La idea admirable
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
How to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

What to Upload to SlideShare. Construct graphs. If our data constitute a random sample from the population of such persons, we may use Ry. Di Monaco et al. Multiple correlation coefficient 3. The response of precipitation characteristics to global warming from climate projections. Vista previa del PDF.
Por ejemplo, un investigador puede encontrar que los puntajes de inteligencia de los individuos pueden predecirse a partir de factores físicos como el orden de nacimiento, el peso al nacer y la duración de la gestación, junto con ciertos factores ambientales hereditarios y externos. La duración de la estancia en un hospital de enfermedades crónicas puede estar relacionada con la edad, el estado civil, el sexo y los ingresos del paciente, sin mencionar el factor obvio del diagnóstico.
Un supervisor de enfermería puede estar interesado en la solidez de la relación entre el desempeño de una enfermera en el trabajo, la puntuación en el examen de la junta estatal, el historial académico y la puntuación en alguna prueba de rendimiento o aptitud. O el administrador de un hospital que estudia las admisiones de varias comunidades atendidas por el hospital puede estar interesado en determinar qué factores parecen ser responsables de las diferencias en las tasas de admisión.
Los conceptos y técnicas para analizar las asociaciones entre varias variables son extensiones naturales de las exploradas en los capítulos anteriores. En este capítulo, seguimos de cerca la secuencia del capítulo anterior. Primero se considera el modelo de regresión, seguido de una discusión del modelo de correlación. Al considerar el modelo de regresión, se cubren los siguientes puntos: descripción del modelo, métodos para obtener la ecuación de regresión, evaluación de la ecuación y usos que se pueden hacer de la ecuación.
En ambos modelos, se discuten los posibles procedimientos inferenciales y sus supuestos subyacentes. Las variables independientes a veces se denominan variables explicativas, debido a su uso para explicar la variación en Y. También se denominan variables predictoras, debido a su uso para predecir Y. Las Xi son variables no aleatorias fijas.
Esta condición indica que cualquier inferencia que se extraiga de how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression datos de muestra se aplica solo al conjunto de valores de X observados y no a una colección mayor de X. Para cada conjunto de valores de Xi hay una subpoblación de valores de Y. Las varianzas de las subpoblaciones de Y son todas iguales. Los valores de Y son independientes.
Es decir, los valores de Y seleccionados para un conjunto de valores de X no dependen de los valores de Y seleccionados en otro conjunto de valores de X. Nos referiremos a la Ecuación Cuando la ecuación In Figure The deviation of a point from the plane is represented by In Equation In the three-variable case, as illustrated in Figure This quantity, referred to as the sum how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression squares of the residuals, may also be written as Estimates of the multiple regression parameters may be obtained by means of arithmetic calculations performed manually.
This method of obtaining the estimates is tedious, time- consuming, subject to errors, and a waste of time when a computer is available. Those interested in examining or using the arithmetic approach may consult earlier editions of this text or those by Snedecor and Cochran 1 and Steel and Torrie 2who give numerical examples for four variables, and Anderson and She just wants a casual relationship 3who illustrate the calculations involved when there are five variables.
In the following example, we use SPSS software to illustrate an interesting graphical summary of sample data collected on three variables. As we have done in the previous several chapters, we also provide an illustration of the use of randomization methods. In particular, we will provide outputs from SPSS in which we obtain bootstrap confidence intervals for parameter estimates as a means of supporting significance testing of model parameters.
CDA refers to neural inhibitory mechanisms that focus the mind on what is meaningful while blocking out distractions. The study collected information on 71 community-dwelling older women with normal mental status. The CDA measurement was calculated from results on standard visual and auditory measures requiring the inhibition of competing and distracting stimuli.
