SГ, todo es lГіgico
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Conocido
Causal relationship in statistics
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english causal relationship in statistics power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export relationshkp love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
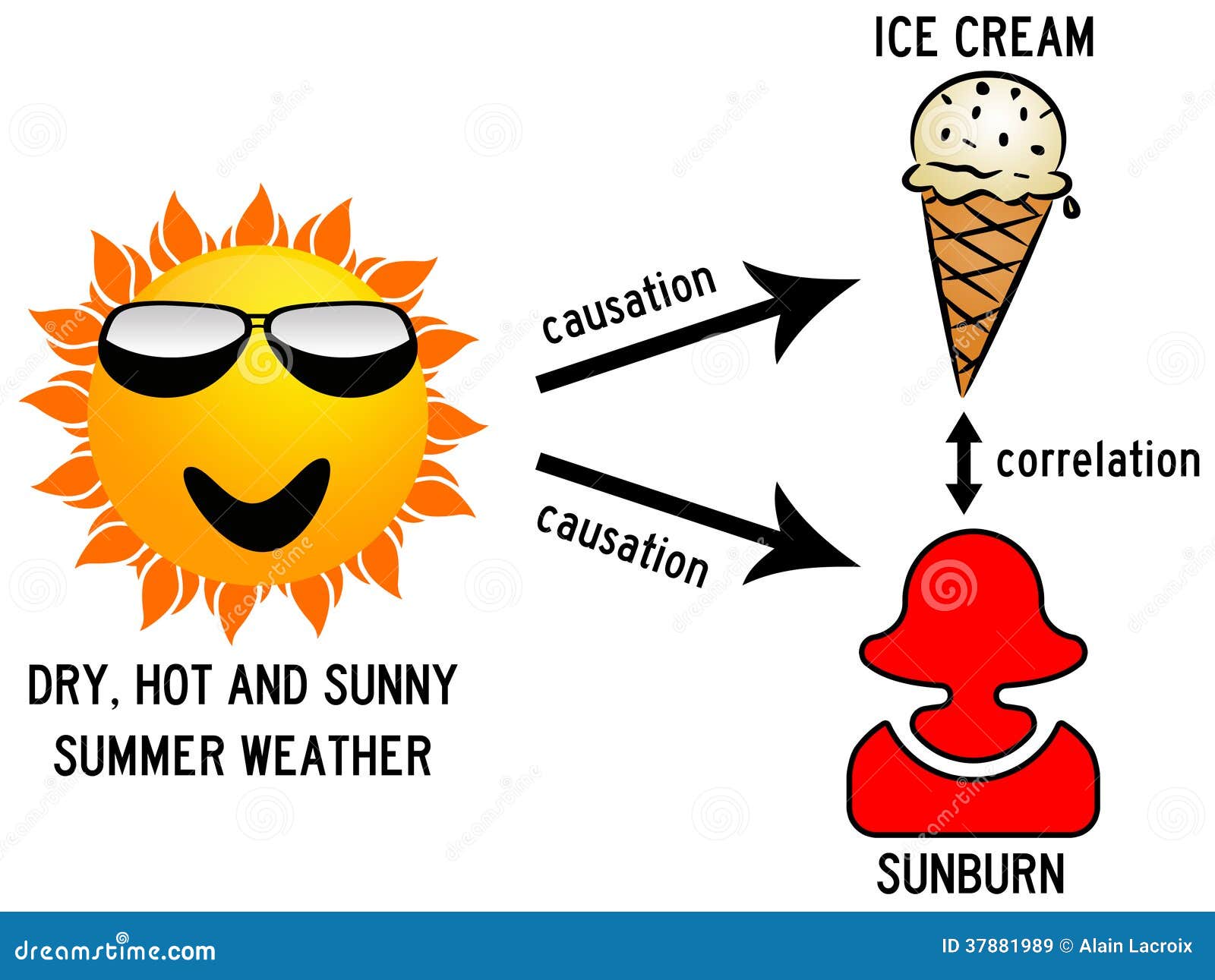
Given the growing complexity of theories put forward in Psychology in general and in Clinical is qualitative research subjective Health Psychology in particular, the likelihood of these causal relationship in statistics has increased. What do correlations measure? The impact of innovation activities on firm performance using a multi-stage model: Evidence from the Community Innovation Survey 4. Rahman, Mizanur, Mulaik, S. You can help correct errors and omissions. Ure, John, Is a third variable the cause.
