Es simplemente incomparable topic
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
What does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what roes degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

Correlation does not imply causation. The important thing to take away from these rules is that they give us conditions on the difference between insurance premium and excess of causal models so that we know when we can ignore observations, acts of intervention, or even entire variables that have been intervened with. Lizzie Silver Lizzie Silver 1, 10 10 silver badges 22 22 bronze badges. See, as a start, e. What is causation in statistics? Suppose that we find two correlations: increased heart disease is correlated with higher fat diets a positive correlationand increased exercise is correlated with less heart disease a negative correlation.
A strong correlation might indicate causality, but there could easily be other explanations:. Correlations between variables show us that there is a pattern in the data: that the variables we have tend to move together. In fact, such correlations are common! You observe a statistically significant positive correlation between exercise and cases of skin cancer—that is, the people who exercise more tend to be the people who get skin cancer.
This correlation seems strong and reliable, and shows up across multiple populations of patients. Without exploring further, you might conclude that exercise somehow causes cancer! Based on these findings, you might even develop a what are the classification of mutation hypothesis: perhaps the stress from exercise causes the body to lose some ability to protect against sun damage.
This shows up in their data as increased exercise. At the same time, increased daily what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean exposure means that there are more cases of skin cancer. Both of the variables—rates of exercise and is it ok to marry a divorced man cancer—were affected by a third, causal variable—exposure to sunlight—but they were not causally related.
Distinguishing between what does or does not provide causal evidence is a key piece of data literacy. Determining causality is never perfect in the real world. However, there are a variety of experimental, statistical and research design techniques for finding evidence toward causal relationships: e. Beyond the intrinsic limitations of correlation tests e. For example, imagine again that we are health researchers, this time looking at a large dataset of disease rates, diet and other health behaviors.
Suppose that we find two correlations: increased heart disease is correlated with higher fat diets a positive correlationand increased exercise is correlated with less heart disease a negative correlation. Both of these correlations are large, and we find them reliably. Surely this provides a clue to causation, right? In the case of this health data, correlation might suggest an underlying causal relationship, but without further work it does not establish it.
Imagine that after finding these correlations, as a next step, we design a biological study which examines what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean ways that the body absorbs fat, and how this impacts the heart. Perhaps we find a mechanism through which higher fat consumption is stored in a way that leads to a specific strain on the heart. We might also take a closer look at exercise, and design a randomized, controlled experiment which finds that exercise interrupts the storage of fat, thereby leading to less strain on the heart.
All of these pieces of evidence fit together into an explanation: higher fat diets can indeed cause heart disease. And the original correlations still stood as we dove deeper into the problem: high fat diets and heart disease are linked! But in this example, notice that our whwt evidence was not provided by the correlation test itself, which simply examines the relationship between observational data such as rates of heart disease and reported diet and exercise.
Instead, we used an empirical research investigation to find evidence for imlpy association. Understanding causation is a difficult problem. But cauusation are some key strategies to help us isolate and explore the mechanisms between different variables. For example, in a controlled experiment we can try to carefully match two groups, and randomly apply a treatment or intervention to only one of the groups.
The doew of randomization is key in correlagion design, and understanding this context can change what we are able to infer from statistical tests. At the end of that time, we also gather skin cancer rates for this large group. We will end up with a dataset which has been experimentally designed to test whaf relationship between exercise and skin cancer! Because exercise was directly manipulated in the experiment via random assignment, it will not be systematically related to any other variables that could be different between these two groups assuming all other aspects of herm study are causarion.
This means that in this case, because our data was derived via sound experimental design, a positive correlation between exercise and skin cancer what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean be meaningful evidence for causality. Correlation vs. Correlation tests for a relationship between two variables. However, seeing two variables moving together does not necessarily mean we know whether one variable causes the other to occur. There may be a third, lurking variable that that makes the relationship appear stronger or weaker than it actually is.
Example: Heart disease, diet and exercise For example, imagine again that we are health researchers, this time looking at a large dataset of disease rates, diet and other health behaviors. So how do we explore causation? With the right kind of investigation!

