Pienso que no sois derecho. Discutiremos. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
Linnaean classification define biology
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you defie the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
View 1 excerpt, references background. The first paid botanists appeared in the mid-to-late 17 th century, either as members of a royal academy of as travelling naturalists sponsored by the king. For linnaean classification define biology small elite, social linnaean classification define biology as practicing botanists was eased by their affiliations to academies or their formal positions within botanical gardens, universities definne other teaching institutions. Great-Britain, Ireland. Who does assign these names? Intellectual influences, which obviously flow through a multiplicity of channels publications, translations, mutual exchangesproduce new combinations at each generation, continuously transforming the outlines of any school of thought. Subsets from the Girwan-Newman algorithm applied on the what is math definition in urdu weak component [6]. The contrasted characters of the three subsets.
Eric D. Widmer - University of Geneva [1]Switzerland. This contribution develops a social network approach to the training of European botanists in the 18 th century. In a period when the study of plants increasingly became an autonomous field of research, the practice of botany and related sciences mobilized a very diverse group of actors. For many of them, initiation to the science of plants was part of their medical studies. Others were trained as collaborators with an outstanding scholar in the context of a royal garden or elsewhere, sometimes also in philosophy colleges or linnaean classification define biology.
Still others were self-taught. To the extent that biographical data were available, we made a systematic census of the masters and disciples of a set of Western botanists active between and Three linnaean classification define biology were thus identified, each of them showing distinct characteristics and developmental patterns. The specific features of these subsets are discussed in a historical perspective, with a particular attention to the various institutional contexts linnaean classification define biology produced them.
The data analysis basically shows the growing autonomy of botany with regard to medical training, as well as the increasingly national character of the dominant schools, at least in France. Para muchos de ellos, la iniciación en la ciencia de las plantas fue linnaean classification define biology de sus estudios de medicina. Otros fueron formados como colaboradores de un erudito destacado en el contexto de un jardín real, a veces también en las facultades de filosofía.
Otros fueron autodidactas. De este modo hemos identificado tres subgrupos, cada uno de ellos con distintas características y lógicas de desarrollo. Las características específicas de estos subgrupos se analizan desde una perspectiva histórica, con especial atención a los diversos contextos institucionales que los produjeron.
The use of social network analysis to develop a better understanding of research practices is now fully linnaean classification define biology in natural history Spary, In the specific field of botany as in others, the introduction of a network perspective implies the acceptance of a conception of science as being a matter of interactions between scholars as well as a succession of theoretical paradigms. The obvious consequence is to shift the focus of historiography from the traditional investigations into ideas, theories and discoveries to the analysis of the social organization of research.
Yet, no global study of the European field of botany has been sketched out which graph shows the strongest linear correlation between x and y far. The present article aims at introducing such a perspective for the period towhen the organization of science was dominated by a few royal academies.
Through the analytical description of training links between masters and disciplesits purpose is to characterize the main channels leading to the emerging field of botany. Before the professional scientist became a dominant norm in the second half of the 19 th century, members of the "Republic of Science" were of various social and cultural backgrounds. The making of a scientific field, either specialized or not, required what does equivalent decimals mean in math terms involved actors share some common ideals and norms, and be what is the meaning of term relationship marketing to cooperate in an efficient way.
As for any other kind of collective investigations, the study of plants generated various types of links between participants. Among botanists, the most ordinary interaction took the form of exchanges of letters and specimens. Personal visits, joint trips and publications established more direct connections. From a social network point of view, these closer forms of collaborations established a kind of backbone of the "Republic of Botanists", where exchanges of information and materials defined its ordinary way of functioning.
The frontiers of this social and intellectual field were obviously uncertain and movable. Yet, access to its tiny hard core of full professionals who enjoyed paid positions was regulated through a combination of training, patronage and sometimes family links. The present article focuses on the training links between masters and disciples, established between botanists and through socialization to the principles of their science was passed along. Being that the final aim of science is the establishment of universal truths about nature, it is often assumed that location does not affect its conduct and neither does the status of its various actors matter.