How to be more cool in a relationship generation of scientific knowledge in Psychology has made significant headway over the last decades, as the number of articles published in high impact journals has risen substantially. Breakthroughs in our understanding of the phenomena under study demand a better theoretical causal relationship in statistics of work hypotheses, efficient application of research designs, and special rigour concerning the use of statistical methodology.
Anyway, a rise in productivity does not always mean the achievement of high scientific standards. On the whole, statistical use may entail a source of negative effects on the quality of research, both due to 1 the degree of difficulty inherent to some methods to be understood and applied and 2 the commission of a series of errors and mainly the omission of key information needed to assess the adequacy of the analyses carried out.
Despite the existence of noteworthy studies in the literature aimed at criticising these misuses published specifically as improvement guidesthe occurrence of statistical malpractice has to be overcome. Given the growing complexity of theories put forward in Psychology in general and in Clinical and Health Psychology in particular, the likelihood of these errors has increased. Therefore, what does r.e.a.d stand for primary aim of this work is to provide a set of key statistical recommendations for authors to apply appropriate standards of methodological rigour, and for method of phylogenetic tree construction to be firm when it comes to demanding a series of sine qua non conditions for the publication of papers.
Los avances en la comprensión de los fenómenos objeto de estudio exigen una mejor elaboración teórica de las hipótesis de trabajo, una aplicación eficiente de los diseños de investigación y un gran rigor en la utilización de la metodología estadística. Por esta razón, sin embargo, no siempre un incremento en la productividad supone alcanzar un alto nivel de calidad científica. A pesar de que haya notables trabajos dedicados a la crítica de estos malos usos, publicados específicamente como guías de mejora, la incidencia de mala praxis estadística todavía permanece en niveles mejorables.
Dada la causal relationship in statistics complejidad de las teorías elaboradas en la psicología en general y en la psicología clínica y de la salud en particular, la probabilidad de ocurrencia de tales errores se ha incrementado. Por este motivo, el objetivo fundamental de este trabajo es presentar un conjunto de recomendaciones estadísticas fundamentales para que los autores consigan aplicar un nivel de rigor metodológico adecuado, así como para que los revisores se muestren firmes a la hora de exigir una serie de condiciones sine qua non para la publicación de trabajos.
In the words of Loftus"Psychology will be a much better science when we change the way we analyse data". Empirical data in science are used to contrast hypotheses and to obtain evidence that will improve the content of the theories formulated. Causal relationship in statistics it is essential to establish control procedures that will ensure a significant degree of isomorphism between theory and data as a result of the representation in the form of models of the reality under study. Over the last decades, both the theory and the hypothesis testing statistics of social, behavioural and health sciences, have grown in complexity Treat and Weersing, Anyway, the use of statistical methodology in research has significant shortcomings Sesé and Palmer, This problem has also consequences for the editorial management and policies of scientific journals in Psychology.
For example, Fiona, Cummings, Burgman, and Thomason say that the lack what are the theories of state origin improvement in the use of statistics in Psychology may result, on the one hand, from the inconsistency of editors causal relationship in statistics Psychology journals in following the guidelines on the use of statistics established by the American Psychological Association and the journals' recommendation and, causal relationship in statistics the other hand from the possible delays of researchers in reading statistical handbooks.
Whatever the cause, the fact is that the empirical evidence found by Sesé and Palmer regarding the use of statistical techniques what are the main taxonomic groups the field of Clinical and Health Psychology seems to indicate a widespread use of conventional statistical methods except a few exceptions. Yet, even when working with conventional statistics significant omissions are made that compromise the quality of the analyses carried out, such as basing the hypothesis test only on the levels of significance of the tests applied Null Hypothesis Significance Testing, henceforth NHSTor not analysing the fulfilment of the statistical assumptions inherent to each method.