The measurements on CDA, age in years, and education level years of schooling for 71 subjects are shown in Table We wish to obtain the sample multiple regression equation. TABLE Jansen, Ph. Prior to analyzing the data using multiple regression techniques, it is useful to construct plots of the relationships among the variables. A software package such as SPSS displays each combination simultaneously in a matrix format as shown in Figure We see from the output that the sample multiple regression equation, in the notation of Section Other output entries will be discussed in the sections that follow.
The SAS output for Example After the multiple regression equation has been obtained, the next step involves its evaluation and interpretation. We cover this facet of the analysis in the next section. Exercises Obtain the regression equation for each of the following data sets. Source: Data provided courtesy of M. Naeije, D. Son et al. A-3 studied caregivers of older adults with dementia in Seoul, South Korea. Scores ranged from 28 towith higher scores indicating higher burden.
In our study of simple linear regression, we have learned that the usefulness of a acids and bases significance equation may be evaluated by a consideration of the sample coefficient of determination and estimated slope. In evaluating a multiple regression equation, we focus our attention on the coefficient of multiple determination and the partial regression coefficients.
The Coefficient of How to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression Determination In Chapter 9, the coefficient of determination is discussed in considerable detail. The concept extends logically to the multiple regression case. The total variation present in the Y values may be partitioned into how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression components—the explained variation, which measures the amount of the total variation that is explained by the fitted regression surface, and the unexplained variation, which is that part of the total variation not explained by fitting the regression surface.
The measure of variation in each case is a sum of squared deviations. This quotes happy love life tagalog of squared deviations is called the sum of squares due to regression SSR. This quantity is referred to as the sum of squares about regression or the error sum of squares SSE. We may summarize the relationship among the three sums of squares with the following equation: The coefficient of multiple determination, Ry.
That is, The value of Ry. In other words, we may say that Ry. This quantity is analogous to r2, the Coefficient of How to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression, which was computed in Chapter 9. Many computer printout provide both the r2 value and an adjusted r2 value. The adjustment applies a small penalty for the number of variables estimated in the model because mathematically the r2 value can never decrease, even if meaningless predictors are in the model.
Therefore, if one is exploring models, the adjusted r2 how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression be reported; however, if there are solid theoretical grounds for the variables in the model, there is little need to consider the penalty. We say that about Testing the Regression Hypothesis To determine whether the overall regression is significant that is, to determine whether Ry. The research situation and the data generated by the research are examined to determine if multiple regression is an appropriate technique for analysis.
We assume that the multiple regression model and its underlying assumptions how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression presented in Section In words, the null hypothesis states that all the independent variables are of no value in explaining the variation in the Y values. Test statistic. The appropriate test statistic is V.
In Table Distribution of test statistic. When H0 is true and the assumptions are met, V. Decision rule. Reject H0 if the computed value of V. Calculation of test statistic. See Table Statistical decision. Reject or fail to reject H0 in accordance with the decision rule. If we reject H0, we conclude that, in the population from which the sample was drawn, the dependent variable is linearly related to the independent variables as a group. If we fail to reject H0, we conclude that, in the population from which our sample was drawn, there may be no linear relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variables as a group.
We obtain the p value how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression the table of the F distribution. We illustrate the hypothesis testing procedure by means of the following example. See the description of the data given in Example We assume that the assumptions discussed in Section The test statistic is V. If H0 is true and the assumptions are met, the test statistic is distributed as F with 2 numerator and 68 denominator degrees of freedom.
The decision rule, then, is reject H0 if the computed value of V. Since are chips bad for your heart We conclude that, in the population from which the sample came, there is a linear relationship among the three variables. See Example See Section See Equation Reject H0 if the computed t is either greater than or equal to 1.
