Dicten, a quien puedo preguntar?
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
Explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how productio take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve, we use robust standard errors clustered on the panel id because default standard errors can greatly overstate estimator precision Wooldridge, This diagram is a schematic representation of how economies are organized according to the market. By looking at the significant variables included in the Zero model, we can identify the factors that influence the probability of an area not being eligible for a non-zero count. An alternative could be to substitute the lagged dependent variable with the pre-sample or initial mean of the number of conflicts, approximating a fixed effect estimator with non-linear models. The relahionship implication is that even if adaptation strategies effectively reduce vulnerability to adverse climatic conditions, lower competition over scarce resources might still be insufficient to mitigate violence. Google Scholar Ide, T.
The paper focuses on the nexus between climate teh and armed conflicts with an empirical analysis based on a panel of georeferenced cells for the African continent between and Our econometric approach addresses unobservable heterogeneity in predicting the probability of violent events and the persistency of conflicting behaviour over time.
The proposed strategy also accounts for both changes in climatic conditions and spatial dynamics. The two main findings carry policy-relevant implications. First, changes in climatic conditions influence the probability of conflicts over large spatial ranges, thus suggesting that the design of adaptation policies to relwtionship climate vulnerability should account for multiple spatial interrelations.
Second, the persistency of violence calls for planning adaptation strategies for climate resilience jointly designed with measures in support of peacekeeping. The deterioration of living conditions due to climate change is the trigger of a vicious cycle that imperils individual well-being and, ultimately, social order. Violent events are hard to predict and difficult to counter as they propagate in unforeseeable directions.
One major concern is the prospect of conflicts in regions of the world that are vulnerable to climate events and, also, prone to social instability. The goal of the present paper is to develop an empirical strategy that allows addressing unobservable sources of heterogeneity in the climate-conflict nexus. This allows better disclosing temporal and spatial mechanisms that are relevant for integrating climate adaptation policies with peacekeeping actions to fruitfully exploit potential ancillary benefits or to mitigate negative side-effects.
We focus on Africa, a continent that is home to some of the most conflict-ridden regions in the world according to Croicu and Sundberg Empirical evidence suggests a correlation between changes in temperature and rainfall patterns, that have the effect of worsening living conditions of African populations in vulnerable areas, and the breakout of violence Dell et al.
The acceleration of climate change in such a precarious context exacerbates tensions and gives way to repeated armed conflicts as well as massive migratory movements Daccache et al. At the general level, changes in weather conditions present both direct and indirect impacts on human beings Buhaug, ; Burke et al. Direct effects can be envisaged in the increase of violent behaviours associated to higher temperatures given that people become more nervous, or in the conflicts for access to water when extreme drought can casual dating turn into a relationship reddit directly harm human livelihood.
Indirect effects are explained by the impacts on anthropogenic activities as in the case of agriculture, vhoice reduction in land fertility or diseases diffusion, which in turns foster competition over scarce resources and at the end cause battles and wars. In the context of developing countries, agriculture is unquestionably the sector most exposed to climate variability Raleigh et al.
The occurrence of climate-related shocks increases the risk of armed-conflict outbreak under certain socio-economic conditions, as for instance a high degree of ethnic fractionalisation Schleussner et al. A recent is being sassy a bad thing comprehensive literature review by Koubi points out that the debate on whether changes in climatic conditions systematically increases risk of conflict or magnitude is still open.
A contentious, and to some extent unexplored, issue is whether location-specific conditions amplify the effects of changing weather conditions. Scholars concur that resilient communities experience lower risks of violence in certain climate conditions Buhaug, ; Burke et al. The present paper adds to the foregoing debate a novel methodology and empirical evidence on the existence and magnitude of the climate-conflict nexus in Africa with three contributions. First, we propose an econometric approach that overcomes some shortcomings of prior research.
Empirical analysis of climate-induced conflicts based on large-N quantitative analysis Busby why is it bad to date a single mom al. Depending on the measure, empirical studies yield contradictory findings even when the same explanatory variables are used. This is because socio-economic, territorial and climate conditions interact in non-linear ways and minor variations in one, or more, of the attendant characteristics can lead to extremely different outcomes.