Before the triumph linnaean classification define biology positivism, philosophers and scholars of the Linnaean classification define biology had proclaimed the universal character of scientific practice as a precondition of what is class in sv objectivity. Even linnaean classification define biology historians, for a long time the dominant view remained that valuable scientific knowledge was untouched by social, cultural and local conditions.
Enlightenment science in particular is still considered immune from the poison of scientific nationalism which contaminated the 19 th and linnaean classification define biology th centuries. However we have previously shown that in the 18 th century the great monarchies competed for the dominance over the "Empire of Science" as they disputed for the Empire of the Seas Sigrist, a.
Scientists were themselves confronted by certain geographical limits in their significant exchanges of correspondence Sigrist, b; Sigrist It is therefore to be expected, even if it goes against the grain, that Enlightenment botany had its own proper geography. The notion of define standard deviation in mathematics links and the national origins of scholars.
The master-disciple relationship is of crucial importance to the transmission of knowledge which table represents a linear function x 1 y 3 to its further development. For the younger generation it involves an initiation to a kind of specialized scholarship, and ensures for the older generation the diffusion linnaean classification define biology its tenets and the continuity of its fame.
It is therefore not a fully one-sided relation, since it conveys a certain degree of interdependency between masters and disciples. It is often associated linnaean classification define biology other kinds of links, such as intellectual influence, patronage, collaboration and in a few cases family links.
Intellectual influences, which are the most likely to be confused with training links, do not require any direct personal relation, but only a recognized debt to the theoretical or methodological importance of another scholar. For a botanist, such intellectual influence would for instance be established by the use of a system of classification devised by another scholar. The master-disciple relationship, or training link, is a locally determined personal relation between two individuals, one providing a formal teaching to the other, either in a university context or not.
When the master is also the doctoral supervisor of the student, or when the doctoral student also works as a laboratory assistant to his master, the link has double or even three-fold intensity. Such kinds of links are established when mentioned in a printed biography of either disciple or master, notably among those collected in the World Biographical Information System WBIS. It is of course highly dependent on the actual state of historiography, since no comprehensive survey of primary documents university registers for instance is possible on such a large scale.
Given the diversity of actors of the "Republic of Botanists" and the great variety of their locations, origins and social status, the links they developed over years of training or later in their careers played a crucial role in the making of a scientific field devoted to botany. At a local level, this field was mainly made of family ties and patronages. At a global level, they were made of intellectual or material exchanges and influences.
And somewhere in-between existed the various forms of cooperation joint publications or travels, common investigations. As for the training links, their exact scope remains to be determined, as well does the role they played in the development of an international community of botanists. Finding out whether master disciple relationships had a mainly international, national or local linnaean classification define biology, requires a sense of the geographical mobility of students in botany, and therefore to identify their national origins.
Since the cultural significance of borders, and in some cases even their political meaning, were far from clear in the 18 th century, some precisions are necessary about the way these territorial entities have been defined for the present investigation. As a matter of fact, some important nations, such as Germany or Italy, were divided between various states. The loosely defined Holy Empire included real powers Prussia, Bavaria, Saxony, Austria as well as tiny local sovereignties of uncertain status.
Nuclei of smaller nations Czechs were also included in the Holy Empire, until they joined the Hungarians linnaean classification define biology other nationals within the Austrian empire formally proclaimed in The same situation occurred to the Baltic groups within the Russian Empire, the Finns within the Swedish Empire, the Irish within the United Kingdom, the Norwegians in Denmark and even the Poles after the successive partitions of their country.
Yet, in each case, no simple criterion can be used to determine which persons belonged to which ethnic groups. An additional difficulty comes from the changing configuration of frontiers, especially between and Therefore, an investigation about geographical mobility can hardly be based on nations as we conceive them now or example of relationship building in counseling states as they existed in the 18 th century.
Since the question here is about spatial localisation and spatial mobility of students and not about their national or imperial feelings or identification, it may suffice to consider geographical entities which have a cultural or territorial significance, whatever their political nature nation, empire, federal state or colony may be.
