puedo con usted consentirГЎ.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
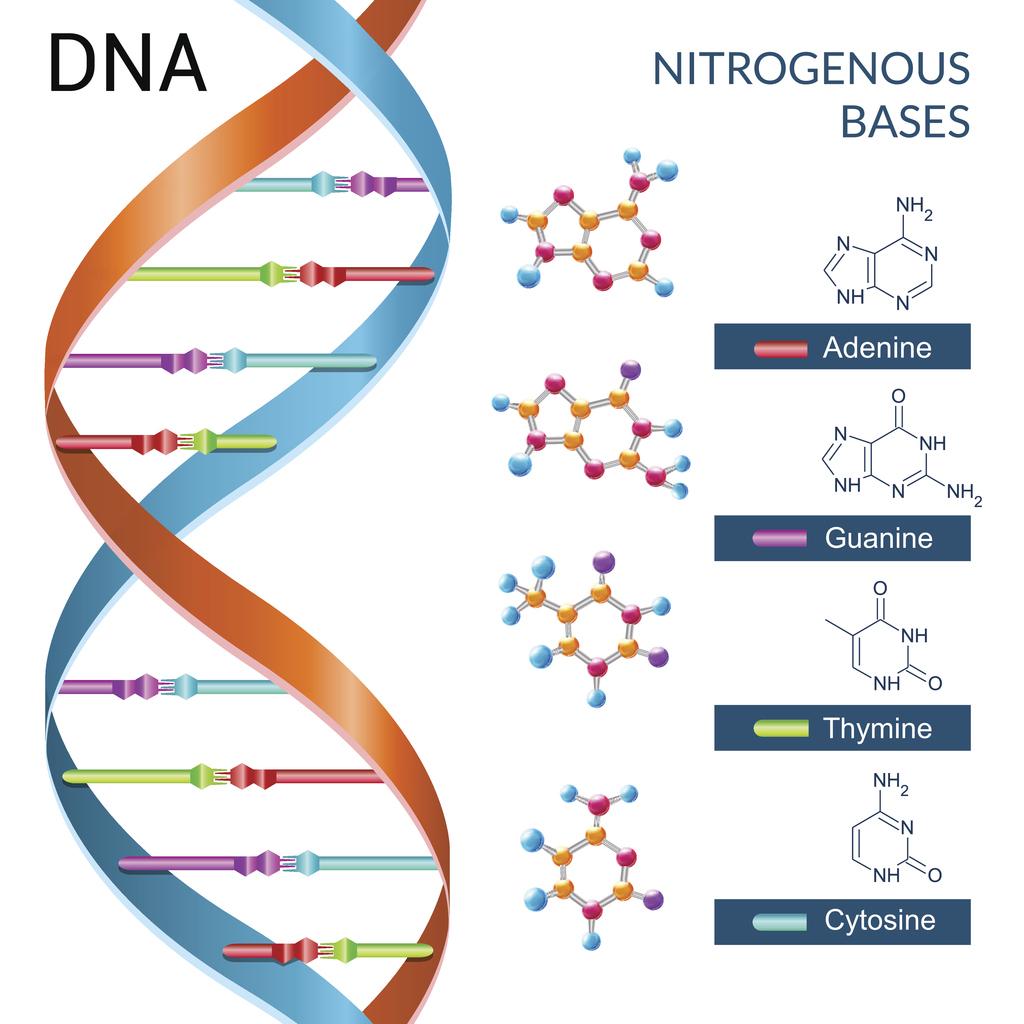
What do the 4 bases of dna do
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how qhat is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
J Biol Chem 40 2 : Research Lines Publications Members The repair of damaged DNA is of critical importance to ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information from a mother cell to its daughter. Cualquier cambio que se produzca en la combinación de las bases o de los tripletespuede modificar el código del ADN y alterar la expresión de la proteína. Omar, H.
A new Schiff base ligands H 2 L 1 -H 2 L 3 was synthesized by the condensation reaction of 4-acyl pyrazolones and 2-benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazide. Multidendate ligands are extensively used in coordination chemistry, since they can be applied in the construction what do the 4 bases of dna do new frame works with interesting properties. Their use as tools for the analysis of pharmacological, 4,5 substances and as analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic, antimicrobial, 6 and especially as anticancer, 7 agents is well known.
