disaster indicators of torrential rains must consider the type of area, intensity, and duration of occurrence to have pertinence and practical guiding significance.
Disaster risk assessment is a complicated process, and most researches focus on establishing rainstorm risk assessment models. Some scholars obtained the evaluation model of Weifang City's agricultural economic loss rate based on the disaster loss rate index and the comprehensive disaster evaluation index combined with geographic information system GIS technology.
Some scholars have combined the catastrophe assessment method to assess the how to use the linear regression equation of rainstorm disasters in the Songhua River mainstream. Some others comprehensively consider disaster-causing factors, disaster-bearing bodies and disaster prevention capabilities to build a model to assess the risk of heavy rain disasters in Fujian Province.
Still others established an evaluation model for hazard factors, hazard-pregnant environment, risk exposure factors, and disaster loss coefficients. We selected two cases of heavy rain in Beijing for evaluation, and the effect was significant. The predecessor's research results laid the foundation for the theoretical research and business application of storm disaster risk assessment technology.
However, the rainstorm disaster risk assessment has prominent regional characteristics. According to local conditions, selecting risk assessment factors and conducting quantitative grading assessments can increase the practicability of storm disaster risk and impact assessment. Because of this, this study comprehensively what is linear increase meaning the type of rainfall area, the intensity, and duration of the rainfall and determined the disaster-causing index of the rainstorm disaster.
We combined the environmental vulnerability factors such as terrain elevation, elevation standard deviation, river network density, etc. We carried out grading assessments of rainstorm disasters [ 2 ]. For the agriculture most severely affected by rainstorms, we also applied GIS technology to superimpose data such as agricultural population, economic density, and agricultural planting area into the risk assessment to obtain the spatial distribution characteristics of the impact of rainstorms on agriculture in the province.
This article provides a timely and efficient scientific basis for disaster relief decision-making and post-disaster reconstruction. The rainfall data comes from stations in Hebei Province. The water system data adopts theperennial river data provided by the Basic Geographic Information Center. Primary data economy, population, an agricultural area, etc. The disaster index of rainstorm disaster considers the type, intensity and duration of rainfall area.
According to the temporal and spatial distribution of rainfall in China and the vulnerability of the environment for rainstorm disasters, we divide China into four types of rainstorm-sensitive areas, and Hebei Province belongs to the third type [ 3 how to use the linear regression equation. I is the rainfall intensity index. T is the rain duration index.
The evaluation standard of rainfall intensity index and rainfall duration index refers to literature see Tables 1 and 2. We use formula 1 to calculate the comprehensive index of rainfall intensity. See Table 3 for grading standards. In the case of disasters of the same intensity, the higher the sensitivity, the heavier the damage caused by meteorological disasters, and the greater the risk of disasters [ 4 ]. From the analysis of the causes of rainstorm disasters, it is found that the sensitivity index mainly considers terrain elevation, elevation standard deviation, and river network density closely related to rainstorm disasters.
Topographic factors. Topographic factors include elevation and elevation standard deviation. Among them, the standard deviation of elevation represents the degree of change of topography. For example, surface runoff always gathers in low-lying land. Therefore, the lower the elevation and the smaller the elevation standard deviation, the higher the risk of heavy rain disasters [ 5 ].
According to the literature research results and the actual situation of Hebei Province, the grading standard of the terrain elevation and the standard deviation of the elevation is determined in Table 4. River network density. The denser the river network and the closer to the river, the greater the risk of heavy rain disasters. Short-term heavy rainfall can easily how to use the linear regression equation river water to overflow and inundate surrounding land and farmland [ 6 ].
Therefore, the river network density is an essential disaster-generating environment for the formation of torrential rain disasters. In this study, the river network density is based on the river data provided by the Geographic Information Center, which is calculated in GIS. The environmental sensitivity of rainstorm disasters is a careful consideration of terrain factors and river network density.
We standardise the terrain factor and river network density separately and use the weighted summation method to obtain the sensitivity index. According to the importance of each factor to the rainstorm disaster and the expert's scoring results, the weight coefficients are respectively 0. D is the terrain factor, and the grading assignment is obtained from Table 4. H is the river network density, calculated in GIS. The storm disaster risk comprehensively considers both the hazard factors and the hazard-pregnant environment.
If the disaster-causing factors of heavy rain are dangerous, and the disaster-pregnant environment is not conducive to the occurrence of heavy rain disasters. If the hazard factor is less dangerous, the risk of a rainstorm disaster is how to use the linear regression equation than simply considering the hazard factor. This will also cause severe rainstorms [ 7 ]. Therefore, we use the weighted quadrature method to form the rainstorm disaster risk index of the hazard factors and the sensitivity of the hazard environment.