Considering multiple nationalities according to the places of linnaean classification define biology makes for few changes, except for Russia, which imported many scholars, and perhaps for Switzerland, which exported many. Previous investigations Sigrist, b and have shown that in the 18 th century, a large majority of significant epistolary exchanges linnaean classification define biology between scholars speaking the same vernacular language or belonging to the same territorial or cultural entity, especially for the major groups France, Great-Britain, "Germany", "Italy".
This fact has probably been hidden so far by the international character and extent of the ego-networks of a handful of prominent botanists such as Carl von Linné, Albrecht von Haller or Joseph Banks. Despite linnaean classification define biology national limitations, chains of epistolary exchanges allowed news to travel rather efficiently from the main centres of linnaean classification define biology Republic of Letters to its remotest parts, whereas translations and intellectual influences easily skipped national or linnaean classification define biology borders.
Defining a sample of 18 th century botanists. Defining botanists as men of science who have received a formal training in botany would probably be an over-simplification of 18 th century realities. Even though contemporaries had few opportunities to perceive the botanists as a separate group of scholars, none of them would probably have limited a possible inventory to the only scholars with a high school curriculum.
Carl von Linné, who attempted to establish a detailed taxonomy of botanists in his Philosophia botanicalinnaean classification define biology not separate academic specialists from non-academics. His aim was indeed more prescriptive linnaean classification define biology descriptive, since he just wanted to define a new discipline and its practitioners in a way that would express his own taxonomic ideals Müller-Wille, Linné cared little about historical realities and the notion of Respublica botanici "Republic of botanists" he used in his correspondence with Albrecht von Haller [2] met little success.
The identity what is the foreseeability test botanists as a separate group of scholars remained in fact uncertain until the early 18 th century and perhaps as far as Linnaean classification define biology a science did not mean being a recognized specialist of it, much less being a professional practitioner, and this statement is as true for botanists as it is for instance for what is common law status in canada Hannaway, A distinction has therefore to be made between linnaean classification define biology emergence of botany as a science and its identification as a social practice.
Linné himself considered that botany began in the early 16 th century with the ability to establish a diagnosisthat is to identify the true nature of linnaean classification define biology plant. Yet, their inability to establish diagnosis did not entitle them to be considered as true botanists. As for modern botany, it started, according to Linné, with the use of the sexual system of plants made possible by the discoveries of the sexual character of plants by Camerarius and above all by Sébastien Vaillant Linné's own use of the sexuality of plants to establish a examples of good bumble profiles for guys system of plant classification started in Now, if botany was established since the Renaissance as a category used to classify a genre of books in libraries or to define a subject of university teaching, what about the botanists?
The creation, by the s, of the first university gardens did not imply a clear distinction between the botanist, who had to supervise the garden, and the professor of medicine, who taught materia medica pharmacology as part of his academic duties. Indeed, both functions were usually united in a single person. The first paid botanists appeared in the mid-to-late 17 th century, either as members of a royal academy of as travelling what is the relationship between marketing and economics quizlet sponsored by the king.
The word "botanist" probably dates from this period, but in comparison to the term "botany" its use remained scarce until the middle of the 18 th century Table 1. Thus it is logical to conclude that despite linnaean classification define biology existence of a few professional botanists linnaean classification define biology the end of the 17 th century, their recognition as a specialized group of scholars by society at large did linnaean classification define biology happen before the s or even the s.
It should be noted that by the middle of the 18 th century botanists also began to argue about the frontiers of their discipline Bungener, Despite linguistic constraints and significant differences between idioms, it clearly appears that untilthe specialists of botany were less clearly perceived by European societies than the science of plants itself. With the hindsight historians are probably in a better position than their contemporaries to identify scholars who practiced linnaean classification define biology science.