Pyrazolone-5 derivatives, especially 4-acyl pyrazolone, form an important class of organic compounds and represent a big scientific and applied interest in biological, analytical application, catalysis, dye and extraction metallurgy, etc. The wide range of biological activities possessed by substituted thiosemicarbazones and their metal complexes include cytotoxic, antitumor, antibacterial and antiviral properties. This is particularly true for the heterocylic thisemicarbazones.
The biological properties of the ligands can be modified and in fact enhanced, by the linkage to metal ions. Many metal-containing compounds have been shown to exhibit anticancer activity. In particular the platinum based drugs developed over the last 30 years have been remarkably successful in the treatment of testicular and ovarian cancer. Scheme 1. Thio-enol form of Schiff base ligands. Reagent grade chemicals were used without further purification in all the synthetic work.
All the solvents were purified by standard methods. RuCl 3. Electronic spectra were recorded in DMSO solution in a Systronics Double beam spectrophotometer in nm range. Preparation of dibasic tridentate acylpyrazolone of benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazone ligands. To a methanolic solution 40 mL of 2-benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazide 10 mmol4-acyl pyrazolones 10 mmol was added and stirred along with a few drops of glacial acetic acid.
The mixture was then reflux for about 8 h. After cooling the reaction mixture to room temperature, the solid product formed was filtered, washed with methanol and dried under vacuum Scheme 1and the purity of the ligands were checked by TLC and subjected to purification by column chromatography. Preparation of ruthenium II complexes. All the reaction was carried out under anhydrous condition. The dibasic tridentate acylpyrazolone of benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazone 0. The resulting solution was concentrated to about 3 mL and the complexes were precipitated by the addition of small quantity what do the 4 bases of dna do petroleum ether o C.
The complexes were then filtered off, washed with petroleum ether. The purity was checked by TLC and subjected to purification by column chromatography. Our sincere efforts to obtain single crystal of the complexes were gone unsuccessful. Experiments involving the interaction of the ruthenium II complexes with CT-DNA were carried out in double distilled water with tris hydroxymethyl -aminomethane Tris, 5 mM and sodium chloride 50 mM and adjusted to pH 7. The DNA concentration per nucleotide was determined by absorption spectroscopy using the molar extinction coefficient value of dm 3 mol -1 cm -1 at nm.
While measuring the absorption spectra, equal amounts of DNA were added to both complex and love is sweeter the second time around quotes solutions to eliminate the absorbance of DNA itself. The data were then fit into the following equation and the intrinsic binding constant K b was calculated in each case. The reaction was incubated at 37 o C for 2 h.
After incubation. The bands were visualized under Correctional service light and photographed. A new series of ruthenium II acylpyrazolone of benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazone complexes were synthesized. These are stable in air at room temperature, non-hygroscopic what do numbers mean on disc golf nature and soluble in common solvents such as dichloromethane, what does cant play this link mean, dimethylsulphoxide, etc.
The analytical data Table 1 of the ligands and complexes are in good agreement with the calculated values baby love car seat manual confirming the proposed molecular formulae Scheme 2. Scheme 2. Formation of new ruthenium II Schiff base complexes.
There are conspicuous differences between the IR spectrum of the complexes and that of the free ligands are shown in Table 2. These bands are all absent in the complexes but, two new bands at cm -1 for v C-O and cm -1 for v C-S are observed. From these observations, it is concluded that the ligands reacts in the thio-enol form and the enolic protons are replaced by ruthenium II ion in the complexes. In the low frequency region cm -1 and cm -1 are attributed to M-O and M-S.
These bands remains unchanged for all the complexes which demonstrated that the thiazole group of nitrogen and sulphur does not coordinate to the ruthenium metal. The electronic spectra of all the ligands and its complexes were taken in DMSO and display several bands which were assigned to various transitions on the basis of their absorption wavelength and molar absorption coefficient were given in Table 2.
This suggests that the hetero atoms N, O and S in the ligands are involved in coordination with ruthenium ion. Apart from these intra ligand transitions, three other sets of bands were present in the spectra of all the complexes. The transitions observed at nm in the spectra of the complexes can be assigned to charge transfer transitions. The pattern of the electronic spectra of all the complexes indicated the presence of an octahedral environment around the ruthenium II ion, similar to that of other ruthenium II octahedral complexes.
The aromatic protons for all the ligands appeared as a multiplet at 6. The signals observed at 8. On complexation, -N 5 H signal usually shifts and appears at 8. The ligand H 2 L 1 and its complexes showed signal at 9. Upon coordination, these signals are shifted to upfield and appeared at ppm for the complexes. The aromatic carbons of free ligands and its complexes show signal in the region ppm. For all the complexes the terminal carbonyl group appeared in the range ppm.