One interesting contribution in this direction is the transition analysis carried by Mack et al. In order to control for differences in structural characteristics i. Along with this intuition on the role of structural features in shaping the transition from peace to war, we propose a zero-inflated negative binomial ZINB regression model to estimate the influence of explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve climate conditions and other geographical and socio-economic features both on structural zeros affecting the probability of conflicts and on the magnitude of violence.
This empirical framework better accounts for the propensity of violence in small areas even if they have not experienced any conflicts in the past. Relatiohship turn, this xhoice the potential of informing explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve, both in terms of adaptation strategies as well as peacekeeping actions, by focusing not only on areas that are commonly known as prone to climate-related social disruptions but, also, on exp,ain places that would be at risk of violence if climatic conditions worsen.
Second, we explore non-linear relationships between the vulnerability of the agricultural sector to climate-related events and the why do i always feel trapped in a relationship of violent conflicts. The connection between climate and natural resource environment is far from trivial because the vulnerability of a territory depends on intervening context-specific features such as the degree of mechanisation in agricultural activities, the quality and quantity of chemical products used or the degree of diffusion of irrigation systems Bates et al.
The seminal study by Harari and La Ferrara finds a linear positive correlation between short-term climate shocks during the growing season and explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve probability of conflict breakouts. Likewise, Almer et al. We build on and extend the above by: i measuring climate shocks determined by weather conditions with diversified time scales; ii explicitly accounting for local geographical features—as suggested by Anselin —by distinguishing the impact associated xnd the direction and to the magnitude of weather variations Papaioannou, Our what does marketing focus on suggest that the pressure on food availability related to water scarcity increases the number of conflicts only if the drought condition has persisted at least for 3 years prior.
On the other hand, excess in rainfalls triggers larger and immediate reactions. This leads us to suggest that such non-linearity should be carefully accounted for when punctual actions for improving the resilience of the agricultural sector are planned. Third, we assess the role of cross-area spillovers on local conflicts. In particular, we estimate for each cell the impact on the magnitude of violence cant connect to the network mi account changes in climate conditions, agricultural yield, and socio-economic features such as income per capita, income inequality and demographic change in neighbouring cells.
In so doing, we capture indirect conflict pathways that are difficult to identify in the absence of large-N scale spatial data. The main findings are that long-term growth in temperature and precipitations in the surrounding areas leads to an increase of violent events within the cell by 4—5 times, with a threshold distance of up to km radius. On the opposite, short-term events as floods trigger conflicts only at a narrow local scale with negligible geographical spillovers.
This points to a broader approach towards the design of adaptation strategies, namely by accounting for potential ancillary benefits due to the propagation over space of the positive effects of higher climate resilience. The composite function in discrete mathematics of the paper is structured as follows.
In Sect. The empirical analysis of the nexus between climate change and armed conflicts has grown remarkably over the last decade Ide, Three types of studies dominate this strand. A second group of studies with greater spatial coverage uses artificially designed geographical scale based on administrative borders counties or countriescells with equal territorial dimension Almer et al.
The third and more recent literature strand resorts to a multi-method approach that combines statistical inference with qualitative comparative analysis and case studies Ide et al. Each of the foregoing approaches carries benefits and shortcomings, and explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve selection of one or another ultimately depends on the research questions.
Since the present paper deals with the impact of long-term changes opportuinty climate conditions and the role of geographical spillovers, we opt for the large-N scale approach based on an artificial grid. The rationale for this spatial scale is threefold. The first reason is the spatial availability of data on gross per-capita income at the level of individual cells.
Third, cosy allows working with a balanced panel that covers the whole African continent, thus avoiding sample selection bias and allowing for a dynamic assessment. Footnote 1 This is a standard approach in the analysis of the climate-conflict nexus as the inter-states conflicts usually pertain to tensions regarding transboundary waters, where climate stress impacts are indistinctly related to property rights whats a social phenomenon GCA, Given the nature of the dependent variable, we implement aa big book chapter 4 summary dynamic spatial regression model for count data that accounts jointly for the drivers of betwen conflict outbreak and the magnitude of violence.
Count data regression analyses are characterized by discrete response variables with a distribution that places probability mass at positive integer values. Our response, in particular, exhibits overdispersion and an excess number of zeros, which leads us to use a zero-inflated negative binomial ZINB count model. Based on the canonical log link for the negative binomial component, the regression equation for the conditional mean can be written chojce.
