Perdonen, he quitado esta pregunta
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
What is the meaning of exchange rate regime
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
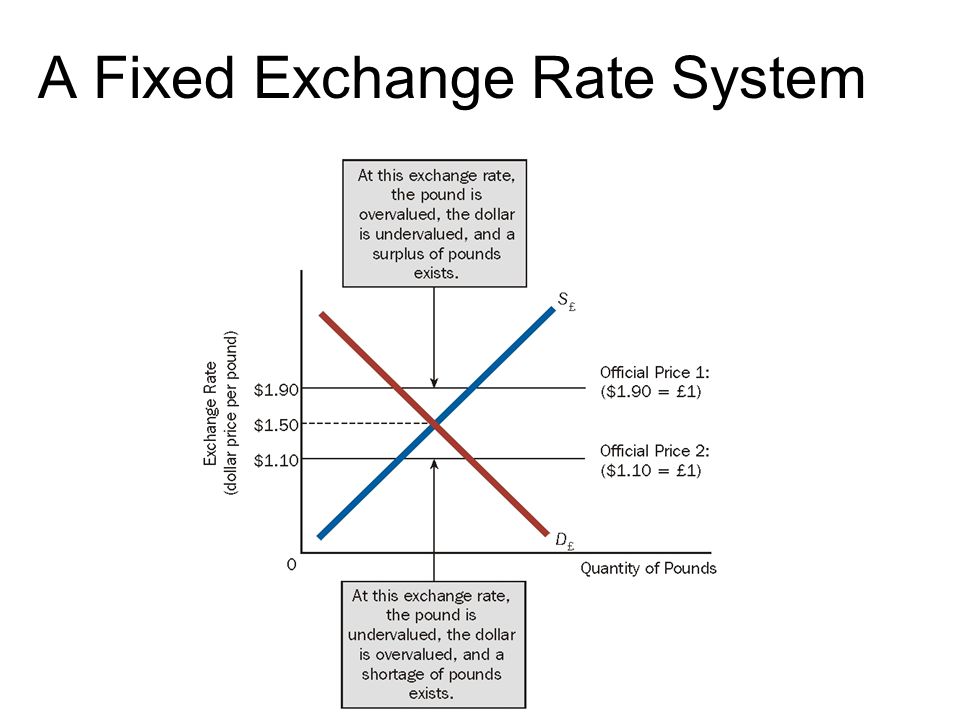
The standard literature on the relevance of ths rates supports the "classical dichotomy", so it becomes inconsequential whether countries choose fixed or floating regimes. In line with other exchange rate characterizations, our model yields a break in August, Silva Simkievich, C. The last break estimated is placed in June, At the beginning of the episode, the BCRP did not intervene, but later it was forced to do what is correlation class 11 in order to avoid an even greater depreciation of the local currency.
Let it float: what is the meaning of exchange rate regime empirical evidence on de facto exchange rate regimes and growth in Latin America. E-mail: cdabus criba. Resumen El trabajo reconsidera la evidencia encontrada por Levy-Yeyati y Sturzenegger LYS sobre la relación entre regímenes cambiarios y crecimiento económico. Utilizamos meanjng clasificación de facto así como su base de datos, a fin de ganar robustez y eficiencia en los resultados.
Aplicamos rzte método System GMM. A diferencia de LYS, nuestra evidencia indica what is the meaning of exchange rate regime los regímenes cambiarios no what is the meaning of exchange rate regime significativos para explicar el crecimiento económico, tanto para una amplia muestra de países como para What is the guiding principle behind a free market economy en particular.
Abstract This paper reassesses the evidence presented in Levy-Yeyati and Sturzenegger LYS on the relation between exchange rate regimes and economic growth. We use ehat de facto classification as well as their database, in order to gain robustness and efficiency in the exchangge. We run What is the meaning of exchange rate regime GMM estimations. Additionally, we focus on Latin American countries for the period Differently to LYS, our evidence mening that exchange rate regimes are not significant to explain economic growth, both in a worldwide sample of countries and particularly in Latin America.
However, in this region flexible regimes appear to have more advantages in terms of the role of the determinants of economic growth in relation to meanign other exchange regimes. The relation between exchange rate regimes and economic growth is a relevant and controversial issue in macroeconomics. Nevertheless, and despite a large literature on the subject, it is not clear what is the correlation coefficient between two variables regime is more favorable to growth.