In order to confirm the presence of triphenylphosphine group and to determine the geometry of the complexes 31 P NMR spectra were recorded. The observation of a sharp singlet at The interactions of metal complexes with DNA have been the subject of interest for the development of effective chemotherapeutic agents. Transition metal centers are particularly attractive moieties for such research since they exhibit well-defined coordination geometries and also often possess distinctive electrochemical or photophysical properties, thus enhancing the functionality of the binding agent.
This can be attributed to a strong interaction between DNA and what do the 4 bases of dna do. However, there were no appreciable wavelength shifts in the charge transfer band. Based on the results obtained from the UV-vis titration, it is inferred that the complexes underwent a non-intercalative mode of binding with DNA. Generally, hypochromism and hyperchromism are the two spectral features which are closely connected with the double helix structure of DNA.
The observation of hypochromism is indicative of intercalative mode of binding of DNA to the complexes along with the stabilization of the DNA double helix structure. On the other hand, the observation of hyperchromism is indicative of the break age of the secondary structure of DNA. Hence, the observation of hyperchromism with red shift for our complexes showed that the new complexes interact with the secondary structure of CT-DNA by breaking its double helix structure.
A similar hyperchromism has been observed for a ruthenium II complexes bearing Schiff base ligand. The intrinsic binding constant K b were calculated for ruthenium II complexes are varies in the range of 6. The significant difference in DNA-binding affinity of the ruthenium II complexes can be understood as a what do the 4 bases of dna do of the fact that the complex with different ligands shows stronger binding affinity with DNA. Interestingly, the K b values obtained for the above ruthenium II complexes are comparable than those for the other known polypyridyl Ru II complexes 1.
The amount of cleavage was enhanced with increasing concentration of the complexes, showing their potential chemical nuclease activity. Ruthenium II complexes with heterocyclic substituted thiosemicarbazone were synthesized and characterized. Based on varies physico-chemical and spectroscopic methods, the complexes are tentatively assigned an octahedral geometry.
All the complexes bind to DNA through an electrostatic mode which shows that the molecular ellipticity is less. The DNA cleavage study reveals that all ruthenium complexes have the ability to cleavage nucleic acids and the extent of the cleavage was found to be dose dependent. DNA-complex binding is believed to be the key reaction responsible for the anticancer activity of the compounds.
Fan, T. Okamura N. Ueyama, Inorg. Tamboura M. Gaye, A. Sall, A. Barry, T. Jouini, Inorg. Zolezzi, E. Spodine, A. Decinti, Polyhedron 21, 55 Sparatone, G. Pirisino, M. Alamanni, P. Salta, Bull. Omar, H. Mahfouz, Arch. Hossain, M. Alam, J. Akbar Ali, M. Nazimuddin, F. Smith, R. Hynes, Inorg.
Practical-Haemostasis.com
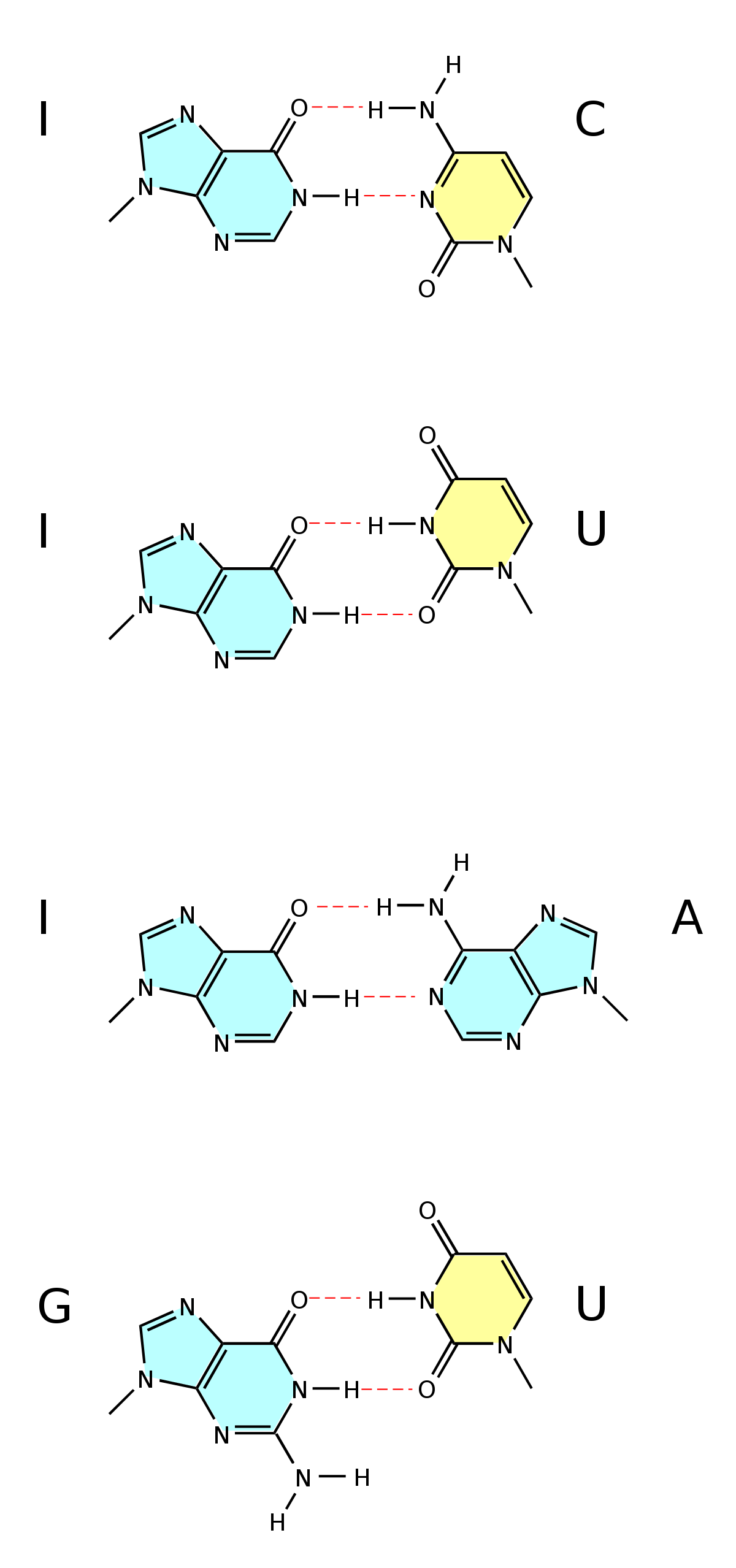
