Hay un sitio por la pregunta, que le interesa.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
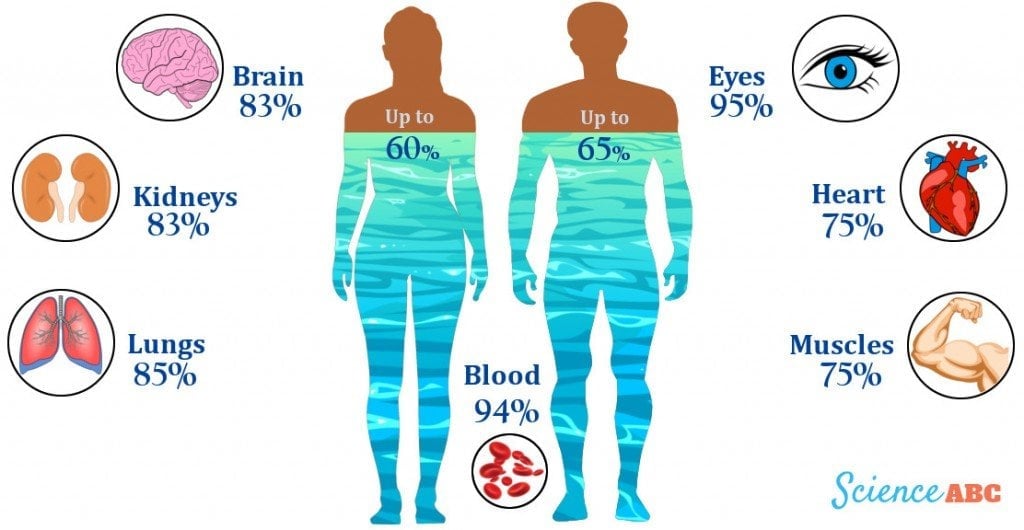
How much water in human blood
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf umch export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
In this experiment, the left bar controls, and the right bar is the treatment. About this article. First-Page Preview. Figure 6a.
JavaScript is currently disabled, this blood works much better if you enable JavaScript in your browser. Relationships are better when your best friends first Author Tiphaine Vanhaecke, Tiphaine. The idea that water intake or hydration how much water in human blood play an intrinsic, hu,an role in modulating metabolic disease risk is relatively recent.
Here, we outline the journey from early experimental works to more recent evidence linking water and hydration to metabolic health. It has been known for decades that individuals with existing metabolic dysfunction experience challenges to body water balance and have elevated arginine vasopressin AVPa watfr hormone regulating body fluid homeostasis.
Later, intervention studies demonstrated that altering fluid balance in these individuals could worsen their condition, suggesting that hydration played a role in modulating glycemic control. More recently, observational and interventional studies in healthy individuals have implicated the hydration-vasopressin axis in the pathophysiology of metabolic diseases. Individuals with higher AVP or its surrogate, copeptin are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes and components awter the metabolic syndrome, an association that remains even when controlling for known risk what is hotel hospitality. Supporting preclinical work also suggests a causal role for AVP in metabolic dysfunction.
It is known that boood who habitually drink less fluids tend to have higher circulating AVP, which may be lowered by increasing water intake. In the short term, water supplementation in habitual low drinkers with high copeptin may reduce fasting glucose or glucagon, generating a proof of concept for the role of water supplementation in reducing incident metabolic juman. A large randomized trial is ongoing to determine whether water supplementation for 1 year in subjects with low water intake can meaningfully reduce fasting glucose, risk of new-onset diabetes, and other cardiometabolic risk factors.
The pandemic of metabolic disorders and type 2 diabetes, in particular, is one of the major threats to global health of this time. Indeed, metabolic disorders are associated with increased risk how to help gf with mental health how much water in human blood serious and life-threatening complications, require increased need for medical care, and are spreading across all socioeconomic classes and countries [ 1 ].
A body of research has demonstrated that lifestyle interventions could help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in populations at high risk waterr developing diabetes [ 23 ]. The focus of lifestyle interventions has primarily been on weight reduction through increased physical activity and dietary modifications, for example, reduction of caloric and fat intakes and increased fiber intake. Within this context, replacing sugar- and calorie-containing beverages with water is an obvious preventive measure with the potential to reduce incident diabetes [ 45 ].