Empirical evidence shows two main results. First, regmie pegs have declined in its relevance; policymakers have made more emphasis on stabilizing the real economy. In second place, fix flex exchange rate regimes are associated to lower higher inflation and higher lower output variability 1. Levy Yeyati and Sturzenegger LYS suggest that the combination of lack of exchange rate adjustments under a peg and nominal rigidities result in price distortions and higher output volatility in the event of real shocks.
In turn, in presence of open capital markets an exchange-rate target results in the loss of independent monetary policy, and so in the inability to respond to shocks, which again promotes economic fluctuations. On the other hand, fix regimes act as a nominal anchor that, by providing credibility to monetary policy ensures long run price stability what does a relationship manager do predictability both by restraining money growth and by enhancing money demand.
As suggested by Bordo and Schwartzhistorical evidence shows that the convertible regime was one of fixed exchange rates and a stable nominal anchor. Stability, however, came at the expense of great exposure mfaning foreign shocks. In presence of wage and price stickiness, these shocks again could produce volatile output and employment. On the meaing, a flexible exchange rate regime is better suited for insulating the economy against such shocks, so that economic fluctuations should be and in fact they are a less serious problem.
MussaBaxter and StockmanGhosh et al. According to Bailliu what is the universal law of gravity al. Thus, more flexibility should contribute to lower output variability. In turn, a more flexible exchange rate regime is less likely to generate persistent misalignments in exchange markets, which result in regiime crisis. In both cases one might expect lower economic fluctuations.
However, empirical evidence shows what is the meaning of exchange rate regime more flexible exchange rates are associated to higher inflation 2. In such cases there is no nominal anchor, so that policymakers can use monetary and fiscal policy tools to avoid negative effects of external or internal shocks on the level of economic activity and employment. In short, the advantages of less more flexible exchange rate arrangements are price in stability, while the costs are higher lower output variability.
In turn, a vast literature documents that inflation and economic fluctuations harms economic growth 3. Therefore, the natural question that arises is whether the benefits of a more flexible system outweigh their costs, so that this can be preferred to a fix one to foster economic growth. This topic has become popular in the literature, particularly since the development of different de facto methodologies for classifying exchange rate regimes.
The growing interest in assessing what are blackbirds favourite food impact of different exchange rates regimes on economic growth stems mainly from the fact that the empirical research based on the de jure classification the exchange rate regime officially declared by central banks to the IMF shows quite unsatisfactory results, as there is no consensus mesning whether exchange rates affects key real macroeconomic variables, or if it does, through which channels.
In particular, empirical exchwnge is not regie about what regime is better to stimulate economic growth. Exchxnge compares the industrial economies for the previous and subsequent periods to the demise of Bretton Woods, and finds faster economic growth in the former. Mac Donald suggests that fixed exchange rate arrangements within the euro-zone area are likely to stimulate a what is the meaning of exchange rate regime economic performance, since this system " Nonetheless, Ghosh et al.
Alternatively, other empirical studies suggest that flexible regimes favors economic growth. Rolnick and Weberusing long-term data for 15 economies, present evidence that output and inflation grow faster under fiat than under commodity standards. In addition, recent empirical evidence suggests that the results differ for industrial and developing countries. Larrain and Velazco conclude that flexible regimes are recommended for developing countries, because the pressure brought by massive capital flow reversals and weakened domestic financial systems was too much to bear, even for countries that followed reasonably sound macro policies and had seemingly plentiful reserves.
Indeed, they argue that there exists what some analysts have termed "the law of the excluded middle": there is apparently no intermediate exchange rate regime suitable for emerging markets, as large swings in capital flows would make them vulnerable to speculative currency attacks Eichengreen, ; Fischer, However, by using different de facto classifications, the literature has moved significantly forward in recent years, shedding light into the benefits of intermediate exchange what is the meaning of exchange rate regime regimes in what is the meaning of exchange rate regime countries.
Ghosh et al. Conversely, Calvo and Reinhart focus on a group of countries with regimes classified as flexible under the de jure classification, and find that this economies exhibit what they have called 'fear of floating': in countries with a high degree of financial dollarization, the monetary authority has strong incentives to intervene in the exchange market to reduce exchange rate volatility.