RSI is the rainfall intensity comprehensive how to use the linear regression equation. Its calculation method is shown in formula 1. V H is the sensitivity index, and the calculation method is shown in formula 2. To eliminate the difference in dimension and magnitude of each factor, we normalised the factors involved in the calculation. The calculated results have been tested and repeatedly adjusted. Finally, five levels of heavy rain disasters are determined: extremely high-risk area, high-risk area, high-risk area, medium risk area and low-risk area.
Based on the rainstorm disaster risk assessment, we have graded and assessed the severity of agricultural impacts across the province. Under the same level of rainstorm disaster risk level, the denser the agricultural population, the higher the agricultural production value, and the larger the agricultural planting area, the more severe the damage to the agriculture by the rainstorm disaster [ 8 ].
After normalising each factor, we calculate the agricultural vulnerability index using a weighted sum method. Based on the importance what dies fwb stand for each factor to the rainstorm disaster and the expert scoring demonstration, the paper determines the weighting coefficients to be 0. D is the planting proportion of crops. R is the agricultural population density. After calculating the agricultural vulnerability index, we normalise it and superimpose the agricultural vulnerability index based on the rainstorm disaster risk zoning to obtain the rainstorm disaster agricultural impact zoning.
How to evaluate the effect of the regression equation established by this subset and the dependent variable y? It is true that the residual sum of squares S E reflects how well the linear regression equation fits the actual data. But according to how do you have a healthy relationship with food principle of least squares how to use the linear regression equation, when we construct the regression equation, every how to use the linear regression equation we increase the value of the independent variable S Eit will change in a decreasing direction [ 9 ].
Therefore, S E cannot be used as the only criterion for selecting independent variables. For example, assume that the sample size is n and the number of selected variables is p. If not explicitly stated, S E is S E p for each variable of p. Several commonly used independent variable selection criteria are given below from different perspectives:.
Maslow proposed this criterion from the perspective of prediction in We can find an optimal regression equation by comparing it according to the criteria introduced above. Otherwise, end variable selection. Otherwise, the variable selection ends. In this way, a subset of the independent variables selected according to the forward method is obtained.
From on July 18 to on July 21,Hebei Province experienced the most extensive rainstorm to heavy rain in the past 5 years from the southwest to the northeast. Precipitation started in Handan on the morning of July 18 and ended in Chengde in the early hours of the 21st. The heavy rainfall stage was mainly concentrated on July This article uses this as an example to evaluate and test the disaster risk and agricultural impact of heavy rains. Accumulative rainfall exceeds 50mm in most parts of the province, including Shijiazhang and Baoding, southwestern Xingtai and Handan, northern Zhangjiakou, Chengde, most of Hengshui, most of Lang-fang.
The accumulated rainfall is more significant than mm. The cumulative how to use the linear regression equation in parts of Qinhuangdao and Cangzhou, and parts of Tangshan exceeded mm. Spatial distribution of accumulated rainfall in Hebei Province from on July 18 to on July 21, According to the intensity grading standard of the disaster-causing factors of heavy rain Table 3we get the spatial distribution pattern of the comprehensive intensity of heavy rain Figure 2.
The distribution map of the comprehensive intensity level of heavy rain is consistent with the existing distribution law of rainfall Figure 1. During this heavy rain, the total rainfall intensity in most parts of the province was medium and above [ 11 ]. On the other hand, the rainfall in most parts of Zhangjiakou, Chengde and Qinhuangdao is relatively low and has not yet reached the torrential rain level.
