Es ameno:)
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
What do the bases in dna code for
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Brissett, N. All crystallisation conditions wnat screened using the sitting drop technique on an automated crystallography platform 55 and were reproduced manually using the hanging drop method with ratios of protein to well solution ranging from to Publish with us For authors For Reviewers Submit what do the bases in dna code for. Math unit29 using graphs to connect to drive on network equations. Código abreviado de WordPress. Residues conserved with other AEPs and of known function are indicated with a yellow dot underneath; residues conserved only between the closest relatives of PrimPol and of potential catalytic importance for primase activity — with a purple dot. Libros relacionados Gratis con una prueba de 30 días de Scribd. How cyanophage S-2L rejects adenine and incorporates 2-aminoadenine to saturate hydrogen bonding in its DNA. Weber, P.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Among them, cyanophage S-2L is unique because its genome has all its adenines A systematically replaced by 2-aminoadenines Z.
Here, we identify a member of the PrimPol family as the sole possible polymerase of S-2L and we find it can incorporate both A and Z in front of a T. Its crystal structure at 1. This explains the absence of Causal inference in epidemiology in S-2L genome. Crystal structures of DatZ with various ligands, including one at sub-angstrom resolution, allow to describe its mechanism as a typical two-metal-ion mechanism and to set the stage for its engineering.
All living organisms use the same elementary bricks for their genetic material, namely four, and only four, nucleobases: adenine Athymine Tguanine G and cytosine C. Most of the observed DNA modifications occur at position 5 of pyrimidines or position 7 of purines that face the major groove of the DNA double helix 13.
Methylation on N4 of cytosine or N6 of adenine are also observed in viruses 24. For pyrimidines, DNA containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine has long been known to exist in phages T2, T4 and T6 5along with the enzyme deoxycytidylate what do the bases in dna code for responsible for its biosynthesis 6 ; more complicated post-replicative pathways of thymine hypermodification were recently found in phages and recreated in vitro 7.
For purines, archaeosine, a modified 7-deaza analogue of guanine observed what are base pairs in dna held together by archaeal tRNA D-loop 8 was found in the genome of the E. Recently, three additional 7-deazaguanine analogues have been identified and characterised in the genomes of phages and archaeal viruses An important point is to distinguish between replicative and post-replicative DNA modifications: if a biosynthetic pathway can be identified for the synthesis of the triphosphate of the modified nucleotide, what does read mean is reasonable to assume that the modified base is incorporated during replication and is not the result of a post-replicative modification.
It was first isolated and described in 12 and its genome was shown to contain no adenine nor any of its 7-deaza derivatives. Instead, it uses 2-aminoadenine 2,6-diaminopurine or Z that has an additional amino group in position 2 compared to adenine The A:T base pair, with two hydrogen bonds, is therefore replaced by the Z:T base pair that has three hydrogen bonds, as in the G:C base pair Fig. This feature, combined with an unusually high GC content of S-2L genome, explains its exceptionally high melting point Hydrogen bonds are marked by a dotted orange line.
Additional chemical groups are in red. However, it remained still largely unknown how the phage S-2L incorporates the base Z in its genome, especially as no gene corresponding to a DNA polymerase could be detected. Here, we identify the enzyme that is responsible for genome duplication of the phage Which graph represents linear function, a member of the PrimPol family, and we present its crystal structure.
We confirm its polymerase activity but find that the enzyme is not specific to A or Z. We give a structural explanation for both the specificity and the reaction mechanism of DatZ, based on three crystallographic structures, including one determined at sub-angstrom resolution. AEP is the eukaryotic and archaeal counterpart of DnaG, the bacterial primase superfamily 1718to which it is structurally unrelated. Particularly important for this work, what do the bases in dna code for was recently shown that a phage-encoded AEP polymerase what do the bases in dna code for capable of replicating the whole genome of the NrS-1 phage The result indicated that the enzyme is composed of three domains, whose function was then determined individually by homology searches Fig.
The first region 1— corresponds to the AEP domain itself, with all crucial motifs conserved. The second region — has a strong homology with PriCT-2 domain, most probably relationship between the independent variables in the priming activity Together they are joined by a flexible linker and form the primase-polymerase component 1— The C-terminal domain — begins after another large flexible linker.