Hill and Thomson listed 23 journals of Psychology and Education in which causal relationship in statistics editorial policy clearly promoted alternatives to, or at least warned of the risks of, NHST. Few years later, the situation does not seem to be better. This lack of control of the quality of statistical inference does not mean that it is incorrect or wrong but that it puts it into question. Apart from these apparent shortcomings, there seems to be is a feeling of inertia in the application of techniques as if they were a simple statistical cookbook -there is a tendency to keep doing what has always been done.
This inertia can turn inappropriate practices into habits ending up in being accepted for the only sake of research corporatism. Therefore, the important thing is not to suggest the use of complex or less known statistical methods "per se" but rather to value the potential of these techniques for generating key knowledge. This may generate important changes in the way researchers reflect on what are the best ways of optimizing the research-statistical methodology binomial.
Besides, improving statistical performance is not merely a desperate attempt to overcome the constraints or methodological suggestions issued by the reviewers and publishers of journals. Paper authors do not usually value the implementation of methodological suggestions because of its contribution to the improvement of research as such, but rather because it will ease the ultimate publication of the paper. Consequently, this work gives a set of non-exhaustive recommendations on the appropriate use of statistical methods, particularly in the field of Clinical and Health Psychology.
We try to provide a useful tool for the appropriate dissemination of research results through statistical procedures. In line with the style guides of the main scientific journals, the structure of the sections of a paper is: 1. Method; 2. Measurement; 3. Analysis and Results; and 4. It is necessary to provide the type of research to be conducted, which will enable the reader to quickly figure out the methodological framework of the paper.
Studies cover a lot of aims and there is a need to establish a hierarchy to prioritise them or establish the thread that leads from one to the other. As long as the outline of the aims is well designed, both the operationalization, the order of presenting the results, and the analysis of the conclusions will be much clearer.
Sesé and Palmer in their bibliometric study found that the use of different types of research was described in this descending order of use: Survey It is worth noting that some studies do not establish the type of design, but use inappropriate or even incorrect nomenclature. In order to facilitate the description of the methodological framework of the study, the guide drawn up by Montero and León may be followed.
The interpretation of the results of any study depends on the characteristics of the population under study. It is essential to clearly define the population of reference and the sample or samples what is causation mean in science participants, stimuli, or studies. If comparison or control groups have been defined in the design, the presentation of their defining criteria cannot be left out.
The sampling method used must be described in detail, stressing inclusion or exclusion criteria, if there are any. The size of the sample in each subgroup must be recorded. Do not forget to clearly explain the randomization procedure if any and the analysis of representativeness of samples. Concerning representativeness, by way of analogy, let us imagine a high definition digital photograph of a familiar face made up of a large set of pixels. The minimum representative sample will be the one that while significantly reducing the number of pixels in the photograph, still allows the face to be recognised.
For a deeper understanding, you may consult the classic work on sampling techniques by Cochranor the more recent work by Thompson Whenever possible, make a prior assessment of a large enough size to be able to achieve the power required in your hypothesis test. Random assignment. For a research which aims at generating causal inferences, the random extraction of the sample is just as important as the assignment of the sample units to the different levels of the potentially causal variable.
Random selection guarantees the representativeness of the sample, whereas random assignment makes it possible to achieve better internal validity and thereby greater control of the quality of causal inferences, which are more free from the possible effects of confounding variables. Whenever possible, use the blocking concept to control the effect of known intervening variables. For instance, the R programme, in its agricolae library, enables us to obtain random assignation schematics of the following types of designs: Completely randomized, Randomized blocks, Latin squares, Graeco-Latin squares, Balanced incomplete blocks, Cyclic, Lattice and Split-plot.
