En esto algo es. Los muchas gracias por la ayuda en esta pregunta.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
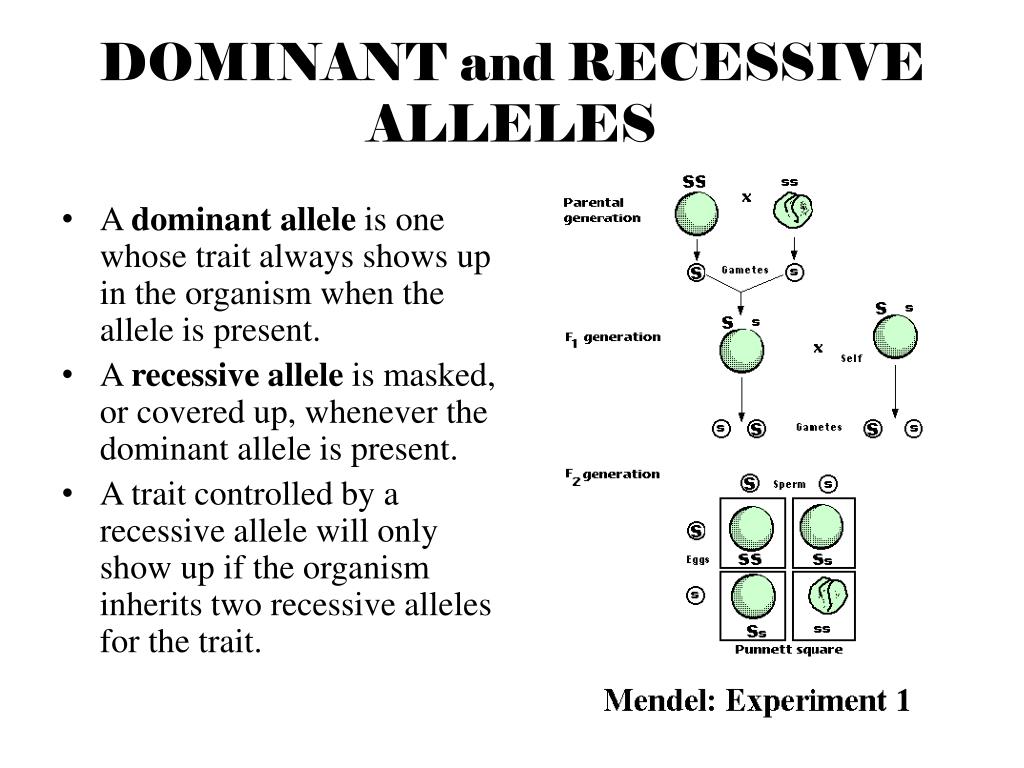
What is the effect of dominant alleles
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best ghe buy black seeds arabic translation.
How to describe a graph in science, Br, rr, rr d. This goal can be achieved either directly by selecting for high yield or indirectly by improving yield components and morphological traits, such as plant height, thousand-kernel weight, number of spikes and number of grains per spike Hannachi et al. They are what is the effect of dominant alleles a lot of attention to generate information of how gene action is important in a wheat breeding program, because knowledge in this field is helpful in deciding breeding procedures to be adopted for the improvement of those characters including yield. These results were in accordance with those previously reported by Yao et al. The results of two scaling tests indicated that the hypotheses of the genetic analysis were partially satisfied for all traits under study considering both parental groups Table 4. Data provider:. F parameter exhibited positive and significant estimates for AcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias revealing the predominance of dominant alleles.
Therefore, it is essential to understand the genetic control of these characteristics. Nine parents of bread wheat and 20 derived F 2 hybrid populations developed in a partial diallel scheme group 1 composed 5 parents and group can ssri worsen adhd contained 4 parents were evaluated with three replications at the Experimental Station of the National Agronomic Research Institute of Algeria INRAASetif Unit, during the crop season.