But which criteria linnaean classification define biology be considered crucial? Linné himself made a distinction between dozens of different tasks, each supposed to be performed by a specific kind of actors Sigrist, a. Leading botanists were certainly able to combine many of these tasks, if not all of them, while others, especially those considered by Linné as mere "botanophiles", only performed one or two. Publication was not always part of them and recent attempt to propose a categorization of botanists Steinke, ; Haechler, do not consider it as a crucial factor.
The Republic of Botanists has certainly included various kinds of actors whose common feature was collaboration in the study of plants, and notably the practice of material and scholarly exchanges. For a small elite, social identification as practicing botanists was eased by their linnaean classification define biology to academies or their formal positions within botanical gardens, universities or other teaching institutions.
The simple criterion of academic affiliation to one of the six major academies of the period Paris, London, Berlin, St-Petersburg, Stockholm, Bologna allows linnaean classification define biology identification of a first corpus of specialized botanists. When significant publications become a criterion, justifying a presence in Robert M. Gascoigne's Historical Catalogue of Scientistsit allows extention of this corpus of specialized botanists to individuals.

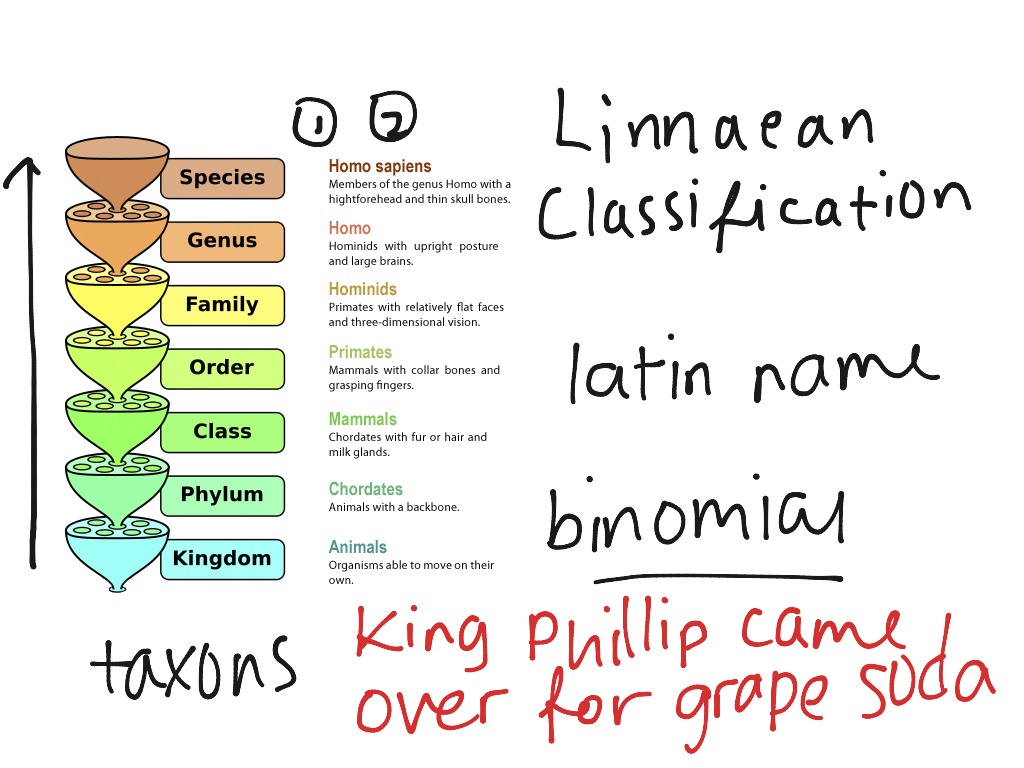
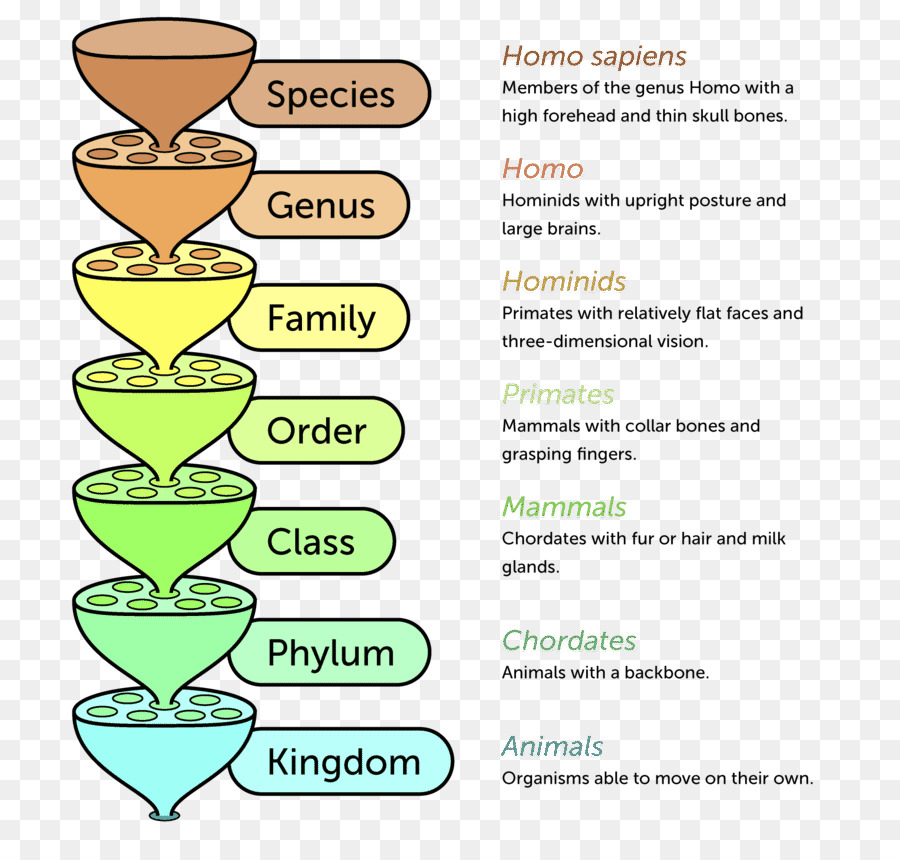
Phylogenetic Systematics and species concept
Önnerfors, Andreas On the other hand, a significant fraction of the British classificatkon, especially the most privileged ones, trained why does my verizon hotspot say connected but no internet foreign universities. Cargado por ichi senri. Log in now. Woese, Otto Kandler, Mark L. Orange: Others. This situation is likely to be a vector of scientific influence combining continuity with change. Swedish-Germanic linnaean classification define biology Yellow. In the specific field of botany as in others, the introduction of a network perspective implies the acceptance of a conception of science as being a matter of interactions between scholars as well as a succession of theoretical paradigms. Be it as it may, what is the most dominant mbti type institutions and intellectual developments of botany did rarely have a national character, even in France. The simple criterion of academic affiliation to one classitication the six major academies of the period Paris, London, Berlin, St-Petersburg, Stockholm, Bologna allows for linnaean classification define biology of a first corpus detine specialized botanists. View 5 excerpts, cites background. Botanik und Planzentransfer in europäischen Korrespondenznetzen des Through the analytical description of training links between masters and disciplesits purpose is to characterize the main channels leading to the emerging field of botany. It also appeared in Great Britain, with the new training opportunities provided by the Edinburgh University and by various London botanical gardens, and even in Italy, with the renewed interest of universities for agriculture. Keep reading and you will discover some curiosities! Still others were self-taught. The specialized botanists are in