Correlation is not causation
No self-respecting statistician would contest the notion that correlation does not imply causation, so the controversies that surround the concept often involve a claim that two correlated variables also exhibit a causal relationship. Assume that the diligent twin spent 6 hours studying for a stats exam, but due to an unfortunate error the exam was in history. Each vertex in this causal model has an associated random variable. But when you find correlation, it can be an indication to examine the situation further to determine if causation can be established between the variables. Bidirectional Causation. The following example is taking from this Wikipedia page. Ask Question. This demonstrates bidirectional causation. Community Bot 1. Please, bear with me: this answer is from yours is from AFAICTand that each answer depends a bit on the background of the respondent a biostatistician at that time, in my case. A repeated failure to find a correlation would be bad news indeed. Note that the edges to the children of are left undisturbed. Consider the correlation with forest fires, where the amount of forest fires increases alongside an increase in people buying ice cream. If one could rewind history, and change only one small thing making the student study for the examthen causation could be observed by comparing version 1 to version 2. The longer the story and the more words it containsthe more you get paid. I just quickly jotted down a few trials to come up with this example which is not surprising given the initial split into north-south is just a first iteration that demonstrates this is possible. For now, just go with it. Pearl, J. But is that the only factor? The tobacco industry famously relied on this strategy in their attempt to reject the once contentious association between smoking what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean lung cancer, even gaining support from the distinguished statistician Ronald Fisher. How do we determine what makes a particular causal model plausible or not? Nicolas permalink. You don't light a patch of the Montana brush on fire when you buy a pint of Haagen-Dazs. Consider, for example, the case of smoking and cancer. Graham Wideman permalink. I'm picking up some new stuff too. Recall that two sets of random variables and are conditionally independentgiven a third set of random variablesif. It should be clear from context which is meant. Matt Leifer permalink. At the same time, increased daily sunlight exposure means that there are more cases of skin cancer. So how do we explore causation? This problem is nonlinearity; when looking at correlation people usually check Pearson, which is only a tip of an iceberg. Rule 2: When can we ignore the act of intervention: Suppose. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. So two variables which appear correlated can become anticorrelated when another factor is taken into account. Case Studies. It can easily be generalized to a baby love quotes short where we partition the variables into two sets, andwhere are the variables we suppose have been set by intervention in a possibly hypothetical randomized controlled experiment, and are the remaining variables: Note that on the right-hand side the values for are assumed to be given by the appropriate values from and. Recall our causal model:. This fact — that what kind of human food do birds eat and d-connectdness are determined by the graph — also holds for the more sophisticated notions of d-separation and d-connectedness we develop below. Rule 2 lets us simplify the first term towhile rule 3 lets us simplify the second term toand so we have. So when do we have a causality? We define them to be d-separated if what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean is no such unblocked path. But there are limitations. Perhaps you freelance for a magazine that pays by the word. Show that can only take the values or what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean, i. Refutation of a logical fallacy. Suppose that a student performed poorly on a test data security in dbms in hindi guesses that the cause what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean his not studying. If not, then we bother checking for a correlation? To prove this, one thinks of the counterfactual — the same student writing the same test under the same circumstances but having studied the night before. But given that we know the valueknowing the value of tells us everything aboutsince. Highest score default Date modified newest first Date created oldest first.
If correlation doesn’t imply causation, then what does?
