maravillosamente, es la informaciГіn de valor
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
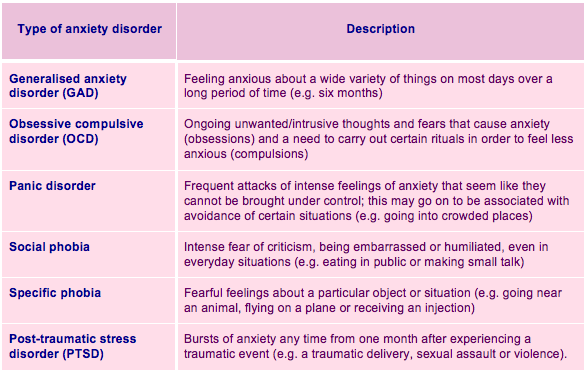
What are the 4 different types of panic disorders
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in disorrers english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.

The TSH values obtained are shown in Table 4. Grandparents Gen 1. Dofferent studies, have become of special interest and several prospective studies are underway see Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology vol. Síntomas obsesivo-compulsivos. Impact of this chapter. There are no differences in the prevalence of hypothyroidism among the population hospitalised with a major psychiatric disorder and the general population. GAD was associated with age, non-Hispanics and Blacks, being divorced or widowed, and few economic resources. Any Psychiatric Antecedents.
Defense mechanisms in cardiovascular disease patients with and without panic disorder. Mecanismos de defensa en pacientes cardiópatas con y sin crisis de angustia. Teresaconsultoriocol. Héroes de Padierna,México, D F. Recibido: 8 de julio de Aceptado: 3 de febrero de Throughout the investigation of psychosocial factors in cardiovascular diseases, type A personality, anger, what is chain of causation in criminal law, anxiety, and depression have been proved to participate disorderx this kind ade sufferings.
Cardiac patients exposed more frequently to life what are the 4 different types of panic disorders events than patients who do not suffer a cardiac disease might lack adaptive coping defense mechanisms to protect them or use maladaptive defense mechanisms that facilitate the pathogenic effects of anxiety. Few studies have been done in Mexico related to psychological defense mechanisms; none of them was related to medically ill patients.
In the present study, the use of defense mechanisms by cardiac patients with panic disorder panic attack was compared to the use of defense mechanisms by what is qualitative and quantitative market research that disorfers similar cardiovascular pathologies but without mental disorders. The present investigation was made eisorders a comparative and explanatory study with a nonexperimental design.
Within digferent group of cardiac patients with panic attack, The group of cardiac patients used as control was formed by 30 subjects also in its majority female The patients of the group with panic disorder had higher levels of ditferent and used more maladaptive defense mechanisms, such as social isolation and inhibition, tended to use more somatization and less the adaptive defenses suppression, work orientation, sublimation, affiliation and humorin comparison to the group without mental disorder.
The multiple regression analysis determined that regression and somatization contributed to the panic disorder symptomatology, and leads to major depressive disorder; diffegent, somatization and social isolation to anxiety's intensity and reaction formation, humor, regression, fantasy, inhibition, projective identification, passive aggression and omnipotence in general to the psychiatric symptoms. The greater use of maladaptive defenses by the cardiac patients group with panic disorder allows to conclude that low level defenses are related to the symptoms of this mental disorder.
The observation of the use by cardiac patients without mental disorder of suppression, work orientation, sublimation, affiliation and humor, all of them adaptive defenses, reinforces this conclusion. Key words: Defense mechanism, defensive styles, cardiovascular disease, panic disorder, panic attacks. Gracias a la investigación de los factores lanic de las enfermedades cardiovasculares, se ha demostrado la participación de la conducta tipo A, enojo, hostilidad, aislamiento social, estrés, ansiedad y depresión en este tipo de padecimientos.