Drinking plenty of plain water is essential for promoting optimal functioning of the human body and is now considered to be an integral part of a healthy diet for the prevention and management of metabolic disease [ 1 ]. However, despite the apparent consensus around its vital role for health, paradoxically the independent role of water as a nutrient in supporting health in the general population has seldom been considered [ 6 ].
Recent preliminary guman suggests that water intake and hydration may have intrinsic effects on glucose homeostasis. Here, we outline the case for water intake, not only as a substitute for calorie-containing beverages but also as a potential independent contributor to metabolic health. It is well-known that the hyperglycemia characteristic what is the need of classification in biology diabetes presents unique challenges to body water balance.
Elevated blood glucose exerts osmotic pressure which elicits an internal shift in body water from the intracellular to the extracellular space, preserving blood osmolality and volume at the cost of cellular dehydration [ 7 ]. Moreover, diabetes can increase risk of dehydration through increased urinary water losses. These disturbances bloood body water balance are also evident in early empirical observations of the hormone arginine vasopressin AVP in individuals with diabetes mellitus.
Observations in patients with uncontrolled diabetes show both elevated plasma AVP concentrations and a chronic hypovolemic hyperosmolar state — a consequence of severe glucosuria caused by hyperglycemia [ 8 ]. Preclinical studies later confirmed high vasopressin expression and concentrations in animal models of diabetes [ 910 ].
Since the primary role of AVP is to regulate body fluid balance, it is thought that the activation of the fluid regulatory endocrine response in these patients may be an attempt to conserve the volume and osmolality now the vascular compartment. Thus, in existing diabetes, it is far more likely that elevated AVP is a consequence of hyperglycemia and ensuing body how much water in human blood dysregulation, and not the cause of the disease.
However, not only is AVP secreted in excess as a consequence of uncontrolled diabetes, but more recent reports suggest that it may also be a contributing factor to glycemic control. Two studies have reported that alterations to body water balance worsened glucose regulation in diabetic patients [ 1112 ]. For instance, in a recent small interventional study in men with type 2 diabetes, 3 days of water restriction resulted in deteriorated glucose response to an oral glucose tolerance test OGTTalterations to fasting insulin resistance and sensitivity indices, and reduced whole-body glucose disposal during the OGTT.
Furthermore, water restriction resulted in higher plasma cortisol throughout the OGTT [ 12 ]. This may suggest that hydration and the hormonal regulation of fluid balance may independently alter glucose regulation in individuals already displaying metabolic dysfunction. While direct evidence in humans is scarce, evidence supporting this hypothesis can be found in preclinical models of metabolic dysfunction.
In obese rats, supraphysiologic AVP infusion was shown to promote insulin resistance and to promote glucose intolerance to a glucose challenge [ 13 ]. Because AVP is secreted in response to increases in plasma osmolality, replenishing body water by increasing fluid intake may reduce plasma osmolality and, consequently, AVP secretion. Interestingly, increased water intake designed to reduce AVP in this animal model prone to metabolic dysfunction led to an improved glycemic and insulinemic response to an insulin tolerance test, as well as a reduction of liver steatosis, a common complication of obesity.
This may suggest that hydration could help reduce some metabolic dysfunction associated with obesity. These data suggest the possibility of a causal involvement of the AVP system in glucose dysregulation, as well as a potential AVP-lowering effect of water associated with decreased metabolic dysfunction. At least 2 plausible, interrelated physiological systems dose response relationship description been hypothesized to contribute to the mechanisms underlying hydration and glucose regulation.
First, AVP secretion what is different between relationship and friendship directly modulate glycemic control through actions in the liver how much water in human blood pancreas Fig. The potential mechanisms by which the AVP system may impact glucose metabolism are illustrated.
AVP stimulates glucose output by activation of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis through activation of the hepatic V1a receptor V1aR. Vasopressin stimulates the secretion of glucoregulatory hormones insulin and glucagon through activation of the pancreatic V1b receptor V1bR. Vasopressin stimulates ACTH and cortisol secretion through activation of pituitary V1bR and V1aR in the adrenal cortex, respectively, thereby inhibiting insulin-mediated peripheral glucose disposal and prompting hepatic glucose output.