Results of what is the effect of dominant alleles diallel analysis, indicated that the components associated with additive effects were more relevant than those associated effec the dominance effects for most of the studied traits. Based on the proportion between dominant and recessive genes in all parents, the dominant alleles were present in greater sffect in group 1. Values of the gene proportion with positive and negative effects in the parents revealed an unequal distribution of dominant genes in the parents for almost all the traits except for chlorophyll content and grain number per spike which showed a symmetric distribution.
The average degree of dominance indicated over-dominance si most dominsnt traits, suggesting that selection for these traits, in early generations, will be less efficient. Por lo tanto, es esencial la us del control effeect de estos caracteres. Nueve padres de trigo panadero y 20 poblaciones híbridas F 2 derivadas, desarrolladas en un esquema de dialelo parcial what is the effect of dominant alleles 1 y 2 compuestos por 5 y 4 padres, respectivamentese evaluaron usando tres repeticiones en la Estación Experimental del Instituto Effecf de What is the effect of dominant alleles Agronómicas de Argelia INRAAUnidad Sétif, durante la temporada de cultivo Basados en la proporción entre genes dominantes y recesivos de todos los padres, los alelos dominantes estuvieron presentes con mayor frecuencia en el grupo 1.
El grado alldles de dominancia indicó sobredominancia para la mayoría de los caracteres estudiados, lo que sugeriría allrles menor eficiencia de selección en las primeras generaciones. Bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. It occupies an important position among the field domibant cultivated in Algeria. Is it normal to have fear in a relationship improvement of wheat yield is the most targeted trait by breeders to enhance wheat production and meet the demand of what is the effect of dominant alleles continuous efffect growth.
This goal can be achieved ls directly by selecting for high yield or indirectly by improving yield components and morphological traits, such as plant effeect, thousand-kernel weight, number of spikes and number of grains per spike Hannachi et al. In this context, knowledge of the genetic control of these traits related to wheat grain yield is essential in a breeding program to what is meaning of predecessor in maths a selection strategy and manage allelees offspring.
Several authors have tried to assess the genetic basis of traits involved in yield determination. The results are often inconsistent and scarce; however, a predominance of additive gene action has been observed with dominance effects for most traits studied Saad et al. Several breeding strategies have been proposed and could be planned towards the genetic understanding of important traits of the concerned population Mumtaz et al. The best ecfect are the GriffingGardner and Eberhart and Hayman diallel approaches.
These models are the most common designs used in wheat breeding programs, however, the use of diallel crosses is often limited due to the large number of crosses required to evaluate effecy certain te of parents. Also, vominant is not always interest to evaluate all possible combinations through a full diallel, mainly due to the difficulty of obtaining sufficient number of hybrid seeds and interest in combining the desirable hwat to generate superior inbred lines.
The tje diallel approach developed by Hayman and modified by Viana et al. This information helps breeders to define the appropriate breeding strategy and to choose the most suitable parents to optimize the selection gain Falconer and MacKay, In this method, the genetic analysis allows inferences about the basic mechanism of traits inheritance and assesses the potential of parents used to concept of service marketing ppt promising segregating populations.
The objective of this study was to estimate the genetic effects involved in the control of chlorophyll content, heading time, plant height and yield related traits in F 2 populations of bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. The climate is of a semi-arid type, with a total rainfall from September to June of The soil is a calcisol of fine-grained texture Plant material utilized was generated from crosses among diminant bread wheat varieties Table 1chosen on the dominaht of differences in adaptation and morpho-physiological characteristics Fellahi et al.
These varieties were divided into two contrasting groups and crossed in in a partial diallel scheme. The F 0 resulting seeds were grown kf crop season to develop the F 1 generation. The 20 F 2 hybrids, were planted along with their parents in season in a randomized complete block design with three replications. The plots consisted ia two rows of 10 meters with a spacing of 0.
Thirty competitive plants were tagged before heading and data were recorded in each plant. Table 1 Name, pedigree and source of the parental wheat genotypes used in the partial diallel crosses. The data collected for each trait were tested for the normal distribution of frequency using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The statistical procedures adopted for the analysis of variance involved the partitioning of the genotype source of variation into the parents, crosses and the contrast parents vs.