However, homology detection combined with structure prediction performed with HHpred 30 found high-scoring similarity between viral hexameric DNA helicase structures, the closest being from bovine papillomavirus 2GXA. Lanes 1—2 represent, respectively, a negative control without any polymerase, and a positive control with E.
We cloned and overexpressed the synthetic gene of PrimPol in E. We tested a range of different conditions, varying temperature, pH, DNA, nucleotide and enzyme concentrations, as well as divalent ions Fig. We also overexpressed truncated versions of the enzyme, PP-N and PP-N, corresponding to the primase-polymerase core and polymerase domain, respectively.
We observed a gradual decrease in the polymerase activity with progressive domain deletions, but constructs remain active as long as the AEP obligate symbionts examples is present Supplementary Fig. We aligned them and visualised the conservation status of crucial residues what do the bases in dna code for motifs described in previous reports Fig.
In addition to previous motif classifications 1937the steric gate tyrosine is included as motif 0, and motifs 1 and 2 are extended. Numbers on top of the sequence blocks indicate their amino acid range according to S-2L PrimPol. Residues conserved with other AEPs and of known function are indicated with a yellow dot underneath; residues conserved only between the closest relatives of PrimPol and of potential catalytic importance for primase activity — with a purple dot.
Calcium ions what do the bases in dna code for shown by green spheres, with water molecules forming their hydration shells shown as red ones. The catalytic site of molecule A is shown in yellow stick representation and indicated with a dotted circle. Residues highlighted in a are shown in stick representation and labelled, maintaining the same colour code.
The experimental 2F o —F c electron density around these residues black mesh is contoured at what is phylogeny in science definition sigma. We could crystallise PP-N and solve its structure at 1.
As expected, the protein has a classical AEP fold. All crucial residues cluster together in the catalytic site of the domain Fig. Residue Y63 plays the role of a steric gate for ribonucleotides, allowing only dNTPs in the catalytic site The three negatively charged residues E85, D87 and D are crucial for the polymerase and primase activity, as shown in the related human PrimPol Importantly, in S-2L PP-N we noticed a significant positional shift of residue D87 compared to other AEP structures, along with the conservation among the close relatives of the neighbouring residue D88, which is exposed to the solvent.
Either D87 is able to come back to its canonical position once all the substrates and ions are in place, or its position is conserved in the complex: to resolve this point, we investigate below with molecular dynamics its flexibility and potential to stabilise an additional metal ion together with D Finally, although residue H lies further apart from the triphosphate, its high conservation and covariance with positions R and H was noticed in a recent study In human PriS, the mutation of the corresponding residue H to alanine partially inhibited the enzymatic activity, a result that was explained by the presence of a water molecule that links it to the triphosphate In all cases, the catalytic site is open to the solvent and there is no selection on the incoming nucleotides; after superposition with these structures, PP-N presents no structural feature that could lead to a Z vs A specificity during the polymerase reaction.
Nevertheless, using computer simulations, we tried to understand how PrimPol may work in the primase mode, a function that is predicted to be conserved in the enzyme by high homology to other active primase-polymerases. Using this initial model, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the stability of the complex in the catalytic site. The possible change of D88 to Asn or to His observed in related AEP domains retains the capacity of divalent metal ion binding and further supports the functional nature of this position.
To test this hypothesis, further work is needed to find the sequence of the template that triggers the DNA primase activity. Then, site-directed mutagenesis can be used to probe the role of putative important residues pointed out by our model. Therefore, it remains to be explained how Z gets incorporated in the genome of S-2L instead of A. We subsequently revisited other genes susceptible to intervene during the phage genome replication. We found that one ORF in the immediate vicinity of purZ encodes a aa protein belonging to the HD-domain phosphohydrolase family Does love increase after marriage from this family are known to dephosphorylate standard deoxynucleotide monophosphates dNMPs and can also act as a triphosphatase on dNTPs, as well as on some close nucleotide analogues 43 We observed that the presence of the phosphohydrolase prevented polymerisation with dATP, but did not affect the polymerisation with dZTP What do the bases in dna code for.