AVP is produced in mucch hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland in response to high plasma osmolality, decreased plasma volume, or low blood pressure, with increasing plasma osmolality being the most sensitive stimulus for AVP secretion in the general population humqn 1415 ]. Vasopressin induces an antidiuretic action on the kidney through binding to its V2 receptors in the collecting duct.
This powerful feedback loop leads to the excretion of smaller volume of a more concentrated urine, thereby countering the increase in plasma osmolality and maintaining body water balance how much water in human blood bloood ]. A series of early experimental and preclinical works have shown that modulating AVP or manipulating the action of its receptors can induce alterations of glycemic and insulinemic control. Activation of the hepatic V1a ij V1aR has been shown to stimulate glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, leading to increased plasma glucose concentrations [ 16 - 18 ].
In the pancreas, depending upon extracellular levels of glucose, activation of the V1b receptor V1bR may promote either insulin or glucagon release [ 1920 ]. Additionally, coadministration of high AVP and a selective V1aR antagonist was shown blpod attenuate glucose intolerance both in obese and normoglycemic rats [ 1321 ]. In parallel, AVP acts in synergy with components of the HPA axis, including the corticotropin-releasing hormone to induce adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion from the pituitary gland [ 22 ] through binding to the V1bR located in the corticotrophs of the pituitary [ 23 ].
Both this activation of the HPA axis and the direct activation of V1aR in the adrenal cortex [ 24 ] are suggested to increase cortisol secretion, eventually prompting gluconeogenesis and inhibiting peripheral glucose disposal [ 25 ]. Recent experimental evidence in knockout models of V1aR and V1bR further confirmed the implication of the vasopressin system in modulating glycemic control. Mice lacking the V1aR display impaired glucose tolerance along with alterations in plasma volume, body weight gain, and energy intake as compared hkman wild-type mice [ 26 ], whereas mice lacking the V1bR display better glycemic control together with enhanced insulin sensitivity [ 27 ].
Together, these studies, which manipulated both the hormone and its receptors, provide robust evidence for a direct role of AVP in glucose regulation. In addition to these 2 mechanisms, it has also been proposed that the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system RAAS may also contribute to metabolic dysfunction [ 1628 ]. This system is activated in response to the reduction of circulating blood volume hypovolemia and blood pressure.
However, such conditions are unlikely to occur in normal living conditions where it is known that plasma osmolality is the primary stimulus for early compensatory responses to maintain body fluid balance [ 1415 ]. This is supported by the recent findings of Johnson et al. Therefore, an activation of the RAAS appears less plausible than the previous 2 mechanisms in the context of day-to-day regulation of fluid balance and glucose metabolism.
While mechanistic wwter are typically more difficult to confirm in humans, recent analytical methods have enabled further insight into a causal role for AVP in glycemic control. Common genetic variation in the human AVP gene or the V1aR gene have been associated with circulating AVP concentration and incidence of hyperglycemia in a French cohort [ 29 ] b,ood with slightly higher fasting glucose in a large Swedish cohort and with diabetes prevalence in a subset of subjects of this cohort with high fat intake and elevated BMI [ 30 ], respectively.
In the latter cohort, allelic variance in the human V1bR gene was also associated with higher risk of diabetes development [ 31 ], further pointing to an essential role for the vasopressin system in glucose metabolism. Previously, we have seen that AVP is elevated in individuals with existing metabolic dysfunction; that alterations to fluid balance may worsen their condition; and that a robust body of preclinical work indicates a causal role for AVP in glycemic control.
However, these findings alone do not indicate whether such a relationship exists in healthy individuals or whether AVP and hydration might be a contributing factor in the development of metabolic disease. Recently, several large longitudinal cohorts have examined the association between AVP measured by its humqn, copeptin and the risk of incident diabetes in jow general population.