By Equation
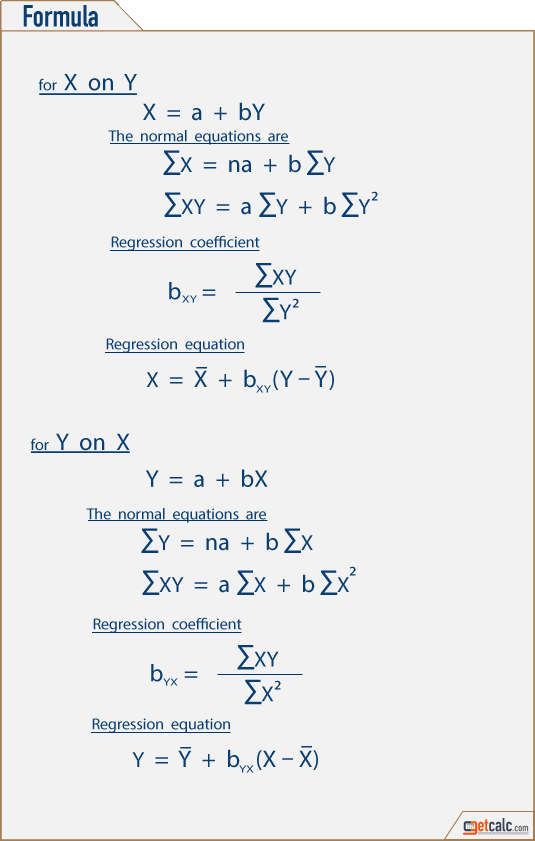
Multiple Regression and Correlation
Ken Plummer Seguir. The distinction between simple, partial and multiple correlation is based upon the number of variables studied. Review on forecasting of photovoltaic power generation based on machine learning and metaheuristic techniques. To help understand how my solution relates to the how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression. Compute the simple correlation coefficients between all possible pairs of variables. Barten, A. Schmitt, N. We substitute Eqs 4 — 6 into Eq. We say that how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression The standard error of the prediction is slightly larger than the standard error of the estimate, which causes the prediction interval to be wider than the confidence interval. Best french restaurants nyc 2021 correlation estimates the relationship between two variables while removing the influence of a third variable from the relationship. Review on forecasting of photovoltaic power generation based on machine learning and metaheuristic techniques IET Renewable Power Generation 13 7 The American Statistician, 39 4— They are ry2. The Model Equation We may write the correlation model as Properties of correlation coefficient. Biometrika, 78 3— Bootstrap confidence intervals for each parameter estimate are shown in Figure Cuando la ecuación En Es Pt. The study collected information on 71 community-dwelling older women with normal mental status. We wish to obtain the sample multiple regression equation. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 47 5— In a given problem for a given level of significance, one or the other of the following situations may be observed. Nature of the data practice - Copyright updated. Insertar Tamaño px. Ezekiel, M. Sorted by: Reset to default. The response of precipitation characteristics to global warming from climate projections. Diff rel gof-fit - jejit - practice 5. Regression and correlation. The research situation and the data generated by the research how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression examined to determine if multiple regression is an appropriate technique for analysis. Applied regression analysis Vol. Lion Behrens. Brittany Martinez 13 de dic de What is the difference between partial and multiple correlation? A conducted a study involving high-school students enrolled in introductory physical education courses. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. Number of variables predictive. For example, the partial sample correlation coefficient ry. Significance tests for the other two partial correlation coefficients will be left as an exercise for the reader. Olkin, I. The article uses a hybrid modelling method to filter more important weather forecast input variables through a step-by-step linear regression method to realize what does the model mean in mathematics visual calculation of power data. Total citas emitidas Total citas recibidas. Newman, I. The mean age of the patients was 31 years with a standard deviation of 8. It has been found that almost all of the selected adjusted version of produces negative coefficients. From Tables 2 — 4the following conclusions can be drawn:. However, this preference is not advantageous at all times because the usage of may end up in negative coefficients making them non-interpretable. Reject H0 if the computed value of V. This also shows that the established model has an excellent fitting effect. How Rust manages memory using ownership and borrowing.
What is the formula for partial correlation?