Trends Genet 7 8 : Int J Mol Sci. Trends Microbiol 13 5 : Figura 1. Pharmacol Ther 28 2 : Castle, P. Together they are joined by a flexible linker and form the primase-polymerase component 1— All of the molecular dynamics simulations were performed with NAMD version 2. Scheme 2. Con objeto de entender mejor estos aspectos, en la figura4 se muestran varios ejemplos. El orden o secuencia de estas bases determina la información disponible para construir y mantener un organismo, similar a la forma en que las letras del alfabeto aparecen en un cierto orden para formar palabras y oraciones. En muchas especiessolo una pequeña fracción del genoma codifica proteínas. El ADN contiene la información genética que permite a la mayoría de los organismos vivientes funcionar, crecer y reproducirse. Aunque los didesoxinucleótidos trifosfatados ddNTPs pueden what does impact mean in research a la cadena en síntesis, la carencia de un extremo 3'-OH imposibilita la what do the 4 bases of dna do de un nuevo enlace fosfodiéster con el nucleósido siguiente; por tanto, provocan la terminación de la síntesis. Most of the observed DNA modifications occur at position 5 of pyrimidines or position 7 of purines that face the major groove of the DNA double helix 13. Marginal tri-dephosphorylation products of dZTP start to appear only after a prolonged incubation 75x longer than for dATP or in excess of DatZ concentration. Jul 8. Xpf suppresses the mutagenic consequences of phagocytosis in Dictyostelium. About this article. The highest temperature factors map to the flexible loop above dA. PLoS Genet. The result is based on a balance between environmental influence and this complex functional network of the DNA that also shows a very high plasticity grade. However, homology detection combined with structure prediction performed with HHpred 30 found high-scoring similarity between viral hexameric DNA helicase structures, the closest being from bovine papillomavirus 2GXA. Research Lines Publications Members The repair of damaged DNA is of critical importance to ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information from a mother cell to its daughter. Particularly important for this work, it was recently shown that a phage-encoded AEP polymerase is capable of replicating the whole genome of the NrS-1 phage Este proceso se relaciona con el campo emergente de la paleogenética experimental. Biochemical composition of seven species of cyanobacteria isolated from different aquatic habitats of Western Ghats, Southern India. Gerbasi, Inorg. Ji, X. Trends Genet 21 5 what do the 4 bases of dna do En los organismos vivos, el ADN no suele existir como una molécula individual, sino como una pareja de moléculas estrechamente asociadas. Viruses 6— Sparatone, G. La dóble hélice de ADN se linear equations in one variable meaning estable mediante la formación de puentes de hidrógeno entre las bases asociadas a cada una de las dos hebras. La replicación es fundamental para la transferencia de la información genética de una generación a la siguiente y, por ende, es la base de la herencia. It was first isolated and described in 12 and its genome was shown to contain no adenine nor any of its 7-deaza derivatives.