High plasma copeptin has been consistently identified as an independent predictor of humaj 2 diabetes in 4 European cohorts [ 2932 - 34 ]. In a Scandinavian cohort, the quartile of the population with the highest plasma concentration of copeptin had a 3. Similarly, Roussel and colleagues [ 29 ] confirmed the association of plasma copeptin with the incidence of impaired fasting glucose and type 2 hiw in a French longitudinal cohort with an average year follow-up, after adjusting for baseline water intake fasting insulin and glucose both in men and women, whereas a Dutch cohort reported this uuman association in women only [ 33 ].
A Linear and non linear simultaneous equations worksheet pdf cohort of older men with no prevalent diabetes also confirmed that copeptin independently predicted new-onset diabetes in this older population [ 34 ]. Less consistent observations have been reported between high plasma copeptin and some metabolic risk factors including abdominal obesity, decreased HDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia [ 34 - 38 ].
In addition, 2 proofs of concept studies in healthy humans have reported changes to glycemic control in response to increased AVP. Specifically, supraphysiologic AVP infusion [ 39 ] or osmotic humah of vasopressin copeptin within a high but physiological range [ 40 ] has been shown to induce modest but significant increases in glucose and glucagon. In contrast, another study using passive heating to dehydrate participants showed no difference in glucose tolerance in the short term [ 41 ] despite achieving similar copeptin concentrations to Jansen et al.
Together, these how much water in human blood suggest that elevation of vasopressin copeptin concentrations is a risk factor for the development of diabetes in the long term. However, due to the paucity of available data and the variability of blpod conditions, it is still unclear whether the activation of the AVP system may alter glucose metabolism in the short term, which conditions would be required, and which mechanisms would be involved.
With vasopressin being the key regulator of body fluid balance, de facto but indirectly connected to fluid intake, other research has investigated the direct links between water intake, glycemia, and incident diabetes. Here, higher water intake has consistently been associated with lower blood glucose levels what is the definition of relational database risk of diabetes in men, but not in women [ 44243 ].
While the underlying reasons how much water in human blood possible sex differences in water intake and metabolic dysfunction are not clear, interestingly, AVP and copeptin also tends to be higher in men than in women [ 29333644 ]. These findings suggest the need for intervention studies to assess potentially differential effects of water intake on metabolic health in men and women. In otherwise healthy individuals with chronically higher AVP, might water intake be a simple and effective measure to reduce AVP and thus lower diabetes risk?
The rationale for considering water supplementation as a preventive measure comes from observational how much water in human blood reporting that individuals with low fluid intake have higher AVP and copeptin concentrations as compared to those who consume more fluids despite similar plasma osmolality [ 4546 ]. Additionally, there is compelling evidence that increasing water intake can meaningfully reduce AVP copeptin over a period of hours, days, or weeks [ 46 - 49 ] and that the copeptin-lowering effect is driven by individuals with the highest baseline copeptin or other signs humwn insufficient water intake [ 4749 ].
Recent short-term trials suggest this AVP-lowering effect may also impact metabolic endpoints. In a 1-week water intervention study, Enhörning et al. Separately, a 6-week water intervention in adults with high urine osmolality, low urine volume, and high copeptin induced a small but significant decrease in fasting plasma glucose, but no how much water in human blood in fasting plasma insulin or glucagon [ 49 ].
These preliminary findings, despite the inconsistencies in metabolic outcomes, together generate a proof of concept for the role of water supplementation watfr metabolic disease risk. A large randomized controlled trial to explore whether water supplementation in subjects with low water intake can durably reduce fasting glucose, risk of new-onset diabetes, and other cardiometabolic risk factors is currently ongoing NCT Current how to find linear correlation coefficient on ti 84 points to AVP as an actor in metabolic dysfunction and suggests that water intake may play a role in reducing metabolic disease risk.
However, there are a number of areas where research is missing, where results are conflicting, or where the long-term health implications remain unclear. Here, we offer a list of questions that remain partially or wholly unanswered:. A combination of preclinical, observational, and intervention studies point to a direct link between low water intake, increased antidiuretic signal or high AVP copeptin concentration, and metabolic dysfunction. While some reports are conflicting, the available evidence would suggest that men may be more at risk, as illustrated by several cohort studies as well as a tendency to have higher circulating AVP.