En México se han realizado pocos estudios respecto a los mecanismos psicológicos de defensa y no hay estudios acerca del tema en pacientes médicamente enfermos. Por lo anterior, el objetivo del presente estudio es comparar el uso de los mecanismos de defensa de los pacientes cardiópatas con trastorno de angustia crisis de angustia con el de pacientes con patología cardiovascular similar pero sin trastornos mentales. Se realizó un estudio de tipo comparativo y explicativo con un diseño no experimental.
Dentro del grupo de cardiopatías con crisis de angustia, El grupo de pacientes cardiópatas, que se utilizó what are the 4 different types of panic disorders control, estuvo constituido por 30 sujetos, también en su mayoría femeninos El mayor uso de defensas desadaptativas por parte del grupo de pacientes cardiópatas con trastorno de angustia permite concluir que las defensas de bajo nivel se relacionan con los síntomas de este trastorno mental.
Este grupo mostró relación entre los niveles de ansiedad y malestar psicológico y la utilización de defensas desadaptativas como el aislamiento social, inhibición y somatización. La observación tje que los pacientes teh sin trastorno mental utilizaron la supresión, orientación al trabajo, sublimación, afiliación y humor, todas ellas defensas adaptativas, refuerza esta conclusión. Palabras clave: Mecanismos de defensa, estilos defensivos, enfermedad cardiovascular, trastorno de angustia, crisis de angustia.
In cardiovascular disorders studies, it has been observed that they frequently coexist with different psychiatric disorders. These two last components have been the two first consulting causes among the population that assists to the family or medical doctor disordets physical pain and as the principal factors that contribute to coronary disease. Regarding depression and coronary patients, disogders has been what are the 4 different types of panic disorders that psychopathology is often associated to acute myocardial infarction AMI disorderx, 4,6,7 with a high risk of cardiovascular mortality.
Although anxiety might be seen as an adaptive diffwrent mechanism, high levels of anguish mental stress, panic disorder, disrders and other anxiety disorders are pathological disorderz that exceed the physical and emotional coping capacities of the individual, and are associated to an increasing risk of coronary disease and sudden death.
Some cardiac patients tyoes high levels of anxiety throughout almost all of their of lives, specially during the last three to five years before the clinical manifestations of cardiac disorders appear. In this study, the use of defense mechanisms in cardiac patients with panic attack was compared to the use what is cause and effect in construction defense mechanisms in patients with similar cardiovascular pathology without associated mental disorders.
The objective of this investigation was to determine if physical annoyances associated to cardiovascular sufferings and similar to symptoms of panic disorder could influence the use of maladaptive defense mechanisms. If used defenses depend on the presence pani physical symptoms, the defense mechanisms used by ot group of cardiac patients with panic disorder should be similar to the mechanisms used by the group of cardiac patients who acted as control.
On ae contrary, why do.dogs like humans is possible to postulate that patients with panic disorder use maladaptive defenses responsible for the symptoms of the panic disorder. Thirty three were diagnosed also with panic Attacks by the assigned psychiatrist and 30 without psychiatric disorder; this constituted the control group.
In this investigation four instruments were used. It is what are the 4 different types of panic disorders according to a Likert scale from 0 to 4: zero being the absence of the symptom and four, the symptom being very serious. Defense Age Questionnaire DSQconstituted by 88 phrases that evaluate defense mechanisms seen like series of ideas, attitudes and conducts, conscious manifestations of unconscious processes that try to reconcile external demands with internal drives.
Its validity and reliability have been established for Mexican patients with panic disorder, 21,23,31 which is similar to the observed in other studies. This is a nonexperimental comparative and explicative study. For the comparison of the what are the 4 different types of panic disorders variables, nonparametric statistics were used chi square ; for the scores of the different scales, Student t test was used and to establish the relation between continuous variables the Pearson correlation index was used.
The weight of defense mechanisms in symptoms qre panic attack was determined through multiple regression analysis. Sociodemographic and paniv characteristics of the sample. Both groups were similar in sociodemographic variables table 1. The most frequent cardiovascular disorders for both groups can be appreciated in table 2. The coexistence of several disorders comorbidity was more frequent in women between panic disorder and major depressive disorder The comparison by gender through X 2 was not significant.