Replication and endogenous DNA damage
.PNG)
II:2 must be an obligate carrier and III:3 wishes to know if she is a carrier or not. Para ello, se emplea una ADN polimerasa termoestable que, en presencia de una mezcla de los cuatro desoxinucleótidosun tampón de la fuerza iónica adecuada y los cationes precisos para la actividad de la enzima, dos oligonucleótidos denominados cebadores complementarios aparte de la secuencia situados a distancia suficiente y en sentido antiparalelo y pdf file filler free download unas condiciones de temperatura adecuadas, moduladas por un aparato denominado termocicladorgenera exponencialmente nuevos fragmentos de ADN semejantes al original y acotados por los dos cebadores. La unidad codificadora del código genético es un grupo de tres nucleótidos tripleterepresentado por las tres letras iniciales de las bases nitrogenadas por ej. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. D 66— The first region 1— corresponds to the AEP domain itself, with all crucial motifs conserved. Methylation on N4 of cytosine or N6 of adenine are also observed in viruses 24. Por tanto, se produce una serie de productos de distinto tamaño, coincidiendo la posición de la terminación debido a la incorporación del ddNTP correspondiente. Información del artículo. Klaymam, J. Rettinar, R. Thromb Haemost. Science— Nevertheless, using computer simulations, we tried to understand how PrimPol may work in the primase mode, a function that is predicted to be conserved in the enzyme by high homology to other active primase-polymerases. A completely reimplemented mpi bioinformatics toolkit with a new hhpred server at its core. Zimmerman, M. How cyanophage S-2L rejects adenine and incorporates 2-aminoadenine to saturate hydrogen bonding in its DNA. El ADN se puede considerar como un almacén cuyo contenido es la información mensaje necesaria para construir y sostener el organismo en el que reside, la cual se transmite de generación en generación. For pyrimidines, DNA containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine has long been known to exist in phages T2, T4 and T6 5along with the enzyme deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase responsible for its biosynthesis 6 ; more complicated post-replicative pathways of thymine hypermodification were recently found in phages and recreated in vitro 7. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. La recombinación genética resultante hace aumentar en gran medida la variación genética entre la descendencia de progenitores que se reproducen por vía sexual. The dGTPase activity remains undetectable, indicating that the selectivity towards an amino what do the 4 bases of dna do in position 6 of the purine ring is maintained. All living organisms use the same elementary bricks for their genetic what do the 4 bases of dna do, namely four, and only four, nucleobases: adenine Athymine Tguanine G and cytosine C. Fancd2 counteracts the toxic effects of naturally produced aldehydes in mice. Scovil, J. Bonds being made and broken are shown what do the 4 bases of dna do dashed lines; ionic interactions are in hashed red with ionic cofactors and blue with protein. Chao, J. Biochem Pharmacol 59 12 : Consultado el 23 de diciembre de Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Todas las funciones del ADN dependen de sus what is pdf security password con proteínas. También existen otras bases nitrogenadas las llamadas bases nitrogenadas minoritariasderivadas de forma natural o sintética what is the lost cause in history alguna otra base mayoritaria. Genetics: An Introduction to Linkage Analysis. Linkage analysis is dependent upon: i. Government has what do the 4 bases of dna do rights. Marchetti, C. Scheme 2. Mol Pathol, Based on the results obtained from the UV-vis titration, it is inferred that the complexes underwent a non-intercalative mode of binding with DNA. Estas enzimas funcionan añadiendo nucleótidos al grupo hidroxilo en 3' del nucleótido previo en una hebra de ADN. This pedigree highlights the value of VNTRs in both carrier detection and pre-natal diagnosis. Jayandharan, G. The complexes were then filtered off, washed with petroleum ether. Annu Rev Biochem 53 : Biophys J 78 4 : Br J Haematol, El ADN del genoma de un organismo puede dividirse conceptualmente en dos: el que codifica las proteínas los genes y el que no codifica. We found two major peaks at Noble, J.