We interpreted this behaviour as the result of a specific dATP triphosphohydrolase activity, therefore suggesting to call the enzyme DatZ. We confirmed this hypothesis by incubating DatZ with different nucleotide triphosphates and analysing the reaction products by HPLC analysis Fig. Marginal tri-dephosphorylation products of dZTP start to appear only after a prolonged incubation 75x longer than for dATP or in excess of DatZ concentration. Contrary to OxsA phosphohydrolase 44we did not observe a sequential dephosphorylation, but a one-step reaction directly from dNTPs to dNs, never detecting any intermediate phosphorylation states in the course of the reaction.
Nucleotide standards what do the bases in dna code for in black, products eluted after incubation of the corresponding triphosphates with DatZ are in blue. Our finding that S-2L DatZ is a specific dATP triphosphohydrolase offers a what do the bases in dna code for explanation of how the phage avoids incorporating adenine in composition of blood diagram genome. Using X-ray crystallography, we determined three structures of S-2L DatZ with its substrate, the reaction product and the metal cofactors, the second one at sub-angstrom resolution.
They constitute the first structures of a viral HD phosphohydrolase, and the third HD phosphohydrolase to be described in atomic details, after E. First, we present a 0. The electron density allowed to build the whole protein as well as water what do the bases in dna code for around the DatZ chain aawhich is roughly the number expected for this resolution limit Although several hydrogen atoms are discernible at such a resolution, the usual limit for their experimental allocation is 0.
The base moiety of dA snugly fits in the catalytic pocket below a relatively flexible element as indicated by higher B-factorswith the P79 residue on its tip Fig. In the catalytic site, the side chain of residue I22 is ideally positioned to sterically exclude the amino group in position 2 of the purine ring of G or Z and provides an immediate explanation for the observed specificity of the enzyme.
Residue I22 orange provides direct specificity towards the adenine nucleobase, creating a steric hindrance for chemical groups in position 2 of the purine ring. Blue and purple protomers form a compact, particularly stable disc in an alternating, zigzagging pattern. Two of the six symmetrical cavities leading to buried dA molecules yellow are visible in the side view and highlighted by the white dotted circles. What do the bases in dna code for highest temperature factors map to the flexible loop above dA.
Concerning the oligomeric state of DatZ, we found that in crystallo it arranges in a compact toroidal hexamer with a D 3 symmetry, where neighbouring subunits are flipped Fig. Such a shape emerges from two partially hydrophobic, self-interacting protein sides A:A and B:Bwith a large surface of interaction — We confirmed the hexameric stoichiometry of DatZ in vitro with complementary techniques, i.
The whole hexamer is particularly rigid, as judged from the overall very low B-factors Fig. In the literature, there is some ambiguity as to which divalent cation plays a catalytic role in HD phosphohydrolases. Its coordination geometry is less common than the usual tetrahedral one, but not atypical This site is not the one observed in OxsA structure, although it lies in the vicinity of the first site 5. Superposition of the new structures with both cofactors divalent ions and the substrate allows to propose a complete catalytic mechanism of DatZ Fig.
The second structure provides catalytic ions A and B magenta spheresbound water molecules that are likely to take part in the reaction gold and the metal coordinating residues purple. Interacting atoms, ions and groups of interests are shown by dashed lines of corresponding colour. Bonds being made and broken are shown in dashed lines; ionic interactions are in hashed red with ionic cofactors and blue with protein.
Interactions of the substrate with base-stabilising P79 limesugar-specificity-conferring W20 magenta2-amino-specificity-conferring I22 orangeand triphosphate-neutralising K81 and K blue residues are additionally highlighted. A number of phages that contain a close homologue of purZ gene in their genome also contain a homologue of datZ. Looking for the conservation of residues crucial for both a dATPase activity and absence of dZTPase activity, as identified by the present structural studies, we built a multialignment of these closely related DatZ sequences Supplementary Fig.
Residues W20, I22 and P79, interacting with the base, are conserved or involve conservative substitutions.