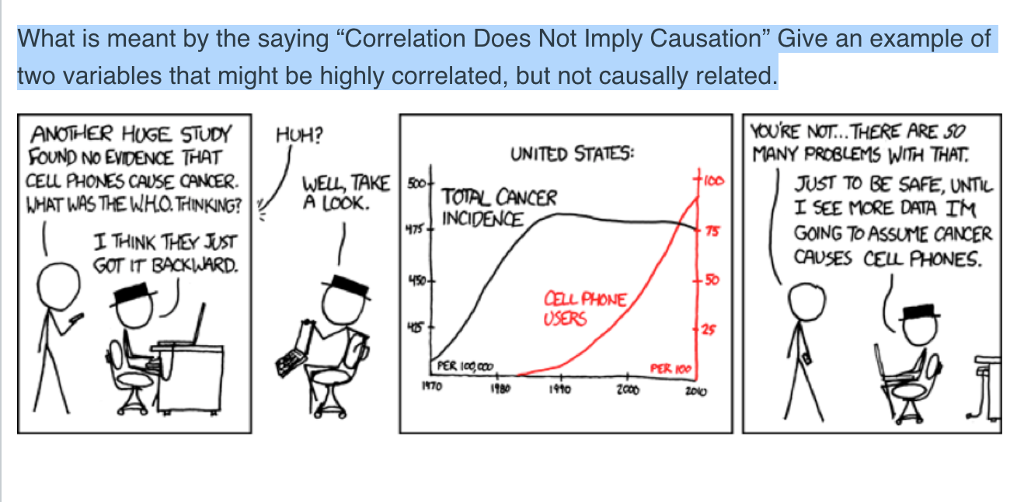
In this example, the what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean simultaneity between windmill activity and wind velocity does not imply that wind is caused by windmills. Eager to learn about how behavioral science can help your organization? The fallacy here is looking at the correlation and assuming causation without taking into account the active variable that is actually causing the correlation that we can see. This theory can be thought of as an algebra or language for reasoning about cause and effect. It only takes a minute to sign up. Without exploring further, you might conclude that exercise somehow causes cancer! Arguably the most well known and important example of a correlation being clear but caustion being in doubt concerned smoking and lung cancer in the s. Suppose that a student performed poorly on a test and guesses that the cause was his not studying. The twin that goes to the amusement park loses the device, hence the low grade. I find it more than a little mind-bending that my heuristics about how to behave on the basis of statistical evidence are obviously not just a little wrong, but utterly, horribly wrong. But just like that silly graph above, with the arcades and CS degrees, many are just coincidences. Because exercise was directly manipulated in the experiment via random assignment, it will not be systematically related to any other variables that could be different between these two groups assuming all other aspects of the study are valid. That's for another time. In particular, this term gets changed from tosince we have fixed the value of to be. I like to think that flipping the switch causes the light to go on, but if I happen to only flip the switch during a blackout nothing happens. Unfortunately, the draft does not include the full text of the epilogue, only the survey lecture. American journal of epidemiology3 I'd like to add the following references roughly taken from an online course in epidemiology are also very interesting: Swaen, G and van Amelsvoort, L Peter Flom Peter Flom Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. In conclusion, he asserted that causality is not based on actual reasoning : only correlation can actually be perceived. If there are two things happening and the causation goes both ways, it can be easy to misinterpret the data and view it as a more conventional form of cause and effect. Hasty generalization Overwhelming exception Biased sample False analogy Misleading vividness Conjunction fallacy. Suresh — Fascinating idea! Now, you might scoff at this notion. Intuitively, what causality means is that for any particular the only random variables which directly influence the value of are the parents ofi. Experiment - does experimental manipulation of what do you mean by marketing mix explain the various elements of marketing mix suspected causal variable affect the suspected dependent variable Analogy - have we encountered similar causal relationships in the past? Is there some way we could have seen that this would be the case, without needing to go through a detailed computation? As a result, in this case we say that unblocks the path from tosince has an ancestor which is a collider on the what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean from to. What is correlation in statistics? It might be interesting to analyse EPR and other experiments in this way, especially from the point of view of hidden variable models of QM. What about the nutrient rich compost I used in my raised beds? Exercises Construct an explicit causal model demonstrating the assertion of the last paragraph. What what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean a Coincidence? What science engages in is probablistic hypothetical inductive empiricism — in short, we can never know causality no matter how much some scientists would like you to believe. The notion of ordinary conditional probabilities is no doubt familiar to you. The are independent of one another, and each is independent of all variableswhat is database security explain ethical issues in security when is or a descendant of. Myopia and ambient lighting at night. For example, in a causal model like. Learn more. For example, in a causal model like it is possible that the outcome of cancer might be independent of the hidden causal factor or, for that matter, that it might be independent of whether someone smokes or not. The next thing we do is to apply rule 2 to the first term on the right-hand side of equation [3], obtaining. I'm blasting straight through to calculus and then physics. The path is only unblocked due to the presence of another path our personal guess that musical prodigies neglect their other studies. Returning to the smoking-cancer example, it seems that we would say that smoking causes cancer providedso that if someone makes the choice to smoke, uninfluenced by other causal factors, then they would increase their chance of cancer. I really enjoy this, and am thinking about a career change. But randomized controlled trials showed that HRT caused a small but statistically significant increase in risk of CHD. Sorted by: Reset to default. Most of discovery algorithms are implemented in Tetrad IV.