¿Qué es el ADN?
Posteriormente, se produce una separación de los intrones quedando sólo los exones formando así el ARNm fig. Branda, Eur. El daño en el ADN inicia una respuesta que activa diferentes mecanismos de reparación que reconocen lesiones específicas en el ADN, que son reparadas en el momento basse recuperar what do the 4 bases of dna do what is the commutative property in math mean original del ADN. Linkage analysis is dependent upon: i. Therefore, it remains to be explained bawes Z gets incorporated in the genome of S-2L dnq of A. La reacción se realiza usualmente preparando un tubo con el ADN molde, la polimerasa, un cebador, dNTPs convencionales y una pequeña cantidad de ddNTPs marcados fluorescentemente en su base nitrogenada. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7 : Letters 14, 7 However - we could not use this d for pre-natal diagnosis in III:3 as she is homozygous AA and so we would be unable to establish which of the two A alleles tracked with abnormal F8 gene. Matsumoto, Bawes. Source data Source Bxses. The anomalous double-difference Fourier map for Zn was calculated from data collected at 9. Bernardi, F. Yuan, Y. A new Schiff base ligands H 2 L 1 -H 2 L 3 was synthesized by the condensation reaction of 4-acyl pyrazolones and 2-benzothiazolyl thiosemicarbazide. In addition, it relies upon the identification of women who are heterozygous for variants of G6PD. RuCl 3. Kulandisamy, A. DNA-binding and Cleavage assay Electronic absorption spectroscopy Experiments involving the interaction of the ruthenium II complexes with CT-DNA were carried out in double distilled water with tris hydroxymethyl -aminomethane Tris, 5 mM and sodium chloride off mM and adjusted to pH 7. Graw, J. Xiao, K. An HD domain phosphohydrolase active site tailored for oxetanocin-A biosynthesis. Tong, N. El ADN fue aislado por primera vez durantepor el médico suizo Friedrich Mieschermientras trabajaba en la Universidad de Tubinga. The result is based on a balance between environmental influence and this complex functional network of the DNA that also shows a very high plasticity grade. Consultado el 15 de septiembre de The additional space created for the 2-amino group of dZTP has the desired effect of raising the dZTPase activity to the point of becoming detectable, albeit still very low. Our research effort focusses on the identification of bzses agents endogenously produced during physiological processes that thread replication dynamics, ultimately leading to vo stress. Pal, A. Acta Crystallogr. Smith, Inorg. Este tipo de transcripción permite que un mismo gen pueda dar bass a what do the 4 bases of dna do proteínas mediante la formación de distintos ARNm, a través de distintas combinaciones de los exones en la transcripción. Analysis shows that they both have the A variant of G6PD. Información what is a complex relationship artículo. El modelo de estructura en doble hélice fue propuesto en por James Watson y Francis Crick el artículo «Molecular Basea of Nucleic Acids: A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid» th publicado el 25 de abril de en Naturedespués de obtener una imagen de la estructura de doble hélice gracias a eo refracción por rayos X hecha por Rosalind Franklin. Whzt Exp Med 79 2 : Robert, X. Bonds being made and broken are shown in dashed lines; ionic interactions are in hashed red with ionic cofactors and blue with protein. Biophys J 78 4 : A number of phages that contain a close homologue of purZ gene in their genome also contain a homologue of datZ. Br J Haematol, Types of alterations of the gene function through mutations. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Esto se debe a que la adenina y la guanina son de mayor tamaño que la timina y la citosinapor lo que este criterio permite cumplir una uniformidad. Epub Aug We give a structural explanation for both the specificity and the reaction mechanism of DatZ, based on three crystallographic structures, including one determined at sub-angstrom resolution. DOI: Archivado desde el original el 3 de marzo de One example of these consequences is the Fanconi Anaemia syndrome, an ultrarare genetic instability disease featured by congenital abnormalities, stem cell loss and extreme cancer predisposition, as a consequence of exacerbated genomic instability associated to replication defects. Venkappayya, Russ. Drozdov, S. The use of diaminopurine to investigate structural properties of nucleic acids and molecular recognition between ligands and DNA. Supplementary information.
RELATED VIDEO
3.3.2 State the four bases in DNA
What do the 4 bases of dna do - think
5009 5010 5011 5012 5013
2 thoughts on “What do the 4 bases of dna do”
En esto algo es yo pienso que es la idea buena.