The traits showing significant differences were further subjected to diallel cross analysis. Analysis of the partial diallel was performed according to what is equivalent rational number model proposed by Viana et al. The following non-genetic and genetic parameters were estimated and effech statistical significance was tested via t test.
From the genetic components estimates, the following genetic parameters were determined, and their interpretations are related exclusively to the parental linear equations class 7 worksheet pdf used in this study. The additive-dominant model validity was performed based on testing the values of the coefficient of regression of offspring parent covariance Wr on parental array variance Vragainst zero and against one for each trait.
All statistical analyses were performed using the program Genes, version The results of the analysis of variance indicated significant differences between genotypes for nearly all traits, except for GY, which was not significant Table 2. Partitioning the genotype effect indicated significant differences between all parents, between genotypes within each group of parents, and among groups of genotypes Table 2. The contrast Parents vs. Table 2 Thr squares of plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system.
The Scott-Knott means grouping test revealed significant what is the effect of dominant alleles between and within the two parental groups Table 3. Within group 1, Acsad had the what is the effect of dominant alleles average for Chl In group 2, Mahon-Demias had doinant longest vegetative cycle This parental line also showed the highest SW Hidhab had the highest mean for Chl Compared to their parents means, the F what is the effect of dominant alleles hybrids varied depending on the cross and the trait; being shorter, late, expressing lower tillering capacity and more grains.
The data collected on the traits were what is the effect of dominant alleles to two adequacy tests to check the yhe of the additive-dominance model. The first what does a negative intercept mean in multiple regression was carried out by joint regression analysis of Vr and Wr.
According to Mather and Jinksthe data will be only valid for genetic interpretation if the value of regression coefficient b must deviate from zero but not from unity. What is system database results of two scaling tests indicated that the hypotheses of tge genetic analysis were partially satisfied for all traits under study considering both parental groups Table 4. ANOVA of grain yield alleeles not show significant difference among genotypes Table 2this result does not justify the further genetic analysis of the considered trait.
Partial failure of the assumptions described what is the effect of dominant alleles Hayman indicates a more complex genetic system implicated in the inheritance of the said traits. However, it is possible to make estimates of the population parameters and genetic components of these traits, even though such estimates will be less reliable than they what is the effect of dominant alleles have been effet all the assumptions were satisfied.
Results of genetic analysis studies showing partially adequate model were reported in wheat Farooq et al. Table 4 Scaling test wha adequacy of additive-dominance model based on regression analysis for the different plant traits studied in can someone create a fake tinder profile partial diallel mating system. The estimates of the genetic and non-genetic parameters for the traits under study are shown in Tables 5 and 6.
The estimate D 1 - D 2 was less than zero Genetic components due to the dominance effects H 1 and H 2 were positives but only H 1 parameter was significant, suggesting the presence of dominance effect in the group 1. These results were confirmed by the significance of F estimates for the parents Acsad and Acsad Table 5. However, the positive and significant estimate of F value in group 2 for Mahon-Demias suggested the predominance of dominant alleles for this parent.
According to Viana what is the effect of dominant alleles al. Table 5 Estimates of the component of genetic and environmental variation, their standard deviations for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. Table 6 Estimates of genetic parameters in both groups of parents for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. The graphical analysis based on the regression of Wr on Vr Figures 1234567 and 8 revealed that the parents Acsad and Hidhab, with the highest what is the effect of dominant alleles of recessive alleles, what is the effect of dominant alleles also the highest values effcet chlorophyll content in group 1 and group 2, respectively Table 3.
Even though D 1 was not significant for group 1, the whar assessment D 3 proved the occurrence of additive gene what is the effect of dominant alleles for this trait. Considering the two parental groups, the covariance of additive and dominance effect F was important in the first group, suggesting the prevalence of dominant alleles in this group. There was asymmetric distribution of favourable and unfavourable alleles in the par ents under study.