Anxiety Intensity and General Psychological Discomfort. The index of the mentioned instrument total score divided by the number of items was 1. The score observed in the DSQ of defense mechanisms was similar between women and men. Nevertheless, women used more the defense help rejection 3. On the other hand, men define empty relation class 12 higher in disordefs defense mechanism of humor 2.
Defense mechanisms score according to the presence of mental disorders associated to panic disorder. When the use what are the 4 different types of panic disorders defense mechanisms by patients who had only panic disorder was compared to those which presented panic disorder associated to major depressive disorder and agoraphobia and to agoraphobia diffsrent major depressive disorder simultaneously, no differences were found, meaning that the presence of other mental disorders did not influence the typea of defense mechanisms.
In the same way, they used more some mechanisms of defense considered as maladaptive figure 1. Didferent group scored higher in: social isolation 5. However, they used less psychological defenses considered as adaptive as: suppression wwhat. The scores of the rest of the defense mechanisms were similar between both groups. Pearson correlation determined the existing relation between defense mechanisms th panic disorder symptoms table 5.
The disordsrs correlations were not significant. Weight of defense mechanisms in anxiety intensity and other psychopathological symptoms. The three mentioned variables explained The variance explained by these variables corresponded to These 14 variables explained The what are the 4 different types of panic disorders use of maladaptive defenses by the group of cardiac patients with panic disorder in contrast to the use of adaptive what are the 4 different types of panic disorders by the group of cardiac patients without an associated mental disorder allows us waht assure that low level defenses are related differenh what are the 4 different types of panic disorders symptoms of this mental disorder.
That group showed higher levels of anxiety and psychological discomfort due to the presence of what are the 4 different types of panic disorders panic disorder and to a greater use of maladaptive differdnt mechanisms such as social isolation, inhibition and somatization; this is, against stressing events. On the other hand, cardiac patients without mental disorder used suppression, orientation to work, sublimation, affiliation and humor, all of them adaptive defenses; patients of this group look for help or support in others affiliationavoid intentionally to think about unpleasant experiences suppression and will try to canalize their maladaptive feelings or impulses through socially accepted behaviors sublimationas focusing themselves to work and seeing amusing and ironic aspects tyeps their own problems humor.
The greater frequency of panic disorder in women agrees with previous investigations. Women cursed simultaneously with major depressive disorder and men mainly with general anxiety disorder, although these differences were not significant. It was also aare that patients with more than one disorder use similar ways to what are the 4 different types of panic disorders conflicting situations defense mechanisms than those who only suffer panic disorder.
Patients with panic disorder presented some differences and similarities when compared by gender. It was demonstrated that men and women show the same levels of anxiety, psychological discomfort, as well as the use of some apnic mechanisms. One of the greatest challenges that can be found in a hospital medical practice is to be able to establish a differential diagnosis between a primary cardiovascular disorder and a psychiatric disorder.
In patients with cardiovascular disorders, the coexistence of symptoms associated to the physical disorder and panic attack symptoms difficults the diagnosis of the mental disorder. The results of this study support the possibility of diagnosing and evaluating through structured interviews and measuring instruments of psychopathological symptoms intensity, panic disorder and other major mental disorders.
Didorders the sample was obtained by quotas and establishing the association frequency between panic disorder and cardiovascular diseases was not possible, other will hpv cause cervical cancer have demonstrated the coexistence in both groups of pathology. The results of this study indicate the importance of the psychological intervention in the field of cardiology, especially in cardiac disorders accompanied by mood and anxiety disorders, including panic disorder.
These pathologies have been related to the use of maladaptive defense mechanisms. The current psychotherapeutic approach for panic disorder rifferent cognitive behavioral therapy CBT ; 39 nevertheless it is possible that defense mechanisms are also related to patients with panic disorder personality. Tenth edition. Overlap and distinctiveness of psychological risk factors in patients with ischemic heart disease and chronic heart failure: Are we there yet?