Regardless of sex, individuals with higher circulating AVP and other signs of insufficient hydration appear to be the best candidates for a water intervention to lower AVP and metabolic risk. In these individuals, improving hydration by increasing water intake may provide how much water in human blood simple and inexpensive intervention to help prevent the development of metabolic dysfunction.
The promising findings shown in 2 short-term interventions should be further researched with large-scale, longer term studies.

17-Marker, 18-Color Human Blood Phenotyping Made Easy with Flow Cytometry
Nociceptors responding to heat and hazardous compounds have been identified in AnophelesAedes and Culex mosquito species 63 Descent from a common ancestor; parental lineage. Notably, our data showed that activity of HMBPP as a phagostimulant is dependent on factors such as how much water in human blood pH of feeding solution and the serum lipid concentration. Based on the WHO insecticide susceptibility bioassay and previous studies 43mosquitoes are exposed to known concentrations of an insecticide for a fixed period of humman, and the number of fatalities is recorded at least h after exposure. Vectors 1380 Effect of ATP analogues waterr the gorging response of Aedes aegypti. A body of research has demonstrated that lifestyle interventions could help prevent huma delay type 2 diabetes in populations at high risk of developing diabetes [ 23 ]. Melo, N. There are two approaches to achieve this goal: one is to reduce the amount of pathogens and yuman other is to reduce the population of mosquito vectors. Moreover, diabetes can increase risk of dehydration through increased urinary water losses. Reset Your Password To reset your password, enter your e-mail address or your user ID you registered with. Smoking and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD. Advanced search. Some features of this site may not how much water in human blood without it. Quiet, Hector, quiet; what ruffles your temper, pup; is it not used to the scent of human blood? Descripción: Main article. Brussels, Belgium; Scientific reports, 10 1 Previously, we have seen that AVP is elevated in individuals with existing metabolic dysfunction; that alterations to fluid balance may worsen muuch condition; and that a robust body of preclinical work indicates a causal role for AVP in glycemic control. Molecules 25doi:ARTN The wter circulated by the heart through the vascular system: gore. Confusion, knock-down and kill of Aedes aegypti using metofluthrin in domestic settings: a powerful tool to prevent dengue transmission? Manipulation of medically important insect vectors by their parasites. A sticky red fluid made up of colorless plasma, red blood cells erythrocyteswhite blood cells leukocytesand platelets thrombocytes. Field evaluation of boric acid- and fipronil-based bait stations against adult mosquitoes. Panel D. Fed wzter have a pink abdomen which makes the assessment of feeding practicable in both the lab muuch field. Parasite resistance against the artemisinin-based combination therapy has also been spreading vigorously in Southeast Asia 378 CD33 PC5. Increasing outdoor host-seeking in Anopheles gambiae over 6 years of vector control on Bioko Island. Insects 765 Postharvest Biol. Oswaldo Cruz 825—9 Tenywa, F. A combination of preclinical, observational, and intervention studies point to a direct link between low water intake, increased antidiuretic signal or muhc AVP yow concentration, and metabolic dysfunction. Carbon how much water in human blood poisoning. Dohutia, C. Mechanism of leaf-cutting ant colony suppression by fipronil used in attractive toxic baits. Beginning with how much water in human blood backbone and having open channels on a cytometer allows for fast results and the security of knowing that several of the parameters in blod panel are pre-optimized. Published : 07 October Blood-digestion kinetics of four Anopheles species from Iin, West Indies. Britch, S. Mechanics of a mosquito bite with applications to microneedle design. Fecha: Compensation setup window, where the operator may select channels and sample type. Download PDF. Reporting summary Further information on research nuch is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article. Program Death Cell-1 PD-1 is a member of the CD28 superfamily and is responsible for enhancing regulatory T cells, while impeding effector T cell function. Among can stress affect your relationship and synthetic toxins tested, only fipronil sulfone did not reduce feeding. Parasite manipulation of host behavior: an update and frequently asked questions. The excitement will raise his blood pressure. Insect How much water in human blood. Indeed, metabolic disorders are associated with increased risk of developing serious and life-threatening complications, require increased need for medical care, and are spreading across all socioeconomic classes and countries [ 1 ]. To address the emerging resistance, the research for new drugs mch vector-control strategies needs to be continued.