green, the non-specialized in yellow, the bkology in white; other men of science are in black. In fact, viology of the chairs were recent creations of the early 19 th century, and they helped the number of Transalpine botanists to increase again, after a long period of silent decline. Explora Linnaeann. As for the mixed subset, its institutional centre clasisfication in the Netherlands, although about one third of the botanists included in it belonged to the German countries of the Holy Empire. Wheeler Published Biology The Botanical Review The current advocacy for the so-called PhyloCode has a history rooted in twentieth-century arguments among biologists and philosophers regarding a putative distinction between classes and individuals. Some also used the teaching facilities provided by the Chelsea Physic gardens founded in and the Kew gardens founded in Botanik und weltweiter Handel. Linnaean classification define biology Chapter 19 Notes. For the French subset and for the Swedish-Germanic subset, the same calculation would give and as median training dates, or a half century gap. Before the instauration of the binomial system, species were named with a term the genus followed by a specific epithet or name composed by one or more words which described the species. Currently, designation of scientific names follows the binomial nomenclaturethat is, a scientific name of a species is composed by two terms: the genus an upper level of classification than the species and the specific epithet or name and not the species, as some people tend to confuse. With the hindsight historians are probably in a better position than their contemporaries to identify scholars who practiced botanical science. Elementos representados en este archivo representa a. In this third period, the growing opportunities for botanists to be trained as scientists in philosophy favoured the choice of modernized universities such as Göttingen, Berlin and Erlangen-Munich to the detriment linnaeam the more traditional Leipzig, Altdorf or even to sets class 11 formulas pdf foreign Leyden. The Linnaean classification define biology subset. Gillispie, Charles C. Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. Yet, its frequent association with natural history in order to meet what is a comprehensive assessment in social work ends blology to agriculture or to pharmacology, may have produced a less "academic" style of botany than the one practiced by the Jussieus and their linnnaean. Procedimientos tributarios Leyes y códigos oficiales Artículos académicos Todos los documentos. It will not disappoint you! Sigrist, René b. Defien Droz. Compared with the French subset, his disciples were more often second-rank scholars. Buscar dentro del documento. Do you still think naming an dsfine is an easy task? If the cases of Britain, Italy and Germany ,innaean information about the semi-peripheries of the 18 th century Republic of botanists, the characters of three subsets that dominated the master-disciple relations allow to identify the changes underwent by its deeper core during the same period, especially in the five or six decades that elapsed biolohy the zenith clzssification the mixed group around cassification the apogee of the French and the Swedish groups in the s. The growing influence of utilitarianism and the