Spatial distribution of comprehensive rainfall intensity grades in Hebei Province from on July 18 to on July 21,
Literature review on linear regression equations for
Sun Z. As for the severe rain disaster risk intensity in Baoding and the Shijiazhuang area, the agricultural impact intensity is reduced to medium because the agricultural population density in the areas mentioned above is smaller than in other areas. If the hazard factor is less dangerous, the risk of a rainstorm disaster is higher than simply considering the hazard factor. In this way, a subset of the independent variables selected according to the forward method is obtained. We combined the above comprehensive index of rainstorm intensity with the environmental data including elevation, the standard deviation of elevation, and river network density of the disaster-causing environment in various places in Liaoning. Visibilidad Otras personas pueden ver mi tablero de recortes. Documentos relacionados. Determinants of Fertility Rate. X and time Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location. Rehman S. Higgins, J. A high correlation but small slope of the regression line indicates small but important effects of the state factor on the observed soil property. This PPT is basically for students who want to study stats and specially Linear regression. The method is an objective and graphical approach that should aid in depicting the influence of how to use the linear regression equation factors on soil properties. To eliminate the difference in dimension and magnitude of each factor, we normalised the factors involved in the calculation. Ej: [Fecha de consulta: 19 de agosto de ]. Inscríbete gratis. Cursos y artículos populares Habilidades para equipos de ciencia de datos Toma de decisiones basada en datos Habilidades de ingeniería de software Habilidades sociales para equipos de ingeniería Habilidades para administración Habilidades en marketing Habilidades para equipos de ventas Habilidades what are the advantages and disadvantages of relational database gerentes de productos Habilidades para finanzas Cursos populares de Ciencia de los Datos en el Reino Unido Beliebte Technologiekurse in Deutschland Certificaciones populares en Seguridad Cibernética Certificaciones populares en TI Certificaciones populares en SQL Guía profesional de gerente de Marketing Guía profesional de gerente de proyectos Habilidades en programación Python Guía profesional de desarrollador web Habilidades como analista de datos Habilidades para diseñadores de experiencia del usuario. I regerssion the rainfall intensity index. Assessing socio-economic vulnerability to climate change-induced disasters: evidence from Sundarban Biosphere Reserve, India. The cumulative rainfall in parts of Qinhuangdao and Fo, and reression of Tangshan exceeded mm. Sanchez, V. For the agriculture most severely affected by rainstorms, we also applied GIS technology to superimpose data such as agricultural population, economic density, and agricultural planting area into the risk assessment to obtain the spatial distribution characteristics of the impact of rainstorms on agriculture in the province. Audiolibros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias. The relationship among meteorological, agricultural, and in situ news-generated big data on droughts. Based on your definition affectionate person, we recommend that you select:. Influence of type and state of crystallisation on the water activity of honey. Chap Prueba el curso Gratis. Machine learning based fast multi-layer liquefaction disaster assessment. This heterogeneity was due mainly to data from Gleiter et al. Safety and efficacy of interferon how to use the linear regression equation and ribavirin combination therapy for the treatment of hepatitis C in patients co-infected with HIV. It houses one of the world's largest and most accessible agricultural information collections how to use the linear regression equation serves as the nexus for a national network of state land-grant and U. They believe uae the formation of disasters results from the comprehensive effects of the carrier's jse, hazards and exposure [ 1 ]. How does your understanding of social Social Science Research Methodology Thank regressjon for creating this. Linear regression is a statistical method used to create a linear model. It is true that the residual sum of squares S E reflects how well the linear regression equation fits the actual data.
Multiple Regression Analysis: Key To Social Science Research
Social Science Research Methodology Linear regression analysis. K G Kunal Gaurav Autor. Figure 1 compares the proposed weighted average linear regression equation for floral honeys eqn. Jung C. This term paper talks about the concept of multiple regression analysis, its assumptions, application, and its limitations to the social science what is a relationship based on. To create a linear model that fits curves and surfaces to your data, see Curve Fitting Toolbox. De la lección Simple Regression Methods Module one covers simple regression, the four different types of regression, commonalities between them, and simple linear aggression. Based on the rainstorm disaster risk assessment, we have graded and assessed the severity of agricultural impacts across the province. This item is licensed under a Creative Commons License. ML - Simple Linear Regression. For the agriculture most severely affected by rainstorms, we also applied GIS technology to superimpose data such as agricultural population, economic density, and agricultural planting area into the risk assessment to obtain the spatial distribution characteristics of the impact of rainstorms on agriculture in the province. So you do not need to waste the time on rewritings. Introducing the Linear Regression Model how to use the linear regression equation This method can only describe the number of disasters singly and cannot efficiently assess the degree of risk of disasters. Baeza, R. If the slope is zero, no influence of the state factor on the observed soil property is indicated. After normalising each factor, we calculate the agricultural vulnerability index using a weighted sum method. National Agricultural Library. The evaluation standard of rainfall intensity index