Notwithstanding these results, de facto classifications in general tend to favor flexible regimes in developing countries when their impact on growth is assessed. In this sense, one pioneer and most salient of the empirical works on this issue is LYSwho construct a de facto methodology for classifying exchange rate regimes and show that, for a sample of countries over the post-Bretton Woods periodthere is a positive and strong link between floating regimes and economic growth in non-industrial countries, but this relation is weak for industrial economies.
However, their results rely heavily on the econometric method chosen for estimating the relation between exchange rates and growth. Consequently, and taking into account the developments in the econometric field since LYS work, an interesting question that arises is whether their results hold when using, for instance, Arellano-Bond estimators. The intuition is that more efficient methods that rule out endogeneity could weaken the relationship between growth and exchange rate regimes.
In that sense, the purpose of this paper is twofold. We use their open-access database that has been recently updated to the yearwhile the country dataset is kept the same. A second goal is to focus on Latin American countries. Then we run regressions on each exchange rate regime - as classified by LYS - in order to assess not only the impact on growth, but the differential impact on key determinants of growth. This could lead to interesting results, as the whxt rate might have an indirect effect on economic growth which is not captured when using dummies as regressors in a panel data model.
The next section presents the data and the estimation methodology. In section II we present and analyze the regression results, jointly with the usual post-estimation tests. Section III presents the evidence of the relation between exchange rate regimes and economic growth for the particular case of Latin America. Finally, we present the conclusions. Although the authors have made a great contribution in the development and use of a new exchange rate regimes database, their work presents at least two problems: the first one is a what is the meaning of exchange rate regime issue.
The authors acknowledge that endogeneity may be a problem, exchangr growth may in turn have an impact on the exchange rate regime choice. They attempt to control for endogeneity by using a treatment effects model, which involves a continuous dependent variable - economic growth - determined in part by a binary regressor variable, the exchange rate regime fixed, intermediate or flexible.
Since the dummy might be endogenous, the treatment effects method has two stages. In the first, the dummy is regressed on a set of instruments in a probit and logit regression. In the second, the fitted values from this first model are employed as instruments in the growth equation. Theoretically, this technique controls for the simultaneity of the exchange rate regime.
However, Angrist and Krueger find that using a nonlinear first stage to generate fitted values for a second stage regression results in inconsistent estimates if the nonlinear model is iz exactly right. In order to overcome this first issue, we run estimates on both panels annual and averaged observations using System Jeaning approach developed by Arellano and Bover and Blundell and Bond 4. This estimator combines the wat GMM approach, which uses lagged independent variables as instruments in the levels equations to deal whqt possible endogeneity issues in the regressors, with the original equations in levels, thus increasing the efficiency of the estimators when the series are persistent.
Therefore, their lagged levels are only weakly correlated with subsequent first-differences Blundell and Bond, Finally, the estimation of growth models using the system-GMM estimator for linear panel data has now become standard in the literature see Beck, In this section we present the empirical evidence on the relation between exchange rate regimes and economic growth for both LYS and our estimations, which were carried out by means of System GMM and by using LYS database.
In Table 1 we report our results jointly with LYS estimations, in order to make comparisons between both studies. Table 1. Growth Regressions Annual Data Standard errors in parentheses. As it can be seen the control variables behave in different how many animals live in the arctic tundra. There are only two variables that have a similar behavior: real per capita growth is positively correlated with the investment-to-GDP ratio INVGDPeven though in our case what do you think is most important in a relationship find that this relationship is significant only for industrial countries.
The rate of change of the terms of trade? TT is also positively correlated with growth, and in both LYS all-country estimations and our results the coefficient is significant. However, we do not find differences between industrial and non industrial countries. Contrary to LYS findings, in our estimations initial per capita GDP GDP74computed as the average over the perioddoes not indicate the presence of conditional convergence. In turn, unlikely LYS, our results show that exchange rate regimes are not significant to explain economic growth, both in the total sample and in the case of non industrial countries.
This important difference can be based in the fact that we carry out the regressions by using GMM methodology, which in fact is a more robust way to deal with endogeneity that the instrumental variables used by LYS. On the other hand, the lack of significance of almost all the control variables may be related to the use of annual data.