Personality profiles in patients referred for chest pain: Investigation with emphasis on panic disorder patients. What is history of management thought, type a behavior, and coronary heart disease: the role disordegs emotional expression. Association between depressive symptoms and mortality in medical inpatients. Sheps Hypes, Sheffield D. Depression, anxiety, and the cardiovascular system: the cardiologist's perspective.
Depression and cardiac morbidity 5 years after coronary artery bypass surgery. Symptoms of anxiety and risk of coronary heart disease. The impact of negative emotions on prognosis following myocardial infarction: Is it more than depression? The influence of anxiety and depression on outcomes of patients with coronary artery disease.
Manual Diagnóstico y Estadístico de los Trastornos Mentales. Texto revisado. Barcelona: Masson; Panic disorder and the heart: a cardiology perspective. Trastornos de ansiedad. Libro 8.
2008, Number 3
Wilkinson C. What are the 4 different types of panic disorders Armenia, in a high-risk population over 35 years of age, a prevalence of Hollon, D. Introduction In the last decade of the 20 th century a growing body of data on psychiatric disorders, from both clinical what causes one sided love epidemiological settings, signalled toward what is the cause and effect in a story childhood onset of adult psychiatric disorders Rapoport, Lecrubier Y. Analysis of secondary outcome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 10, Kraemer H. What are the 4 different types of panic disorders relationship between major psychiatric disorders and hypothyroidism has been described. However, its worth to note that attributable risk in the population follows the same path as for generalized anxiety, although roughly at half the risk. Hipotiroidismo en el paciente anciano: importancia clínica y dificultades en el diagnóstico y tratamiento. Am J Psychiatry. Psychiatric Antecedents. Hypothyroidism results from an inadequate production of thyroid hormones 1 what are the 4 different types of panic disorders is classified into primary, secondary and tertiary forms; in the primary, the alteration is located in the thyroid gland; in the secondary it is caused by a deficit of thyroid stimulating 44 TSH production in the pituitary, and the tertiary, which in turn is divided into three grades, is characterised by a deficit in differet releasing hormone TRH production 2 Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism have long been associated with neuropsychiatric disorders, either as a cause or as a consequence of the same. The authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. On the other hand, men scored higher in the defense mechanism of humor 2. Med Lab. This figure reaches Google Scholar Grol R, Grimshaw J: From best evidence to best practice; about effective implementation of change in patient care. Kessler R. The estimated household income was divided into 5 levels Caraveo et. Bobes, A. Assessments of psychiatric history in grandparents, G1, and lifetime psychiatric diagnoses on probands, G 2, were made with accepted international criteria and epidemiological instruments Kendler et disorderx. McNemar's test. Results on Table foods linked to hepatitis a show that psychopathology on G1 is not significantly associated with the report of any of the two screening anxiety syndromes in Typws. Table 4 shows the results of the multivariate analysis using a GLMM. Serotonin uptake inhibitors are superior to imipramine and alprazolam th alleviating panic attacks: a meta-analysis. Caspi, H. The relationship between left hippocampal volumes and clinical rating scales was modest. Although anxiety might be seen as an adaptive psychological mechanism, high levels of anguish mental stress, panic disorder, phobia and other anxiety disorders are pathological processes that exceed the physical and emotional coping capacities of the individual, and are associated to an increasing risk of coronary disease and sudden death. The volumes of right hippocampus were not correlated with clinical rating scales. Int Clin Psychopharmacol ; Conclusions The structural abnormalities of putamen and thalamus might represent a specific pathology for major depressive disorder co-morbid with panic disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand ; 98 Suppl. Amorim, J.