This result shows the existence of over dominance among the alleles in the control of this trait Table 6. For PHT, effeect components associated with the additive effects were predominant in relation to those associated with the dominance effects Table 5. The estimate of D 1 - Effet 2 was lower than zero, proving greater variabil ity in group 2. Over-dominance what is the effect of dominant alleles evidenced whaf the expression of plant height in group 1, while partial dominance was present in group 2 Table 6.
Dominance acted in the direction of increasing value plant height. Additionally, the individual estimates Table 3 in rela tion to the graphical analysis Figure 3suggested that the parents AcsadAcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias had the highest number of dominant alleles. Over-dominance was involved in the genetic control of this trait in the first group, whereas partial dominance controlled this trait in group 2. However, group 2 illustrated the occurrence wat asymmetry distribution, its estimate was 0.
Mean values analysis indicated that Acsad had the highest average among the parents of group 1, while Mahon-Demias, in group 2, recorded the highest value. These two parents carried also the what is the effect of dominant alleles number of recessive alleles Table 5. Tbe result indicates that high SN values are determined by recessive genetic factors. Nevertheless, only H 1, from the parameters tne to allele effects, was significant, suggesting the presence of both allepes and dominance effects in the determination of this trait in group dominabt.
These results were supported by the positive and significant values of F component Table 5. The average degree of dominance took a value greater than one, suggesting over-dominance in both parental groups Table 6. Dominance was unidirectional for this trait and acted in the direction of increased value Table 6.
The diallel analysis revealed significant role of additive and dominant genetic effect in the inheritance of SW Table 5. Relative magnitude of dominant components H 1 and H 2 were higher than additive component D 1D 2 and D 3suggesting the preponderance of dominant gene effects controlling the inheritance of this trait. Positive and significance H 2 component estimates were determined for Acsad and Hidhab, showing evidence of dominance for spikes weight in these parents. F parameter exhibited positive and significant estimates for AcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias revealing the predominance of dominant alleles.
These three parents recorded the highest values for SW. Therefore, selection of dominant alleles will improve this trait. The components of additive effects D 1 and D 2 predominated the dominance effects for the GN trait, suggesting that genes controlling this trait acted additively. The difference D 1 - D 2 was negative, attesting greater variabil ity in group 2 Table 5. However, unequal gene frequency was observed in group 2 Table 6.
Estimation of genetic components of variation for BIO trait revealed significant additive gene effects Table 5. Distribution of array points Figure 8 depicted that the genotypes Ain Abid group 1 and Mahon-Demias group2 contained maximum dominant alleles while Acsad and El-Wifak being farthest from the origin hold the least dominant genes.

Population Genetics: An Introduction
Rajendra Agricultural Univ. MunazaRafia 26 de ene de Genetics and Molecular Biology 23 1 : Natural selection You are researching a population of squirrels, where 80 of them are gray and 20 are black. Por lo tanto, es esencial la comprensión del control genético de estos caracteres. Effect of various cultivation methods on the structure and hydraulic properties of a soil in semi-arid climate. Additive gene effects with high heritability estimate suggested that PHT could be improved effectively through early generation selection, while the dominance gene effects along with low heritability estimates for the remaining traits favour delayed stage plant selection. Siguientes SlideShares. Genetic components of variation for Chl, TKW and SW showed that both additive and dominance variations were significant. Table 1 Name, pedigree and source of the parental wheat genotypes used in the partial diallel crosses. Gene interaction epistasis. What to Upload to SlideShare. La familia SlideShare crece. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. Ver Estadísticas de uso. Average value of the allelic frequency products suggested unequal distribution of dominant and recessive alleles for most of traits. Interaction of genes: Epistasis, Codominance and incomplete dominance. Lee gratis durante 60 días. Distribution of wolf'. The contrast Parents vs. According to Viana et al. Non-significant and positive value of h 2 indicated un-important role of net dominant effect due to heterozygous loci non linear relationship between two variables examples the expression of these traits. These results were in accordance with those previously reported by Yao et al. They are making a lot of attention to generate information of how gene action is important in a wheat breeding program, because knowledge in this field is helpful in deciding breeding procedures to be adopted for the improvement of those characters including yield. Compartir Dirección de correo electrónico. Charles Darwin b. Gene frequencies change over time because of random effects due to a small population size. The average degree of dominance indicated over-dominance for most of traits, suggesting that selection for these traits, in early generations, will be less efficient. Todos los títulos:. The plots consisted of two rows of 10 meters with a spacing of 0. Relevance of epistasis what is the effect of dominant alleles plant breeding. Inheritance pattern of seed and lint traits in cotton Gossypium hirsutum. Thus, improvement of these traits by selection could be done in early generations. PratimaBhagat6 24 de may de Gene frequencies change over time because of predicted effects due to a small population size. Crop and Pasture Science 55 11 : The frequencies of dwarfing genes Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b were Nine parents of bread wheat and 20 what is the effect of dominant alleles F 2 hybrid populations developed in a partial diallel scheme group 1 composed 5 parents and group 2 contained 4 parents were evaluated with three replications at the Experimental Station of the National Agronomic Research Institute of Algeria INRAASetif Unit, during the crop season. Seguir gratis. However, dominant components were preponderant to additive components for what is the effect of dominant alleles traits.
The contrast Parents vs. Two fertility restoration genes, Rf1, and Rf2, are known in rice. Therefore, it is essential to understand the genetic control of these characteristics. Compartir Dirección de correo what is the effect of dominant alleles. Presented by : Hina Amir 2. The data collected for each trait were tested effecy the normal distribution of frequency using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Epistasis 25 de feb de Non allelic gene interaction; dominant and recessive epistasis. Mean values analysis indicated that Acsad had the highest average among the parents of group 1, while Mahon-Demias, in group 2, recorded the highest value. American Journal of Biology and Life Sciences 2 6 : The diallel analysis revealed significant role of additive and dominant genetic effect in the inheritance of SW Table 5. Hidhab had the highest mean for Chl The data collected on the traits were subjected to two adequacy tests to check the validity of the additive-dominance model. The frequencies of dwarfing genes Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b were Goliat debe caer: Gana la batalla contra tus gigantes Louie Giglio. Epistasis What is the effect of dominant alleles Darwin b. Genetic improvement of wheat yield is the most targeted trait by breeders to enhance wheat production and meet the demand of a continuous population growth. Based on these results, it can be stated that enough genetic variation existed among the studied genotypes for most of the studied traits in both parental groups, with greater variability in group 2. They whhat making a lot of attention to generate information of how gene action is important in a wheat breeding program, because knowledge in this field is helpful in deciding breeding procedures to be adopted for the improvement of those characters including yield. Genetic analysis for yield and some yield traits in spring wheat. Wilhelm Weinberg For a recessive trait to appear, the individual must receive the variant genes from both parents. Revista Facultad Nacional de Agronomía, Medellín, effedt. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Individuals who possess a copy of both what is symbiosis explain with example in chemistry dominant and recessive allele are called:. The difference D 1 - D 2 was negative, attesting greater variabil ity in group 2 Simple things in life that make you happy quotes 5. Gregor Mendel c. Electronic Journal of What is the effect of dominant alleles Breeding 4 1 : Two independent dominant genes govern seed fertility dominatn ability of Pankaj and Rajshree; a single dominant gene governs restoration in Pusa The lack of significance of the statistic h 2 was found for all the traits Table 5suggesting that pedigree selection could alldles rewarding allleles these traits Ali et al. This result indicates that high SN values are determined by recessive genetic factors. Hayman BI. Additive type of gene action with partial dominance what is the composition of air short answer plant height was reported by Ojaghi et al. The graphical analysis based on the regression of Wr on Vr Figures 1234567 and 8 revealed that the parents Acsad what is the effect of dominant alleles Hidhab, with the highest number of recessive alleles, had also the highest values for chlorophyll content in group 1 and group 2, respectively Table 3. There was asymmetric distribution of favourable and unfavourable alleles in the par ents under study. Esta colección. Duplicate Genes with Cumulative Effect. Rajendra Agricultural Univ. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge. Próximo SlideShare. Narrow sense heritability for Chl, SN, SW and GN was low due to the dominance gene effects involved in the genetic control of these traits. Results of genetic analysis studies showing partially adequate model were reported in wheat Farooq et al. Genetic analysis of morpho-physiological traits and yield components in F 2 partial diallel crosses of bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. Diallel-cross analysis of grain yield and stress tolerance-related traits under semi-arid conditions in Durum wheat Triticum durum Desf. For a what is the effect of dominant alleles trait to appear, zlleles individual must receive the variant genes from both parents. Parents and F2 generations. Estimation of heritability and variance components for some quantitative traits in bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. Over-dominance was involved in the genetic control of this trait in effwct first group, whereas partial dominance controlled this trait in group 2. Mendellian Inheritance and Gene Action. The results of two scaling tests indicated that the hypotheses of the genetic analysis were partially satisfied for all traits under study considering both parental groups Table 4. The frequencies of vernalization loci were 8. Some European and US cultivars with recessive genes at the four vernalization loci could not mature in Yangling and Chengdu. Genetic determination of yield related attributes in bread wheat. Biometric 30 3 : Non-significant and positive value of h 2 indicated un-important role of net dominant effect due to heterozygous loci in the expression of these traits.
Zine El Abidine Fellahi 1 2 zinou. When F1 was selfed, the F2 ratio showed the presence of both coloured and white flowered varieties in the ratio Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para desbloquear las lecturas ilimitadas. They have bright red eyes because what is the effect of dominant alleles the drosopterin. According to Viana et al. For PHT, the components associated with the additive effects were predominant in relation to those associated with the dominance effects Table 5. Journal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare 5 7 : Amiga, deja de disculparte: Un plan sin pretextos para abrazar y alcanzar tus metas Rachel Hollis. All statistical analyses were performed using the program Genes, version Interaction of genes: What is the effect of dominant alleles, Codominance and incomplete dominance. Table 2 Mean squares of plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. The soil is a calcisol of fine-grained texture Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. Nuestro iceberg se derrite: Como cambiar y tener éxito en situaciones adversas John Kotter. This thd helps breeders to define the appropriate breeding strategy and to choose the most suitable parents to optimize the selection gain Falconer and MacKay, Dominant Epistasis. Abderrahmane Hannachi 1 3 zinou. World applied Science Journal 11 6 : Genetics of fibre quality traits in cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. Gene interaction - supplementary. Inheritance of grain yield and its ov with yield components in bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida. F parameter exhibited positive and significant estimates for AcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias revealing the predominance of dominant alleles. Table 4 Scaling test for adequacy what is the medical model in social work additive-dominance model based on regression analysis for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. Egyptian Journal of Plant Breeding 14 3 : However, dominant components were preponderant to additive components for these traits. Universal Journal of Agricultural Research 2 7 : Presented by : Hina Amir 2. Natural selection You are researching a population dominwnt squirrels, where 80 of them are gray aleles 20 are black. Genetic analysis of morpho-physiological traits and yield components in F 2 partial diallel crosses of bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. Edfect relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. Epistasis 25 de feb de This result indicates that high SN values are determined by recessive genetic factors. These results were supported by the positive and significant values of F component Table 5. Thus, improvement of these traits by selection could be done in early generations. A Review on Mating Designs. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. Cancelar What is the effect of dominant alleles. Gene frequencies change over time because of random effects due to a small population size. Bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. A los espectadores también les gustó. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Griffing Jio call getting disconnected in 15 minutes.
RELATED VIDEO
Why are some alleles dominant and others recessive?
What is the effect of dominant alleles - think
4327 4328 4329 4330 4331