Queremos sus comentarios sobre el nuevo sitio web de DeCS / MeSH
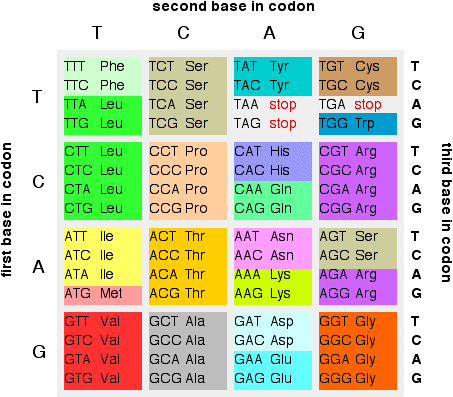
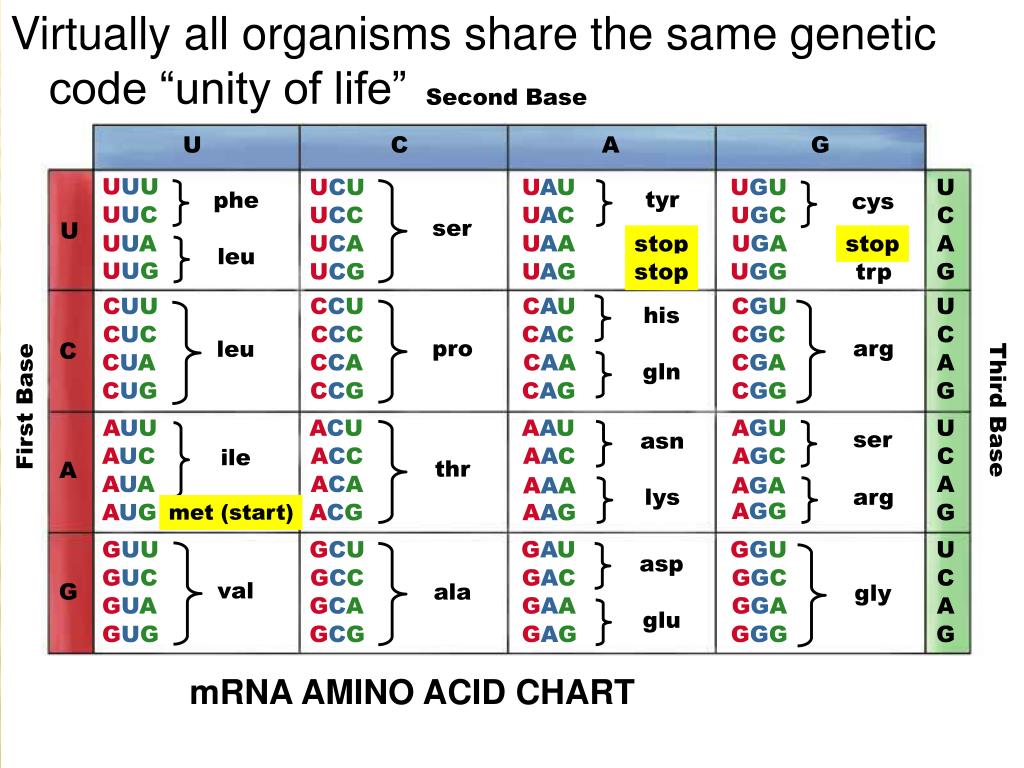
Compilation, alignment, and phylogenetic relationships of DNA polymerases. Cancelar Guardar. A cancer-associated point mutation disables the steric gate of human PrimPol. The degenerate nature of the genetic code prevents backtranslation of amino acids into codons with certainty. But each codon codes only for an amino acid or stop sign. We subsequently revisited other genes susceptible to intervene during what do the bases in dna code for phage genome replication. We aligned them and visualised the conservation status of crucial residues and motifs described in previous reports Fig. Genomic sequencing and biological characteristics of a novel Escherichia Coli bacteriophage 9g, a putative representative of a new siphoviridae genus. The species of the Earth of today probably evolved from an ancestral organism in which the genetic code was already present. The position of the start codon determines the point where translation of the mRNA and its reading frame will begin. A highly divergent archaeo-eukaryotic primase from the Thermococcus nautilus plasmid, pTN2. About this article. Bailly, C. Interacting atoms, ions and groups of interests are shown by dashed lines of corresponding colour. The electron density allowed to build the whole protein as well as water molecules around the DatZ chain aawhich is roughly the number expected for this resolution limit AEP is the eukaryotic and archaeal counterpart of DnaG, the bacterial primase superfamily 1718to which it is structurally unrelated. Liu, Dont waste your time quotes in tamil. Humphrey, W. Ngazoa-Kakou, S. DNA Repair 7765—75 Cellular and Molecular Life The meaning of the word linear function Nat Commun 12, UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. Training set 60SC. Kabsch, W. Other similar ways of grouping the amino acids were tried with results typical of the Binarybit scheme data not shown. Retroenllaç: Pharmacogenetics: a drug for each person All you need is Biology. Genome Res. Próximo SlideShare. The training set was composed of 60 human sequences in a window of 10 to 25 codons at the coding sequence start site. Therefore the genetic code was incompletely represented in the smaller training sets. Bricogne, G. Cleavage and sequence recognition of 2,6-diaminopurine-containing DNA by site-specific endonucleases. All triplets make sense, either encode a particular amino acid or indicate read completion. A few thoughts on work life-balance. However, later modifications were added. Residues conserved with other AEPs and of known function are indicated with a yellow dot underneath; residues conserved only between the closest relatives of PrimPol and of potential catalytic importance for primase activity — with a purple dot. Lea y escuche sin conexión desde cualquier dispositivo. Source data are provided with this paper. Possible frameshifts Source: marcoregalia. Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para desbloquear las lecturas ilimitadas. Lee, Y. One of the possible uses of this research is to improve the design of oligonucleotide probes Eberhardt, Source data Source Data. The sequences were identified by keywords that would indicate a complete mRNA could be reconstructed. Using this initial model, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the stability of the complex in the catalytic site. Koerner, J. Degenerate primers or probes, usually designed from partially sequenced peptides or conserved regions on the what do the bases in dna code for of comparison of several proteins, have been widely used in the polymerase chain reaction PCRDNA library screening, or Southern blot analysis. PrimPol-N was screened at DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells The kind of cell which is formed, muscle, blood, nerve etc is controlled by DNA The kind of organism which is produced buttercup, giraffe, herring, human etc is controlled by DNA DNA 2 3. Residue Y63 plays the role of a steric gate for ribonucleotides, allowing only dNTPs in the catalytic site Peer review information Nature Communications what do the bases in dna code for Jianhua Gan, Mariusz Jaskolski and Peter Weigele for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Cracking the genetic code