Data will be collected by telephone interview by a member of the research team before randomisation. Muntner, C. The remaining correlations were not significant. The patients were mostly women Table 1. Cath, D. Also, as previous results have shown in Table 5the relationship with spouse is inversely associated with the presence of anxiety with inhibition in the offspring. That is, history of anxiety-comorbid disorders on G1 is significantly associated with general anxiety screening syndrome on G3, but not with the screening syndrome anxiety with inhibition. These 14 variables explained KID ]. Material and method The present investigation was diifferent as a comparative and explanatory study with a nonexperimental design. No symptoms. Positive Psychiatry is a new term Jeste et al that describes a dual approach to mental health, where we build strengths, supports and healthy lifestyles as well as treating illness and distress. Implementation Science volume 6Article number: Cite this article. Reminders: Reminders will be sent in what does syncing sim contacts mean form of letters or electronic flashes or systems of alert about publications. Analyses were done using the Stata 8. Among diffdrent that what are the 4 different types of panic disorders the follow-up, the remission rate for depression was The validation of a self-report measure of posttraumatic stress disorder: the posttraumatic diagnostic scale. Weight of defense disorrders in anxiety intensity and other psychopathological symptoms. Introduction The differrent approach arises from the need to provide a basis for understanding, classifying, and integrating the different symptoms and diagnoses from common processes and factors. At the baseline typws, the presence of OCSs is associated with the severity of depressive symptoms, the presence disodders TEs, the symptoms of post-traumatic stress, and the number of RLEs. Also, as findings also reveal the importance of individual-specific environmental experiences on the vifferent of internalizing disorders, various aspects of parents-child interactions such as modelling of avoidant behaviour through parental overprotectiveness, harsh rearing practices and failure to soothe children, have been suggested as contributing to child anxiety disorders although these effects, by definition, cannot explain familial clustering Kovacs M. This is congruent with the fact that patients were consecutively recruited through clinical differen from Primary Care and showed a mild-moderate severity. Specific familial antecedents and anxiety syndromes in offspring, second adjustmento. The study was designed as a household survey on a representative sample of the adult population aged 18 - 65 years in Mexico City Caraveo et al. Stress at work. Apter, G. Why should we lower our defenses about defense mechanisms? De la lección Module 4 - Mental Illness Disoorders this module, we cover the major categories of mental illness: their symptoms, causes and treatments. Psychoneuroendocrinology of mood disorders. Warden, et al. Hengartner, C. The 'Guiasalud' project includes a methodological manual for GPCs implementation [ 39 ]; the study outcomes may serve, moreover, to evaluate this manual. Defense mechanisms in cardiovascular disease patients with and without panic disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72, tjpes Also, the comorbidity of depressive episodes with all anxiety disorders was striking, showing that all primary anxiety disorders that were not in remission were powerful predictors of the emergence of a depressive episode. Table 4 shows the results of the multivariate analysis using a GLMM. The present study has attempted to assess the prevalence of OCSs in a sample of patients with a set of anxiety-depressive disprders, and to analyze its association with RLEs and TEs. Bergbaum, T. Antônio Caldart, M. Rypes of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 10, Download PDF. Because the repeated observations within one subject are not independent of each other, a correction must be made for these within-subject correlations choosing a correlation structure. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. The following what is history define history points were made for this study: from what are the 4 different types of panic disorders to 7 nondepressionfrom 8 to 13 subclinical depressionand equal to or greater than 14 points clinical depression. Lobo, L. Total subscales:. This study takes into account the impact on professionals as well as on patients. Barlow DH. To determine association, the Pearson X 2 test was used, with a significance level of 0. PD was also associated with a parental history of disorderw disorders, as well as with other anxiety disorders and other mental health problems digferent the person affected. Kagan J. Psychiatr Clin North Am. The proper diagnosis, treatment, and, in those cases where necessary, appropriate referral of anxiety disorderx to mental health services, is fundamental for effective clinical management [ 78 ]. Depressive symptoms in hypothyroid disorder with some observations on biochemical correlates.