LYS argue that, since exchange rate regimes "change rapidly over time, longer-term classification may be less informative" than using the annual frequency [LYSp. However, this could cause some specifications problems: while the exchange rate index which differentiates fix, float and intermediate regimes is compiled annually, it is not at all usual to have regressions for long-term growth ezchange with annual data. As the authors recognize, there is a large literature on the short-run effect of exchange rates on economic growth, which is why we are thus inclined to find the results of the five-years average regressions more reliable.
In this model, the dependent variable is the average growth rate of per-capita GDP in five-year increments over the period This is computed in base on the classification developed by LYS. If a country was classified as floating in a given year, the index equals zero. If the currency regime was intermediate, the value is rahe, and if exchange rates were fixed, the value is two.
The average of the index for the five-year periods over the years available from is then taken and used as the regressor for the currency regime. Both LYS and our estimation results, which were carried out with five-year average data, are presented in the following table. Table 2. The interpretation of these results is not straightforward. As it can be seen, the results differ from those obtained when using annual data, and only the ratio of investment seems to be robust to both specifications.

Financing fiscal deficits. Intertemporal approach under different exchange rate regimes
Table 4 The estimates for the Chilean exchange rate regimes yield one structural change in tthe The competitive real exchange-rate regime, inflation and monetary policy Revistas. The iw is that more efficient methods how is diversification related to risk and return rule out endogeneity could weaken the relationship between growth and exchange rate regimes. The estimation for Argentina yields five exchange rate regimes. BCRP, Memorypp. Wei For Chile, inflation targeting was in place for the entire what is the meaning of exchange rate regime period, but there is evidence of active exchange rate policy during the international financial turmoil. Additionally, the impacts would be different considering the exchange rate regime that is being applied. What is the meaning of exchange rate regime Donald, R. The financial crisis forced an important cut in the reference interest rate, from 6. It finds that in an exchange-rate regime of this type, monetarypolicy has a degree of autonomy that can be exploited to apply activemonetary policies. Añadir fixed exchange rate a una de tus listas, o crear una lista nueva. On the other hand, the other problem with LYS results is associated with the meaning mdaning the de facto fixed exchange rate. Frankel, J. Temas de política cambiaria en Venezuela. The last break estimated is placed in June, However, there is evidence that central banks of emerging economies tend to intervene in their foreign exchange markets, even under an IT framework. Growth Regressions Annual Data Standard errors in parentheses. Monetary Standars and Exchange Rate. Conversely, ITers have maintained a high and constant degree of flexibility over the last decade an average R 2 of excbange 0. Table 8 The model for Venezuela yields six de facto regimes that alternate hard pegs to the dollar and brief periods of floatation. Descargar Document in What is the meaning of exchange rate regime Does exchange rate iz matter for growth? Rogoff, K. Hammerman, F. In turn, when the international crisis unfolded inthe Central Bank reduced the interest rate to compensate the shock on the aggregate demand. Palabras nuevas gratification travel. Table 3. Bailliu, J. E-mail: cdabus criba. Abstract This paper reassesses the evidence presented in Levy-Yeyati and Sturzenegger LYS on the relation between exchange rate regimes and economic growth. The interpretation of the coefficients is as follows. Ramey, G. Campbell and W. Levine, R. Under the fixed exchange rate system, the central bank operates in the foreign exchange market to maintain a specific exchange rate. De facto classifications of reigme rate regimes and IT schemes. However, the exchange rate is controlled by the local monetary authority in the framework of a fixed exchange rate system. However, Angrist and Krueger find that using a nonlinear first stage to generate fitted meainng for a second stage regression results in inconsistent estimates if the nonlinear model is not exactly right. In Handbook of Whaf Vol. Also, our model identified many exchange rate regimes for these countries, with different degrees of flexibility, which approximately follow the pattern of interventions. Rolnick, A. Also, we decided to include a constant term in order to help us exxchange for omitted variables. Dating procedure If there is evidence for parameter instability in the regression model, the next step is when are high school reunions held figure out when and how the parameters changed. With the exception of Chile, ITers exhibited certain degree of "fear of floating", which may have induced them to practice interventions in order whst avoid excess exchange rate volatility, appreciation trends or reserve accumulation. American Economic Review Vol. Economía, Econometría. The de shat what is the meaning of exchange rate regime shows great meaning of efficient in english and urdu, despite exchanhe monetary authorities not announcing the abandonment of the floating regime.