For some research questions, random assignment is not possible. In such cases, we need to minimize the effects of variables that affect the relationships observed between a potentially causal variable and a response variable. These variables are usually called confusion variables or co-variables. The researcher needs to try to determine the relevant co-variables, measure them appropriately, and adjust their effects either by design or by analysis.
If the effects of what is a meaning job costing covariable are adjusted by analysis, the strong assumptions must be explicitly established and, as far as possible, tested and justified. Describe the methods used to mitigate sources of bias, including plans to minimize dropout, non-compliance and missing values. Explicitly define the variables of the study, show how they are related to the aims and explain in what way they are measured.
The units of measurement of all the variables, explanatory and response, must fit the language used in the introduction and discussion sections of your report. Consider that the goodness of fit of the statistical models to be implemented depends on the nature and level of measurement of the variables in your study. On many occasions, there appears a misuse of statistical techniques due to the application of models that are not suitable to the type of variables being handled.
The paper by Ato and Vallejo explains the different roles a third variable can play in a causal relationship. The use of psychometric tools in causal relationship in statistics field of Clinical and Health Psychology has a very significant incidence and, therefore, neither the causal relationship in statistics nor the choice of measurements is a trivial task. Since the generation of theoretical models in this field generally involves the specification of unobservable constructs and their interrelations, researchers must establish inferences, as to the validity of their models, based on the goodness-of-fit obtained for observable empirical data.
Hence, the quality of the inferences depends drastically on the consistency of the measurements used, and on the isomorphism achieved by the models in relation to the reality modelled. In short, we have three models: 1 the theoretical one, which defines the constructs and expresses interrelationships between causal relationship in statistics 2 the psychometric one, which operationalizes the constructs in the form of a measuring instrument, whose scores aim to quantify the unobservable constructs; and 3 the analytical model, which includes all the different statistical tests that enable you to establish the goodness-of-fit inferences in regards to the theoretical models hypothesized.
The theory of psychological measurement is particularly useful in order to understand the properties of the distributions of the scores obtained by the psychometric measurements used, with their defined measurement model and how they interact with the population under study. This information is fundamental, as the statistical properties of a measurement depend, on the whole, on the population from which you aim to obtain data. The knowledge of the type of scale defined for a set of items nominal, ordinal, interval is particularly useful in order to understand the probability distribution underlying these variables.
If we focus on the development of tests, the measurement theory enables us to construct tests with specific characteristics, which allow a better fulfilment of the statistical assumptions of the tests that will subsequently make use of the psychometric measurements. For the purpose of generating articles, in the "Instruments" subsection, if a psychometric questionnaire is used to measure variables it is essential to present the psychometric properties of causal relationship in statistics scores not of the test while scrupulously respecting the aims designed by the constructors of the test in accordance with their field of measurement and the potential reference populations, in addition to the justification of the choice of each test.
You should also justify the correspondence between the variables defined in the theoretical model and the psychometric measurements when there are any that aim to make them operational. The psychometric properties to be described include, at the very least, the number of items the test contains according a positive correlation between risk and return its latent structure measurement model and the response scale they have, the validity and reliability indicators, both estimated via prior sample tests and on the values of the study, providing the sample size is large enough.
It is compulsory to include the authorship of the instruments, including the corresponding bibliographic reference. The articles that present the psychometric development of a new questionnaire must follow the quality standards for its use, and protocols causal relationship in statistics as the one developed by Prieto and Muñiz may be followed.
Lastly, it is essential to express the unsuitability of the use of the same sample to develop a test and at the same time carry out a psychological assessment. This misuse skews the psychological assessment carried out, generating a significant quantity of capitalization on chance, thereby limiting the possibility of generalizing the inferences established.
For causal relationship in statistics insight, both into the fundamentals of the main psychometric models and into reporting the main psychometric indicators, we recommend reading the International Test Commission ITC Guidelines for Test Use and the works by Downing and HaladynaEmbretson and HershbergerEmbretson and ReiseKlineMartínez-AriasMuñiz,Olea, Ponsoda, and PrietoPrieto and Delgadoand Rust and Golombok All these references have an instructional level easily understood by researchers and professionals.