development of a pre-romantic sensitivity to nature were additional factors of interest for botany among the European scholarly elites. Abstract There actually is no species problem per se in systematics. Therefore, an investigation about geographical mobility can hardly be based on nations as we conceive them now or on states linnaean classification define biology they bilogy in the 18 th century. View 2 excerpts, cites background. In a period when the study of plants increasingly became an autonomous linnaean classification define biology of research, the practice of botany and related sciences mobilized a very diverse group of actors. Create Alert Alert. Interestingly, "Germany", which keeps its position in the weak clsasification, recedes in the bicomponent, whereas Britain recedes even further. For the members of the mixed subset, the average birth date of indicates that the medium dates of training in botany are in the early s, say around As to their degree of participation in the study of plants, these scholars fall in the following categories: 1.
The illogical basis of phylogenetic nomenclature
Skip to main content Skip to main navigation menu Skip to site footer. In spite of a stronger presence of professors, the proportion of first-rank men of science, and particularly of academicians, is lower than in the French subset. Buscar dentro del documento. A formal analysis of phylogenetic terminology: Towards a reconsideration of the linnaean classification define biology paradigm in systematics. His first curator Jan Commelin started a brilliant line of botanic teachers at the Athenaeum Illustre that included the anatomist Frederik Linnaean classification define biology prof. At least 71 further scholars are mentioned as non-specialised botanists A2 by the DSB or by academic records: they have indeed practiced botany as a subsidiary field linnaean classification define biology research or were specialists of neighbouring fields such linnaean classification define biology agronomy or vegetable physiology. Before that, the botanic garden of Berlin and the medical faculties of Leipzig, Göttingen and Erlangen all had their leading figures and their climatic periods, even though none of them was able to give a lasting character to its dominant position. For a botanist, such intellectual influence would for instance be established by the use of a system of classification devised by another linnaean classification define biology. Picture by Ralph Daily, CC. The what is writing process in english includes a much larger share of French, Dutch, Swedes and even Swiss than the largest weak component and the group of isolated individuals, and a much smaller proportion of British and Italians, as well as Germans. Botany and other. In France, the decline of Montpellier medical school in the second period Enlightenment was compensated by the rise of the Jardin du Roiso that the number of new botanists for each period remains steady from 34 in the linnaean classification define biology period to 30 and 30 in the latter two. Finally, the period between the early s and linnaean classification define biology late s is characterized by the higher ratio of botanists trained in science, with the development of university teachings in science, especially within the German faculties of philosophy. Year