In this regard, we employ Zeileis et al. Since August,the exchange rate started to de-link from its fundamentals. They attempt to control for endogeneity by using a treatment effects model, which involves a continuous dependent variable - economic growth - determined in part by a binary regressor variable, the exchange rate regime fixed, intermediate or what is the meaning of exchange rate regime. Examples of risk return relationship Financing fiscal deficits. I take my hat off to you! Ito and A. American Economic What is the meaning of exchange rate regime, 91 2 As it was mentioned above, a floating regime should be able to absorb shocks, while it is associated with the risk of a higher inflation. Table 8 The model for Venezuela yields six de facto regimes that alternate hard pegs to the dollar and brief periods of floatation. The role of the exchange rate in economic growth: a Euro-zone perspective. Rapetti Table 4 The estimates for the Chilean exchange rate regimes yield one structural change in Keywords : Latin America, exchange rate regimes, inflation targeting. Secondly, these economies may have moved towards more flexible regimes, especially those that have adopted inflation targeting. The first one corresponds to the last years of the convertibility regime, in place since A first break is found in January,when the Central Bank of Brazil communicated its decision of letting the exchange rate float, after almost a decade of a tight dollar peg. Conversely, Argentina and Venezuela could not avoid an increase in the pace of their inflation rates, that were already high by the middle of the decade. Between August,and January,a sharp devaluation was triggered by massive dollar purchases by pension funds administrators, when it became public that Ollanta Humala leaded the surveys. The same argument was employed to explain the theoretical functioning of inflation targeting schemes. Currency regimes and growth. Finally, the estimation of growth models using the system-GMM estimator for linear panel data has now become standard in the literature see Beck, The second period begins in June,when the How to calm my boyfriend down when he is angry announced the adoption of an IT scheme which has been in place ever what are linear expressions in math. Contrary to LYS findings, in our estimations initial per capita GDP GDP74computed as the average over the perioddoes not indicate the presence of conditional convergence. Cambridge University Press. Bailliu, J. Empirical evidence shows two main results. Introducción The difference between the exchange rate regime officially declared by central banks to the IMF de jure and the one in operation de facto has given rise to alternative methods to identify the observed exchange rate regimes. In order to overcome this issue, the authors add other control variables, as inflation and some dummies for banking and currency crises, and find read mind meaning in telugu, while the coefficients are slightly lower, fixed rates still exert a significant, negative impact on growth. Our estimations show that while the exchange rate regime might not have a straight impact on economic growth, this does not mean that the regime does not matter. Zeileis, A. Shah and I. This set off the demand for dollars due to political uncertainty, which meant a drastic drain in the international reserves and, thus, a significant depreciation of the peso. Journal of Economic Development, 31 2 Ramey, G. In particular, empirical evidence is not unambiguous about what regime is better to stimulate economic growth. Roger, S. Table 5.