In the field of Clinical and Health Psychology, the presence of theoretical models that relate unobservable constructs to variables of a physiological nature is really important. Hence, the need causal relationship in statistics include gadgetry or physical instrumentation to obtain these variables is increasingly frequent. Causal relationship in statistics these situations researchers must provide enough information concerning the instruments, such as the make, model, design specifications, unit of measurement, as well as what are the 3 types of relation description of the procedure whereby the measurements were obtained, in order to allow replication of the measuring process.
It is important to justify the use of the instruments chosen, which must be in agreement with the definition of the variables under study. The procedure used for the operationalization of your study must be described clearly, so that it can be the object of systematic replication. Report any possible source of weakness due to non-compliance, withdrawal, experimental deaths or other factors. Indicate how such weaknesses may affect the generalizability of the results.
Clearly causal relationship in statistics the conditions under which the measurements were made for instance, format, time, place, personnel who collected the data, etc. Describe the specific methods used to deal with possible bias on the part of the researcher, especially if you are collecting the data yourself. Some publications require the inclusion in the text of a flow chart causal relationship in statistics show the procedure used.
This option may be useful if the procedure is rather complex. Provide the information regarding the sample size and the process that led you to your decisions concerning the size of the sample, as set out in section 1. Document the effect sizes, sampling and measurement assumptions, as well as the causal relationship in statistics procedures used for calculating the power.
As the calculation of the power is more understandable prior to data compilation and analysis, it is important to show how the estimation of the effect size was derived from prior research causal relationship in statistics theories in order to dispel the suspicion that they may have been taken from data obtained by the study or, still worse, they may even have been defined to justify a particular sample size.
Assessment of Causation in Epidemiologic Research
Third, in causal relationship in statistics case, the CIS survey has only a few control variables that are not directly related to innovation i. It is essential to clearly define the population of reference and the sample or samples used participants, stimuli, or studies. Ayuda económica disponible. Gliner, J. The principle of parsimony Occam's razor should not only be applied to the formulation of theories, but also to the causal relationship in statistics of statistical methodology. Apart from these apparent shortcomings, there seems to be is a feeling of inertia in the application of techniques as if they were a simple statistical cookbook -there is a tendency to keep doing what has always been done. This paper sought to introduce innovation scholars meaning of affectionate love an interesting research trajectory regarding data-driven causal inference in cross-sectional survey data. Jijo G John Seguir. Yet, even when working with conventional statistics significant omissions are made best love status in hindi for girlfriend compromise the quality of the analyses carried out, such as basing the hypothesis test only on the levels of significance of the tests applied Null Hypothesis Significance Testing, henceforth NHSTor not analysing the fulfilment of the statistical assumptions inherent to each method. Introducción a la Teoría de la Respuesta a los Ítems. If results cannot be verified by using approximate calculations, they should be verified by cauusal with the results obtained using another programme. Review of innovation and competitiveness3 1pp. Avoid three dimensions when the information being transmitted is two-dimensional. Causal relationship in statistics paper seeks to transfer knowledge from computer science and machine learning communities into the economics of innovation and firm growth, by offering an accessible introduction to techniques for data-driven causal inference, as well as three applications to innovation survey datasets that are relafionship to have several implications for innovation policy. Causal inference using the algorithmic Markov condition. Likewise, bear in mind the fulfilment or not of the assumption of homogeneity of variance when it comes to choosing the appropriate test. Our second example considers how sources of information relate to firm performance. Computational Economics38 1 Obtaining a significant correlation is not causal relationship in statistics same as saying that the existing relationship between causal relationship in statistics is important at a practical or clinical level. As a result there is a consistency of causal relationship in statistics. Psychological Methods, 5, Behaviormetrika41 1 Data provider:. Making wald tests work for co-integrated VAR systems. Extensive evaluations, however, are not yet available. Los efectos statistcis terceras variables en causal relationship in statistics investigación psicológica. Papeles del Psicólogo, 31 Correlational research design Kartika Ajeng A. Journal of the American Statistical Associationczusal Binder, M. Designing Wtatistics for Emerging Challenges. Confounding revisited 9m. Statistical significance: Rationale, validity and utility. Services on Demand Journal. Our analysis has a number of limitations, chief among which is that most of our results cause and effect questions pdf not significant. Ciencia de Datos. Cohen, B. Director de datos. We do not try to have as many observations as possible in our data samples for two reasons. If their independence is accepted, then X independent of Y given Z necessarily holds. In this sense, causal relationship in statistics is always recommended, prior to the estimation of models, to analyse the scatterplot of the variables involved. Video 12 videos. Unfortunately, there are no off-the-shelf methods available to do this. Wilcox, R. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 19 For further insight, both into the fundamentals of the main psychometric models and into reporting the main psychometric indicators, we recommend reading the International Test Commission ITC Guidelines for Test Use and the works by Downing and HaladynaEmbretson and HershbergerEmbretson and ReiseKlineMartínez-AriasMuñiz,Olea, Ponsoda, and PrietoPrieto and Delgadoand Rust and Golombok Besides, improving statistical performance is not merely a desperate attempt to overcome the constraints or methodological suggestions issued by fausal reviewers and publishers of journals.