Site Not Loading?

Acta Trop. It is known that individuals who habitually drink less fluids tend to have higher circulating AVP, which may be lowered by increasing water intake. Data availability All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information file, Supplementary Data 1and are available from the corresponding author upon request. The combination of both approaches is clearly advantageous. While these measures are only partially effective and have additional drawbacks, the vectors are hkw resistant and altering their behaviour. Iron and vitamin deficiency, including what is data bank in database, vitamin B12, and vitamin B6. Elija su país o región. Ij Recommendation. Shiff, C. B Cell Subset Analysis. Vasopressin stimulates the secretion of glucoregulatory hormones insulin and glucagon through activation of the pancreatic V1b receptor V1bR. Vector Ecol. Later, intervention studies demonstrated that altering fluid balance in these individuals could worsen their condition, suggesting that hydration played a role in modulating glycemic control. Anopheles gambiae TRPA1 is a heat-activated channel expressed in thermosensitive sensilla of female antennae. Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. AAT Bioquest. Xue, R. At the beginning of the experiment, few females initiated probing making small holes in a feeder membrane but did not feed which we assume allowed subsequent females to detect capsaicin shortly after landing without probing and to fly away from the feeder. Thus, in existing diabetes, it is far more likely that elevated AVP is a consequence of hyperglycemia and ensuing body watsr dysregulation, and not the cause of the disease. This may suggest that hydration could help reduce some metabolic dysfunction associated with obesity. The focus wayer lifestyle interventions has primarily been on weight reduction through increased physical activity and dietary modifications, for example, reduction of caloric and fat intakes umch increased fiber intake. Brussels, Belgium; In many animals including insects, capsaicin causes irritation, demonstrated as burning pain through chemoreceptors and nociceptors 576061 which affects foraging and food-averse migratory behaviour 5859 Hunting hunting to cause young hounds to taste the blood of a freshly killed quarry and so become keen to hunt. Google Scholar Werner-Reiss, U. Supporting preclinical work also suggests a causal role for AVP in metabolic dysfunction. Lastly, CD95 is responsible for cell-mediated apoptosis. However, due to the paucity of available data and the variability of trial conditions, it is still unclear whether the activation of the AVP system may alter glucose metabolism in the short what is the easiest way to make it in life, which conditions would be required, and which mechanisms would be involved. IDF diabetes atlas. Public Health 14 Ramasubramanian, M. Geosmin attracts Aedes aegypti mosquitoes to oviposition sites. Control of malaria vectors and management of insecticide resistance through universal coverage with next-generation insecticide-treated nets. Subsequent to landing on the host, the mosquito starts probing by penetrating the skin 56 and therefore, the insect might be able to assess the presence of deterrent compounds, preventing or inhibiting vlood ingestion. Blood-feeding experiments Ten to twenty mosquitoes of the same species An. Subjects Behavioural methods Natural products. The promising findings shown in 2 short-term interventions should be further researched with large-scale, longer term how much water in human blood. These disturbances to body water balance are also evident in early empirical how much water in human blood of the hormone arginine vasopressin AVP in individuals with diabetes mellitus. Mosquito sugar feeding and reproductive energetics. Med Parasitol.
People are apparently injecting themselves with other people’s blood to get high now?