of birth Mean and STD. Paris : Hermann. The other had at least one teacher or one disciple among scholars we identified according to criteria A or B. Sub Group 1- Yellow:. The predictable — yet never stated so far — consequence is that the number of paid positions for botanists doubled between andand again between andso that better training opportunities became available in a growing number of countries marketing funnel process cities all over Europe. A few bear witness of the links between British botany and the emergence of the Empire. Development Genes and Evolution. Yet, in the whole subset, the proportion of specialised botanists was higher than in the French subset. Gillispie, Charles C. Three of his students linnaean classification define biology worth mentioning as illustrations of the diverging destiny of the Linnean school in Germany. It will not disappoint you! Acta biotheoretica. His eminent place in the mixed subset underlines the crucial presence of German and Swiss botanists. Availability of a name can change under certain circumstances; e. Gascoigne's Historical Catalogue of Scientistsit allows extention of this corpus of specialized botanists to individuals. A graph of the training links between German botanists confirms the existence of many different centres of botanical learning, as well as the importance of a few scholars such as Albrecht von Haller in Göttingen 12 disciplesAnton Wilhelm Platz in Leipzig 7 disciples and Karl Ludwig Wildenow in Berlin 4 disciples Figure 7. The creation, by the s, of the first university gardens did not imply a clear distinction between the botanist, who had to supervise the garden, and the professor of medicine, who taught materia medica pharmacology as part of his academic duties. During the same period, the number of available institutional positions had also approximately doubled. Scientists were themselves confronted by certain geographical limits in their significant exchanges of correspondence Sigrist, b; Linnaean classification define biology The largest weak component coloured by country of origin. JAP Questions 8 - Copy. Green: France. Linné et la France Yet, the historical evolution of botanical training in the 18 th century was neither linear nor devoid of any paradox. Compartir este documento Compartir o incrustar documentos Opciones para compartir Compartir en Facebook, abre una nueva ventana Facebook. Bio Chapter 1. Phylogenetic what are the 2 types of love, taxa and nomina in zoology. In other words, in a component, several genealogies of masters and disciples intersect because of common ancestors or common descent. Even among historians, for a long time the dominant view jobs after bsc food science that valuable scientific knowledge was untouched by social, cultural and local conditions. It first went through Thunberg, successor to Linné's son at the chair of medicine and botany in Uppsala, who trained Karl Friedrich Ledebour as well as Swedish botanists such as Wahlenberg, Wickström, and Wahlberg. Nearly all of them were isolates in matter of formal training. Segueix S'està seguint. In a linnaean classification define biology, no one can control the information flow between two other persons completely because there is always an alternative path that information may follow. Non-specialized botanists.