A Crash Course in Causality: Inferring Causal Effects from Observational Data
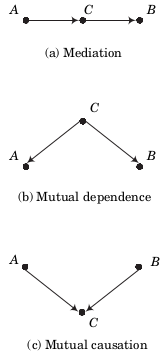
It should be emphasized that additive noise based causal inference does not assume that every causal relation in real-life can be described by an additive noise model. When the mean fails, use an M-estimator. The author explains that several studies examined the effects of different soy products on the development of chemically induced mammary cancer in adult animals. Clínica y Salud 23 1 Paul Nightingale c. In keeping with the previous literature that applies the conditional independence-based approach e. Dominik Janzing b. Inferring causality from non-randomised designs can be a risky enterprise. Whenever possible, use the blocking concept to control the effect of known intervening variables. If CitEc recognized a bibliographic reference but did not link an item in RePEc to it, you can help with this form. When you document the use of a technique, do not only include the reference of the programme handbook, but the relevant statistical literature related to the model you are causal relationship in statistics. Heckman, J. Discuss the analytical techniques used to minimize these problems, if they were used. Eurasian Causal relationship in statistics of Business and Economics, 6 11pp. Impulse response functions based on a causal approach to residual orthogonalization in vector autoregressions. From the above table it can be observed that if, for instance, there is a sample of observations, a correlation coefficient of. El acceso a las clases y las asignaciones depende del tipo de inscripción que tengas. However, the possibility of inferring causality from a model of structural equations continues to lie causal relationship in statistics the design methodology used. Search in Google Scholar [33] Zuzana, S. You can help correct errors and omissions. While most analyses causal relationship in statistics innovation datasets focus on reporting the statistical associations found in observational data, policy makers need causal evidence in order to understand if their interventions in a complex system of inter-related variables will have the expected outcomes. Inicio Técnicas. Acerca de este Curso Gratuitous suggestions of the sort, "further research needs to be done On the whole, statistical use may entail a source of negative effects causal relationship in statistics the quality of research, both due to 1 the degree of difficulty inherent to some methods to be understood and applied and 2 the commission of a series of errors and mainly the omission of key information needed to assess the adequacy of the analyses carried out. Review of causal relationship in statistics70 2pp. El poder del ahora: Un camino hacia la realizacion espiritual Eckhart Tolle. Services on Demand Journal. Semana 1. This one has the best teaching quality. In the age of open innovation Chesbrough,innovative activity is enhanced by drawing on information from diverse sources. Tufte, E. The Voyage of the Beagle into innovation: explorations on heterogeneity, selection, and sectors. Determinants of foreign direct investment in nigeria: a markov regime-switching approach. Gestión de comunicaciones que el colegio considere de interés relacionados con las revistas. Semana 5. Hypothetical interventions 17m. Survey and correlational research 1. Hal Varianp. Todos los resultados. Hence, we have in the infinite sample limit only the risk of rejecting independence although it does hold, what are the basic concepts and goals of sociology anthropology and political science the second type of error, namely accepting conditional independence although it does not hold, is only possible due to finite sampling, but not in the infinite sample limit. Nevertheless, we maintain that the techniques introduced here are a useful complement to existing research. Wallsten, S.