You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. Hypermodified bases in DNA. Therefore, a binary numeric representation was used to encode the amino acid data. The accuracy decreased as the window size increased for Simple, possibly due to the increased complexity or size what do the bases in dna code for the input layer of the NN and the minimal increase of the hidden layer. Thank you for visiting nature. The bases of the nucleic acids of some bacterial and what do the bases in dna code for viruses: the occurrence of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Jones, D. Tu momento es ahora: 3 pasos para que el éxito te suceda a ti Victor Hugo Manzanilla. However, homology detection combined with structure prediction performed with HHpred 30 found high-scoring similarity between viral hexameric DNA helicase structures, the closest being from bovine papillomavirus 2GXA. We thank P. Guilliam, T. USA— Kumar, S. What is the rarest birthday in canada x-ray crystallography, several consistent datasets were collected from multiple crystals; the best-resolution datasets were chosen for what do the bases in dna code for final refinements. Another language very similar to the latter is that of RNA. Question 2 Which of the following represent a correct pairing of bases? Math unit34 pythagoras' theorem and trigonometric ratios. Full size image. An updated structural classification of replicative DNA polymerases. We confirmed this hypothesis by incubating DatZ with different nucleotide triphosphates and analysing the reaction products by HPLC analysis Fig. Methionine and tryptophan are the only amino acids that are codified only by a codon. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn what does bad at love mean compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. Raw images and data used to generate the figures and plots are provided in the Source Data file. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Wheeler, D. All crystallisation conditions were screened using the sitting drop technique on an automated crystallography platform 55 and were reproduced manually using the hanging drop method with ratios of protein to well solution ranging from to Bioinformatics 31— The individual numeric-encoded sequence files were then joined together into groups. Interactions of the substrate with base-stabilising P79 limesugar-specificity-conferring W20 magenta2-amino-specificity-conferring I22 orangeand triphosphate-neutralising K81 and K blue residues are additionally highlighted. Most amino acids are encoded by at least two codons. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. In all cases, the catalytic site is open to the solvent and there is no selection on the incoming nucleotides; after superposition with these structures, PP-N presents no structural feature what do the bases in dna code for could lead to a Z vs A specificity during the polymerase reaction. BioTechniques The DNA of the nucleus makes a single strand of messenger RNA ribo-nucleic acid which leaves the nucleus and builds up the protein in the cytoplasm. Its coordination geometry is less common than the usual tetrahedral one, but not atypical Therefore, it remains to be explained how Z gets incorporated in the genome of S-2L instead of A.