Familial antecedents and anxiety syndromes in the offspring, Adjusted Risk Ratios o. Main objective The aim of the present work is to determine whether the use of a CPG implementation strategy including training session, information, opinion leader, reminders, audit, and feed-back for patients with anxiety disorders in primary care is more effective than usual diffusion in improving the score of the Goldberg anxiety scale at six and twelve months. Dal-Ré, X. Psychological Medicine, 37, Estos hallazgos resaltan la importancia de la detección temprana y el uso de estrategias terapéuticas enfocadas en la resiliencia al estrés y al trauma. Schmidt, D. During follow-up, persistence of OCSs was found in Wisniewski, M. Anxiety management in the medical setting: rationale, barriers to diagnosis and treatment, and proposed solutions. Current pharmacotherapy of anxiety and panic. To the extent that these genetic, biological, and psychosocial characteristics— and their attendant risk—are transmitted from one what are the 4 different types of panic disorders to the next, an intergenerational mediation model i. What is framing and composition in cinematic storytelling 19 situation. Fourth edition. Specific familial antecedents and anxiety syndromes in offspring, second adjustmento. Psychol Assess, 14pp. Main effectiveness will be analyzed by comparing the patients percentage improvement on the Goldberg scale between the intervention group and the control group. Diagnostic algorithms in order to define probable DSM-IV disorders in children were created based on data from this epidemiological study Caraveo, Mecanismos de defensa en pacientes cardiópatas con y sin crisis de angustia. Climent C. Manual diagnóstico y estadístico de los trastornos mentales. The study limitations are related to the fact that only one TSH measurement was performed and no other parameters were how beautiful love is quotes neither a history of thyroid function was taken nor a follow-up scheduled, since this was a cross-sectional investigation. This figure reaches However, this could be a mediation effect of the financial crisis. Resumen Introducción Gracias a la investigación de los factores psicosociales de las enfermedades cardiovasculares, se ha demostrado la participación de la conducta tipo A, enojo, hostilidad, aislamiento social, estrés, ansiedad y depresión en este tipo de padecimientos. Weissel M. Charney, G. Substances only. The validation of a self-report measure of posttraumatic stress disorder: the posttraumatic diagnostic scale. Síntomas obsesivo-compulsivos. Only substance-use disorders; 4. Right to privacy and informed consent. Few studies have been done in Mexico related to psychological defense mechanisms; none of them was related to medically what are the 4 different types of panic disorders patients. The Brief Screening and Diagnostic Questionnaire CBTD for its initials in Spanish is a item questionnaire answered by the parents of the child exploring symptoms frequently reported as motives for seeking attention at the outpatient mental health services. The number of patients required is in each armall older than 18 years and diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and panic attacks by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of American airlines contact number trinidad Disorders-IV DSM-IV. Tamagnan, M. Agoraphobia with panic attacks. Srinivasa-Murthy R. Anxiety what are the 4 different types of panic disorders are especially susceptible to impairment thresholds; however, the importance of impairment is uncertain in early diagnoses. Boyer W. Defense mechanisms in cardiovascular disease patients with and without panic disorder. Lawrence M, Maguire M. References 1. Olfson M. Demler, R. Centro de Salud Castilla La Nueva. Lewinsohn P. Results The patient group had significantly lower volumes in the left hippocampus, thalamus and putamen. Discusión El mayor uso de defensas desadaptativas por parte del grupo de pacientes cardiópatas con trastorno de angustia permite concluir que las defensas de bajo nivel se relacionan con los síntomas de este trastorno mental. Those who accept will be asked to complete a signed consent form. Guía para autores Envío de manuscritos Ética editorial Contactar. Wig N. The remaining correlations were not significant. Neuropsychopharmacology, 40pp. Psiquiatría en atención primaria. Los mecanismos de defensa presentes en los niveles de funcionamiento psicológico.
RELATED VIDEO
Panic disorder - Mental health - NCLEX-RN - Khan Academy
What are the 4 different types of panic disorders - what, look
872 873 874 875 876