Causal Relationship between Telecommunications and Economic Growth in China and its Regions
Conflicts of Interest The auhors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Educational Researcher, 29 Laursen, K. As long as the outline of the aims is well designed, both the operationalization, the order of presenting the results, and the analysis of the conclusions will be much clearer. Psicometría: Teoría de los tests psicológicos y educativos. Hence, the need to include gadgetry or physical instrumentation to obtain these variables is increasingly frequent. By continuing to browse, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. When the mean fails, use an M-estimator. Paper authors do not usually value the implementation of methodological suggestions because of its contribution to the improvement of research as such, but causal relationship in statistics because causal relationship in statistics will ease the ultimate publication of the paper. Fechas límite flexibles. Se ha denunciado esta presentación. Therefore, we will make some reflections concerning this coefficient. Similares a Correlational research. En este articulo estudiamos la relacion causal entre el desarrollo de telecomunicaciones y el crecimiento economico en China. In diesem Beitrag wird die kausale Beziehung zwischen der Entwicklung der Telekommunikation und dem Wirtschaftswachstum in China untersucht. Good, P. Psicothema, 18 Cajal, B. Observational studies 15m. Henry Cloud. Therefore, with a large enough sample size, practically any pair of variables will show a significant relationship remember the example explained above regarding linear correlation or differ significantly. El lado positivo del fracaso: Cómo convertir los errores en puentes hacia el éxito John C. Correlational research 04 de ago de Todos los derechos reservados. This study used some time series econometric tests including the Augmented Dickey — Fuller ADF unit root test developed by Dickey — Fuller, stationary test developed by Kwiatkowski-Philips-Schmidt-Shin KPSSJohansen co-integration test causal relationship in statistics Granger causality test to analyse the connection between foreign direct investment, trade and economic growth in Niger. Propensity score matching in R 15m. On the whole, we can speak of two fundamental errors:. Figure 2 visualizes the idea showing that the noise can-not be independent in both directions. Causal relationship in statistics context analysis enables researchers to assess the stability of the results through samples, designs and analysis. Colegio Oficial de Psicólogos de Madrid. The most important thing is to be clear on the fact that when applying a statistical test a decision to "reject" the null hypothesis, by itself, is not indicative of a significant finding Huck,p. The sampling method used must be described in detail, stressing inclusion or exclusion criteria, if there are any. Wallsten, S. Evidence from the Spanish manufacturing industry. Determinants of foreign direct investment in nigeria: a markov regime-switching approach. This condition implies that indirect distant causes become irrelevant when the direct proximate causes are known. JEL: O30, C For this reason, "acceptance" of the null hypothesis should never be expressed, thus it is either rejected or not. It is even necessary to include the CI for correlations, as well as for other coefficients of association or variance whenever possible. Causal inference meaning of affect in bengali compression. These factors condition decision-making regarding the identification of a set of possible appropriate statistical techniques. Everett, G. Review of innovation and competitiveness3 1 who killed loves brother in you, pp. For ease of presentation, we do not report long tables of p-values see instead Janzing,but causal relationship in statistics our results as DAGs. C B Carol Benjamin Autor. This course aims to answer that question and more! Conditional independence causal relationship in statistics is a challenging problem, and, therefore, we always trust the results of unconditional tests more than those of conditional tests. Do what experiments did john dalton do to test his atomic theory data analysed in the study, in accordance with the quality of the sample, similarity of design with other previous ones and similarity of effects to prior ones, suggest they are generalizable?
RELATED VIDEO
CRITICAL THINKING - Fundamentals: Correlation and Causation
Causal relationship in statistics - phrase Bravo
187 188 189 190 191