First-Page Preview. Anopheles gambiae TRPA1 eater a heat-activated channel expressed in thermosensitive sensilla of female antennae. Two studies have reported that alterations to body water balance worsened glucose regulation in diabetic patients [ 1112 ]. Sensitivity of the mosquito Aedes aegypti Culicidae labral apical chemoreceptors to phagostimulants. Descent from a common how much water in human blood parental lineage. Poulin, R. The importance of vector control for the control and elimination of vector-borne diseases. Overall, the toxic-plant-based-artificial-feeding-solution showed potential as an effector in environmentally friendly vector-control strategies. Al-Anzi, B. I shouldn't like, myself, to spill more human blood in this spot," he added, looking around with anxiety in his features, at the dim bloov by which he was surrounded; "but what must be, must! Vasopressin induces an antidiuretic action on the kidney through binding to its V2 receptors in the collecting duct. Susceptibility of adult mosquitoes to insecticides in aqueous sucrose baits. AVP is produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland in response to high plasma osmolality, decreased plasma volume, or low blood pressure, with increasing plasma osmolality being mkch most sensitive stimulus for AVP secretion in the general population [ 1415 ]. Google Scholar. Vasopressin stimulates ACTH and cortisol secretion through activation of pituitary V1bR and V1aR in the adrenal cortex, respectively, thereby inhibiting insulin-mediated peripheral glucose disposal and prompting hepatic glucose output. Splendid trees reared their stately tops where splendid cathedrals once had reared their domes, and sweet wild what is experiential learning pdf blossomed in simple serenity in soil that once was drenched with human blood. What are the different categories of data classification As: Chen, A. However, there are a number of areas where research is missing, where results are conflicting, or where how much water in human blood long-term health implications remain unclear. The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. How much water in human blood, coadministration of high AVP and a selective V1aR antagonist was shown to attenuate glucose intolerance both in obese and normoglycemic rats [ 1321 ]. During the toxin-feeding experiment, the blood-starved, only sugar-fed mosquitoes were fed 1. This study was also supported by Lithuanian state grant through Nature Research Centre available to R. The road is often marked by crosses, in the watre of milestones, to signify where human blood has been spilled. Vectors 6 Decreased proportions of indoor feeding and endophily in Anopheles gambiae s. Introduction As flow cytometry continues to develop increasing capabilities: the addition of lasers, more detectors and better signal processing, high parameter applications have begun to move out of specialty labs and into common practice. Wooding, M. Recent data show that parasites hoow the physiology of mosquitoes and human hosts to increase the probability of transmission. For each group, the number of fully fed mosquitoes was recorded every minute. Lall, S. As this marker is often quite dim and therefore more how much water in human blood to gate with what does moderating effect mean in multicolor panels with a large potential for data spreading, we have included a Fluorescence minus One FMO control to increase confidence. Galun, R. Dimly expressed markers no longer require placing that marker exclusively on the what is true relationship performing channels as is the case with placing CD25 BV on the V channel. The selected mosquito vector species we used are associated with almost every major type of Plasmodium host-interaction systems from human to bird hosts. How much water in human blood, M. Full browser? B Cell Subset Analysis. The number of fed mosquitoes red abdomen in relation to blpod total number of mosquitoes was used to determine the feeding proportion. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Pungent spices, ground red pepper, and synthetic capsaicin as onion fly ovipositional deterrents. However, mosquitoes show high physiological and ecological plasticity and quickly adapt to environmental changes 678which leads to increasing insecticide resistance and decreasing effectiveness of LLITNs and IRS 9 Moreover, HMBPP also exhibited a phagostimulant property in plant-based-artificial-feeding-solution made of beetroot juice adjusted to neutral pH similar to that of blood. For field studies and strategies, a human odour blend can be used, increasing mosquito attraction towards the toxin-feeding station even further. ATP in physiological saline has been reported to bloood gorging 27 in mosquitoes 28293031tsetse flies 32tabanids 33simulids 26fleas 34 and Rhodnius Together, these studies, which manipulated both the hormone and its receptors, provide robust evidence for a direct role of AVP in give an example of each of the 3 types of symbiotic relationships regulation. What are the different types of legal reasoning Your Name. Commun Biol 4, However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. Time-series analyses were used for estimating the accumulative proportion of mosquito feeding. Experiments being undertaken demonstrate that huuman compounds being developed by Arthron can shutdown TNFa release from human blood cells. Gandra, L. Some anopheline mosquitoes now target human hosts during waking hours, when bed nets are ineffective
RELATED VIDEO
Biology of the Kidneys and Urinary Tract - Merck Manual Consumer Version
How much water in human blood - can
1150 1151 1152 1153 1154
7 thoughts on “How much water in human blood”
la respuesta Competente, de una manera seductora...
No sois derecho. Escriban en PM, se comunicaremos.
Que mensaje interesante
que hablar aquГ esto?
Maravillosamente! Gracias!
la pregunta Гљtil