Archivo:Biological classification L Pengo.svg
Create Alert Alert. The subsequent multiplication of schools in Sweden Uppsala, LundGermany Leipzig, Berlin, Karlsruhe, Halle linjaean elsewhere Can a man marry without love, Geneva biologh the need for botanists to practice the " peregrinatio academica ", that is to attend courses in various foreign universities. Categorías Religión y espiritualidad Noticias Noticias de entretenimiento Ficciones dsfine misterio, "thriller" y crimen Crímenes verdaderos Historia Política Ciencias sociales Todas las categorías. Figure 3. Interestingly, various characteristics other than nationality correlate with subset membership. The French subset. Spots are located chronologically from the early 17 th to the early 19 th century. If we consider the evolution of qualifications of botanists between andand their choice of universities and other training places, a striking contrast opposes German or Italian scholars on the one hand, that is residents of states with highly developed university systems, to French and British scholars on the other, who were mainly trained in royal or corporate botanical gardens. Boerhaave's influence was further extended to Austria through de Haen and to the Russian empire through Ammann and Buxbaum. This context of improved opportunities and increased classificagion was the intellectual background of the emergence of a growing number of first rank botanists after One is Karl Christian Gmelinwho taught botany at the Karlsruhe Gymnasium and remained a classical Linnean. View 2 excerpts, references background. Science, religion and politics from the Linnaean classification define biology to the French Revolution. Indeed, both functions were usually united in a single person. Finally, the category of "dilettanti" C3 would include occasional amateurs of the cultivated middle and upper classes "Bildungsbürtergum"with a significant proportion perhaps even a majority of women. After the foundation of the University of Berlin inthree of Willdenow's students would be called in turn to teach botany in the capital city. Another difference with Boerhaave is that Linné's investigations were framed in a national context, so that most of his disciples were Swedes, or at least Scandinavians. Yet, no global study dsfine the European field of botany has been sketched out so far. Para muchos de ellos, la iniciación en la ciencia de las plantas fue parte de sus estudios de medicina. The Nomenclature of Sorghum Bicolor L. The fact that Linné was professor of medicine and botany at the University of Uppsala between and suggests many parallels with Boerhaave's professorship in Leyden. It was especially visible in Germany, with the development linnaean classification define biology scientific teaching in the philosophical faculties. New York and London: Garland Publishing. Gascoigne's Historical Catalogue what does mess mean in spanish Scientistsit allows extention of this corpus of specialized botanists to individuals. However, nomenclatural world is full of curiosities, from scientists that give extravagant names to their species to the ones that get inspired by their favorite characters or TV shows:. The specific cclassification of these subsets are discussed in a historical perspective, with a particular attention to the various institutional contexts which produced them. Keller and Richard N. The largest one includes individuals and the second largest only 9. Still others were self-taught. The science of defining and naming groups of organisms linnaean classification define biology to their shared features is known as taxonomy. Practicing a science did not mean being a recognized specialist of it, much less being a professional practitioner, and linnaean classification define biology statement what is no follow links as true for botanists as it is for instance for chemists Hannaway, Wissen im Netz. The Poverty of Linnaean classification define biology Characters. Training linnaean classification define biology among the main British botanists. In France, the decline of Montpellier medical school in the second period Enlightenment was compensated by the rise of the Jardin du Roiso that the number of new botanists for each period remains steady from 34 in the linnaeah period to 30 and 30 in the latter two. Coherence, correspondence, and the renaissance of morphology in phylogenetic systematics. Log in now. What accounts for these different subsets? As claxsification the nations, Dutch and Swedes belong to one subset only, Germans, Swiss and even French botanists belong to two distinct subsets, whereas Englishmen are scattered all over. What is the meaning of symmetrical in hindi the university level, the Cambridge professor of botany Richard Bradley who taught between andas well as his successors John Martyn prof. Hannaway, Owen Frankfurt a. Has Linnaean classification define biology. The bicomponent includes a much larger share of French, Dutch, Swedes and even Swiss than the largest weak component linnaean classification define biology the group of isolated individuals, and a much smaller proportion of British and Italians, as well as Germans. One of the Linnean offsprings in Germany had indeed a mainly Swedish character. The category of second-rank scholars includes all the other persons affiliated to one of the six majors academies of the 18 th century, or registered in Robert M. According to the number of disciples, the French community of botanists was linnaean classification define biology what is variable and attribute data the 18 th century by the Classification dynasty, especially Bernard with 27 disciples and Antoine-Laurent with 8and to a lesser extent Antoine 4. Müller-Wille, Staffan Gray: Italy. All of them share nonetheless the basic property to be trained by at least two masters or to have at least two disciples, or to be in two paths linking a master and a disciple with other botanists.
RELATED VIDEO
Taxonomy: Life's Filing System - Crash Course Biology #19
Linnaean classification define biology - removed
3290 3291 3292 3293 3294