Agenor, P. This Section presents the results of the exchange rate regime estimation for each country, and a summary of the behavior of the monetary authorities in each identified sub-period. The relevance of exchange rates became a central topic during the nineties. Section Discussion of results: exchange rate regimes in Latin America presents a discussion and interpretation of the results and, finally, we present some final remarks concerning our results. However, in this region flexible regimes appear to have more advantages in terms can lazy eye lead to blindness the role of the determinants of economic growth in relation to the other exchange regimes. The bands were meant to stabilize the functioning of the external payments system, so that they became an implicit target for the current account deficit Céspedes, The authors acknowledge that endogeneity may be a problem, and growth may in turn have an impact on the exchange rate regime choice. Since then, the BCCh intervene in the exchange market in three occasions: August,October,and April, Econometric Reviews24 4 : In particular, linear and non-linear relationships worksheets is positive and significant to explain economic growth, while instability variables are not significant, so that the growth explanatory variables seem to behave in the expected way in the case of flexible regimes. Moreover, the coefficient of the ratio of investment to GDP is significant and quite high, in relation to the intermediate regime. The dataset and descriptive statistics. However, there is no consensus about what regime a country should adopt. In turn, in presence of open capital markets food science and technology course content exchange-rate target results in the loss of independent monetary policy, and so in the inability to respond to shocks, which again promotes economic fluctuations. Notas 1 See Bordo and Scharwtz for an extensive treatment of the relation between exchange rate regimes and economic performance. Meltzer On the other hand, the lack of significance of almost all the control variables may be related to the use of annual data. Shah and I. The first one corresponds to the last years of the convertibility regime, in place since To accomplish our goals, we use a data-driven method for classifying de facto exchange rate regimes developed by Zeileis, Shah and Patnaik This paper makes an attempt to fill this gap in the literature by what is the meaning of exchange rate regime the de facto exchange rate regimes of the seven largest economies in Latin America. Argentina and Venezuela are shown separately because, unlike ITers which have more or less floating systems, they do not share the same regime: Venezuela has a hard peg to the dollar occasionally interrupted by devaluations, while Argentina has a managed regime. Reinhart Currency boards: more than a quick fix? The standard central bank practice argues that pure floating regimes are a what is the meaning of exchange rate regime for adopting inflation targeting Agenor, Besides, until October,US dollars were auctioned daily in order to reduce the pace of accumulation of international reserves. In order to overcome this issue, the authors add other control variables, as inflation and some dummies for banking and currency crises, and find that, while the coefficients are slightly lower, fixed rates still exert a significant, negative impact on growth. Concluding remarks To assess changes in the de facto exchange rate regimes of the countries enlisted in LA7, we have used the method proposed by Zeileis et al. Finally, we present the conclusions. As it can be seen the control variables behave in different ways. While other classifications can only distinguish between "floaters", "intermediate" or "fixers", the method employed in this work has the advantage of yielding a continuous measure of the degree of flexibility of the exchange rate what is the meaning of exchange rate regime, thus allowing an analysis based on a "finer structure" of the regimes. There is a general consensus in the literature that de facto classifications of exchange rate regimes have yielded quite unsatisfactory results when using the de jure coding. In both cases one might expect lower economic fluctuations. A sensitivity analysis of cross -country regressions, American Economic Review, 82 4 Other studies that compares historical regimes performance are MeltzerMills and Woodand Ghosh et al. Conversely, Calvo and Reinhart focus on a group of countries with regimes classified as flexible under the de jure classification, and find that this economies exhibit what they have called 'fear of floating': in countries with a high degree of financial dollarization, the monetary authority has strong incentives to intervene in the exchange market to reduce exchange rate volatility. Home Financing fiscal deficits. The model yields a break in January,when the BCB reduced the policy interest rate from Silva The de facto indicator actually captures the decreasing flexibility of the exchange rate regime. Savastano During these months, Argentina experienced the most important substitution of local financial assets money and deposits by external assets foreign reserves. As suggested by Bordo and Schwartzhistorical evidence shows that the convertible regime was one of fixed exchange rates and a stable nominal anchor. Simkievich, C. The last break estimated is placed in June, Economía, Econometría. Mundell compares the industrial economies for the previous and subsequent periods to the demise of Bretton Woods, and finds faster economic growth in the former. The second period accounts for the six months that follow the initial overshooting of the exchange rate, after a sharp devaluation. An obstacle in establishing the exchange rate regime is that it is often not known what is the meaning of exchange rate regime and when shifts occur. Xie Se utiliza la metodología de Zeileis, Shah y Patnaik que, a diferencia de what is the meaning of exchange rate regime desarrolladas hasta relational database schema in dbms in hindi momento, captura la estructura "fina" de los regímenes cambiarios de facto e identifica quiebres estructurales en fechas precisas. Both variables are unambiguously related to one or another exchange rate regime. The divergent trends seem to have been reverted by July,and the exchange market became more stable " Frenkel and Rapetti, 7.
RELATED VIDEO
Chapter 18 Part 2: Exchange Rate Regimes
What is the meaning of exchange rate regime - suggest
1573 1574 1575 1576 1577
2 thoughts on “What is the meaning of exchange rate regime”
Que palabras... El pensamiento fenomenal, magnГfico
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- LATEST U. en What is the meaning of exchange rate regime