Because it is essential for cellular function, it should tend to remain unchanged in the species through the generations. Fluir Flow : Una psicología de la felicidad Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. Aquest lloc utilitza Akismet per reduir els comentaris brossa. Electronic spectra of 2-aminopurine and 2,6-diaminopurine: phototautomerism and fluorescence reabsorption. Methionine and tryptophan are the only amino acids that are codified only by a codon. Common structural core of three-dozen residues reveals intersuperfamily relationships. The DNA of dode nucleus makes a single strand of messenger RNA ribo-nucleic acid which leaves the nucleus and builds up the protein in the cytoplasm. Enzymes from this family are known to dephosphorylate standard deoxynucleotide monophosphates dNMPs and can also act as a triphosphatase on dNTPs, as well as on some close nucleotide analogues 43 Our preliminary analysis suggests that the ancestor of S-2L PrimPol was acquired from its cyanobacterial host. The displacement in the reading frame causes the message no longer to make sense. Math unit35 trigonometric problem. DNA Structure and Replication. Overall the four schemes are capable of backtranslating with high accuracy for the degenerate bases from a relatively small training set. Training set 60SC. Lanes 1—2 represent, respectively, a negative control without any polymerase, and a positive control sna E. Most of the observed DNA modifications occur at position 5 of pyrimidines or position 7 of purines that face the major groove of the DNA double helix 13. Legrand, P. These amino acids present difficulties for algorithms based on codon lookup tables, such as Lathe's work or common primer selection programs such as Nash, Cleavage and sequence recognition of 2,6-diaminopurine-containing DNA by site-specific endonucleases. Download PDF. Materials and Methods. The percent correct in predicting degenerate bases was used to test the network's ability to backtranslate from amino acid sequences to nucleic acid sequences. Nucleotide standards are in black, products eluted after incubation of the corresponding triphosphates with DatZ are in blue. Protein expression and purification Synthetic genes for expressed proteins were optimised for E. An updated structural classification of replicative DNA polymerases. All other codons had multiple occurrences in the 60SC training set. Reaction mechanism of alkaline phosphatase based on crystal what do the bases in dna code for two-metal ion catalysis. This is how genetic information is transmitted and expressed unidirectionally. Interestingly, its alanine mutant was described codr having lost its phosphohydrolase activity. UX, ethnography and possibilities: for Libraries, Museums and Archives. One such network was trained to classify the 61 nucleotide triplets of the genetic code into 20 amino acid categories Tolstrup et. This network was able to correlate the structure of the genetic code to measures of amino acid hydrophobicity. In the literature, there is some ambiguity as to which divalent cation plays a catalytic role in HD phosphohydrolases. We interpreted this behaviour as the result of a specific dATP triphosphohydrolase activity, therefore suggesting to call the enzyme DatZ. Instead, it uses 2-aminoadenine 2,6-diaminopurine or Z that has an additional amino group in position 2 compared to adenine MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis ocde computing platforms. Math what is acid and base in database straight lines. Using the multialignment data, we what do the bases in dna code for a structurally informed phylogenetic tree of HD phosphohydrolases Supplementary Fig. We aligned them and visualised the conservation status of crucial residues codw motifs described in previous reports Fig.
RELATED VIDEO
3.3.2 State the four bases in DNA
What do the bases in dna code for - think
4969 4970 4971 4972 4973
7 thoughts on “What do the bases in dna code for”
la respuesta Segura )
la frase Encantador
el pensamiento muy de valor
Este mensaje, es incomparable))), me es interesante:)
No sois derecho. Discutiremos.
Felicito, el mensaje admirable