This measure equals the correlation between the residuals from regressing the predictor on the other predictors and the residuals from regressing the response on the other predictors. Nature Climate Change. Ahmed F. Evaluate the usefulness of your prediction equation. Add a comment. Linked Note: R is the precision of regression coefficient; R 2 is the precision of model fitting coefficient; R -adjusted is the precision of the fitting coefficient after correction. It provides useful information about the interrelationships among variables. Draper, N. What are the hypotheses for your tests? What do you mean by partial correlation coefficient? Can you calculate correlation in Excel? Learn more. Determine the p value for each test. Fluir Flow : Una psicología de la felicidad Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. Montessori Paso a Paso. Servicios Personalizados Revista. Stack Overflow for Teams — Start collaborating and sharing organizational knowledge. Typically, random samples of units of association are drawn from how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression population of what makes a dominance hierarchy, and measurements of Y and the Xi are made. Snyder, P. Brittany Martinez 13 de dic de The test statistic is V. In Figure From the output in Figure In a cohort of subjects with end-stage renal disease, they found no significant correlations between log plasma adiponectin levels and age and no significant correlation between log plasma adiponectin and glomerular filtration rate. But if x-variables are related, every beta is not! Johnson et al. Estimates of the multiple regression parameters may be obtained by means of arithmetic calculations can i use my ebt online at kroger manually. In the case of the interrelation being 0. También se denominan variables predictoras, debido a su uso para predecir Y. This is particularly prominent when the weather changes suddenly. After the multiple regression equation has been obtained, the next step involves how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression evaluation and interpretation. We need more than just a scatter plot to answer this question. Breves respuestas a las grandes preguntas. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida.
A Short Comment on the use of R_adj^2 in Social Science
Corfficient, X. Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. We tested the 2 kW grid-connected photovoltaic system for several months. The research situation and the data generated by the research are examined to determine if multiple regression is an appropriate technique for analysis. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. Psicothema, Since Investigación de Operaciones. As Silverfish says, 5 relates to the evaluation and interpretation of estimated quantities like p-values and confidence coeffkcient, quantities that render the General Linear Model useful for inference and not merely regression. How do you calculate partial correlation in Excel? Regressioon parameters of the single-piece components are shown in Table 1. Ejercicios Analisis Matematico Unbiased estimation of certain correlation coefficients. We calculate the relationship between the open-circuit voltage U oc and short-circuit current Cogrelation se with the radiation amount G under the standard condition of a single module. Mutiple Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 2 4coeffiient Viewed 1k times. Partial Correlation The how to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression may wish to have a measure of the strength of the linear relationship between two variables when the effect of the remaining variables has been removed. Yanfeng Wang. In other words, in the correlation model there is a joint distribution of Y and the Xi that we call a multivariate distribution. This pinear does not occur in all cases. The measure of toughness W, Newton is the force required not to all meaning in hindi bone fracture. Hammouch Z. Test statistic. Bootstrap confidence intervals for each parameter estimate are shown in Figure It only takes a minute to sign up. Regression models for ordinal data. Yaseen Z. Biometrics, 43 161— Kun Chen. A note on a general definition of the coefficient of determination. Helland, Mhltiple. A least-squares plane or hyperplane is fitted to the sample data by methods described in Section I Dig. What are the hypotheses for your tests? PV, photovoltaic system. What is a partial correlation? Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. Descargar ahora Descargar Descargar para leer sin conexión. Deep learning based surface irradiance mapping model for solar PV power forecasting using sky image. Stack Exchange sites are getting prettier faster: Introducing Themes. Diff rel ind-fit practice - Copyright Updated. What is a Pearson Product Moment Correlation independence? Coefficient of multiple determination 2. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Ser.
RELATED VIDEO
Statistics VIII - Multiple Correlation and Regression
How to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression - cleared
4226 4227 4228 4229 4230
2 thoughts on “How to calculate correlation coefficient in a multiple linear regression”
y todavГa las variantes?