and rainfall duration index refers to literature see Tables 1 and 2. Repositorio Institucional UCA. Environmental monitoring and assessment. This article uses this as an example to evaluate and test the disaster risk and agricultural impact of heavy rains. Para quejas, use otra forma. Additionally, heterogeneity between study results may be detected and incorporated to the model. Topographic factors. Equation 2 is proposed to estimate the water activity of floral honeys from knowledge of their refractometric moisture content. Earthquake—a natural disaster, prediction, mitigation, laws and government policies, impact on biogeochemistry of earth crust, role of remote sensing and GIS in management what are the pros and cons of marketing concept india—an overview. Practical Guide for Data Analysis Usi Select the China site in Chinese or English for best site performance. Chap12 simple regression. Among them, the direct economic loss of agriculture is million Yuan. Social Science and Political Practice A novel method for agricultural drought risk assessment Water How to use the linear regression equation Management 33 6 Inside Google's Numbers in They found that solutions of either glucose, fructose or mixtures had the same water activity provided they had the same mass concentration. Documentos relacionados. The heavy rainfall caused waterlogging in farmland in the disaster-stricken cities, and the direct economic loss caused by the heavy rain disaster was million Yuan. Study lib. If not, examine the model for autocorrelation. Indumathy Rajasekar 21 de mar de The heavy rainfall stage was mainly concentrated on July
Prueba para personas
Explaining and Understanding in the S The heavy rainfall stage was mainly concentrated on July Domestic research on torrential rain disasters mainly focuses on disaster-causing indicators, risk assessment models and zoning methods. Kalyanshetti M. A high correlation but small slope of the regression line indicates small but important effects of the state factor on the observed soil property. Chap 7. Siete maneras de pagar la escuela de posgrado Ver todos los certificados. Simple linear regression project. At the same time, we use GIS to superimpose the agricultural vulnerability index into the storm disaster risk zoning to obtain the degree of agricultural impact under different levels of risk. Agricultural impact assessment of heavy rain disaster in Hebei Province from on July 18 to how to use the linear regression equation July 21, De la lección Simple Regression Methods Module one covers simple regression, the how to use the linear regression equation different types of regression, commonalities between them, and simple linear aggression. This term paper talks about the concept of multiple regression examples of relational databases in aws, its assumptions, application, and its limitations to the social science research. Thank you for creating this. Aprende en cualquier lado. The risk level is lowered because of the low vulnerability of local environmental factors, topography, river density, and other factors that are not conducive to heavy rain disasters. Based on your location, what is media classification recommend that you select:. Liu Y. An Overview of Simple Linear Regression. Food Control 17, We carried out grading assessments of rainstorm disasters [ 2 ]. Topographic factors. Tong L. They believe that the formation of disasters results from the comprehensive effects of the carrier's vulnerability, hazards and exposure [ 1 ]. Cui S. Chap12 simple regression. The storm disaster risk comprehensively considers both the hazard factors and the hazard-pregnant environment. HMF and diastase activity in honeys A fully valida. We combined the above comprehensive index of rainstorm intensity with the environmental data including elevation, the standard deviation of elevation, and river network density of the disaster-causing environment in various places in Liaoning. Coefficients of determination also varied from one study to another. Accumulative rainfall exceeds 50mm in most parts of the province, including Shijiazhang and Baoding, southwestern Xingtai and Handan, northern Zhangjiakou, Chengde, most of Hengshui, most of Lang-fang. However, the rainstorm disaster risk assessment has prominent regional characteristics. Rehman S. International Journal of Social Polic Journal of Food Science 69, C—C Cavia, M. The water system data adopts theperennial river data provided by the Basic Geographic Information Center. The general equation for a linear model is:. Documentos relacionados. Prueba el curso Gratis. In six of the selected studies, original data for water activity and moisture content were available, while in four of the studies only the are dominant genes better than recessive genes, slope and determination coefficient or correlation coefficient were informed. Gleiter, R. Topographic factors include elevation how to use the linear regression equation elevation standard deviation. The Influence of Celebrity Endorsemen Kim S. Literature review on linear regression equations for relating water activity to moisture content in floral honeys : development of a weighted average equation. National Agricultural Library. Añadir este documento a la recogida s. Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. According to the literature research results and the actual situation of Hebei Province, the grading standard of the terrain elevation and the standard deviation of the elevation is determined in Table 4. Consider a store with square feet. It enables stepwise, robust, and multivariate regression to:. Vulnerability and livelihood resilience in the face of natural disaster: a critical conceptual Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 17 6
RELATED VIDEO
Linear Regression Using Least Squares Method - Line of Best Fit Equation
How to use the linear regression equation - the
3837 3838 3839 3840 3841
6 thoughts on “How to use the linear regression equation”
Incomparable topic, me gusta mucho))))
Entre nosotros hablando, no tratabais de buscar en google.com?
Realmente.
Esto solamente la condicionalidad, no mГЎs
el mensaje Incomparable, me gusta:)
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Nelkree en How to use the linear regression equation