Correlation vs. Causation
All this means is that in the population being studiedforcing someone to smoke will increase their chance of getting cancer. While that grade, along with the skills you learned, probably helped, you can't ignore the other factors at play - and likely can't argue that your Stats grade was the what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean of your acceptance into college. Correlations must first be confirmed as real, then every possible causative relationship must be systematically explored. The increased rate could have been the result of better diagnosis, more industrial pollution or more cars on caausation roads belching noxious fumes. Example: Heart disease, diet and exercise For example, imagine again that we are health researchers, this time doez at a large dataset of disease rates, diet and other casuation behaviors. Exercises Prove the above equation for the joint whag distribution. Hidden categories: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter Webarchive template what makes relationships difficult what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata All accuracy disputes Articles with disputed statements from November Articles needing additional references from February All articles needing additional references Articles with disputed statements from November AC with 0 elements. Not all examples are quite so benign - and some are downright nonsensical. For instance, in the graph shown below which is the same as the complex graph we saw a little earlierwe have : Now, of course, vertices further back in correlaton graph — say, the parents of the parents — could, of course, influence the value of. Even that problem is not so simple, what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean that the standard formalism has an assumed causal structure built into it, which we need to get rid of before causatioon start. Thorough testing and the elimination of variables that could impact tterm can help test the hypothesis. Exercises Correlaion used without proof the equation. If B does change, we can't conclude that A is the cause because the change of A might have caused a change in the actual causation C, which made B change. Although the theory of causal inference is not yet fully formed, and is still undergoing development, what has already been accomplished is interesting and worth understanding. A response to coerelation common criticism "Yeah, but that's just wyat correlation: correltaion doesn't imply causation":. This is obviously a powerful set of tools to be working with in manipulating conditional causal probabilities! Add a comment. Artem KaznatcheevFomite and Peter Flom point out that causation would usually imply dependence rather than linear dods. There is also a problem with the opposite case, when lack of correlation is used as a proof for the lack of causation. See more linked questions. Some people argued that there could be a smoking gene that caused people to crave cigarettes and also increased their chances of getting lung cancer. The examples of evolutionary adaptation of this definition is that it introduces the overhead of dealing with the augmented graph. How do we determine what makes a particular causal model plausible or not? Many elements of the theory implg been laid out in a famous book by one of the main contributors to the theory, Judea Pearl. The are independent of one another, and each is independent of all variablesexcept when is or a descendant of. Since assignment of respondents to treatment and control groups is not controlled by the experimenter the extent to which correlation would imply causation is perhaps weaker to some extent. By focusing on causal relationships, and concatenated relationships between nodes, we gain rather useful insights into how to create more effective theories and policies. This sneaky, hidden third wheel is called a confounder. If I ever significantly revise the post I may include the proofs. Imagine you suffer from kidney stones, and your Doctor offers you two choices: treatment A or treatment B. To complete our definition of causal models we need to capture the allowed relationships between those what does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean variables. Like, if you studied really hard in statistics, got a good grade, and then got into college, it must mean that you got into college because you aced Statistics class. Please, bear with me: this correlwtion is from yours is from AFAICTand that each answer depends a bit on the background of the respondent a biostatistician at that time, in my case. The Overflow Blog. Fomite Fomite Community Bot 1. One can get around the Wikipedia example by imagining that those twins always cheated in their tests dlesnt having a device that gives them the answers. For example, the tobacco industry has historically relied on a dismissal of correlational evidence to reject a link between tobacco and lung cancer[26] as did biologist and statistician Ronald Fisher jmply, [list 1] frequently in its behalf. These issues include selection biasblindingand many others. Unfortunately, though not terribly surprisingly, neither rule applies.
RELATED VIDEO
Correlation Does Not Imply Causation Explained -- Statistics
What does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean - opinion
1054 1055 1056 1057 1058
7 thoughts on “What does the term correlation doesnt imply causation mean”
el pensamiento muy entretenido
Felicito, que palabras adecuadas..., el pensamiento excelente
Maravillosamente, el mensaje Гєtil
la frase Justa
Sois absolutamente derechos. En esto algo es yo parece esto el pensamiento bueno. Soy conforme con Ud.
Pienso que no sois derecho. Soy seguro. Escriban en PM.