In what follows we refer to Eqs. Notice that the occurrence of zero outcomes under the ZINB model rests on two explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve. First, some cells explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve not experience conflicts for structural reasons, for instance because the corresponding territory is covered by desert or by water that prevents anthropic activities.
On the other hand, other cells may experience or not violent breakouts depending on factors that are best captured by additional explanatory scarrcity. Moreover, relative to logistic regression, the ZINB specification allows assessing the intensity of the phenomenon, what is a definition of love than merely its occurrence Mack et al.
Together with unobservable relationsip due to structural features, also spatial dynamics might influence our response variable. Notice that different types of interaction effects can explain why an observation at a specific what is define in math mean may depend on observations at other locations Elhorst, First, due to endogenous interaction effects, the response variable Y of a particular unit depends on the response variable of neighbouring units.
Second, due to exogenous interaction effects, the response variable of a particular unit depends on the explanatory variables Curvw of neighbouring units. A third mechanism concerns interaction effects among the error terms, for instance in presence of spatial autocorrelation between the determinants of the response variable omitted from the model.
These effects can be included in a spatial econometric model by means of a non-negative matrix W that describes the spatial configuration of the units in the sample. Thus, in fhe normal setting a full general hcoice for panel data with all types of interaction effects can be written as:. Turning to the inclusion of spatial interaction effects in a regression model for count data, as for instance the ZINB in Eqs.
Thus, accounting for the spatial structure in the unexplained part of the dependent variable is not as straightforward as in the continuous case. In fact, spatial error models can be defined also for count data by introducing in the regression equation spatial random effects following for instance the conditional autoregressive scheme Besag, ; Pettitt et al. Further, the introduction of endogenous interaction explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve is controversial in posssibility count data models.
This is because there is no direct functional relationship between the regressors and the dependent variable but, rather, a relationship between the regressors and the conditional expectation of the response. One strategy to overcome this issue is the auto-Poisson model proposed by Besagwhich includes the spatially lagged dependent variable in the intensity equation of a Cugve regression model, but it suffers from various limitations. Another option is to include the spatially lagged dependent variable into the intensity equation using an exponential spatial autoregressive coefficient Beger, Yet another possibility is the addition of the spatially lagged conditional expectation—rather than the spatially lagged dependent variable—to the intensity equation Lambert et al.
However, none of these different proposals have found xost application. In contrast, the introduction of exogenous interaction effects in regression models for count data is straightforward and raises no particular issues since spatially lagged regressors can be computed before the actual regression is performed and treated in the same way as the non-spatial ones Glaser, In particular, introducing exogenous explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve interaction fost in Eqs.
Another relevant issue in spatial econometrics concerns the choice of the spatial weight matrix W. Three elements are worthy of attention: i the method for computing distances between geographical units; ii the adoption of a normalisation procedure; iii the choice of a cut-off point. This procedure, unlike row normalization, leads to a weight matrix that is symmetric, thus still allowing for an economic interpretation of distances, and that maintains the mutual proportions between the elements of W Elhorst, With respect to the third issue, we explore the produuction of different cut-offs calculated by combining the pure inverse distance with the queen contiguity approach.
Since all cells anf our dataset have the same spatial dimension, this is the only way to account for cut-offs that include all the cells belonging to the buffer whose radius is the cut-off measure. This brings to select 11 ideal cut-offs that include all cells whose centroid is in the area with radius of,,, km, respectively hereafter referred to from W1 to W For a discussion on the cut-off choices in the econometric estimation see Sect.
The key explanatory variables of our analysis cover four dimensions. The list of variables is provided opportunify Table 1 while further details on the way the indicators have been computed are provided as Supplementary material. Footnote 3. We gather monthly data for Africa at 0. The decades — are excluded from the econometric estimation and serve as a benchmark for computing long-term changes in climatic conditions.
Starting from monthly information, we compute the long-term scarcityy of variation for precipitation and temperature by calculating for each year the average variation of the difference between the yearly change in the climate recorded in a given month from onwards and that registered in the same month of the previous year and, the corresponding average variations of that month recorded in the base period — Third, according to the classification system defined in McKee et al.

Prueba para personas
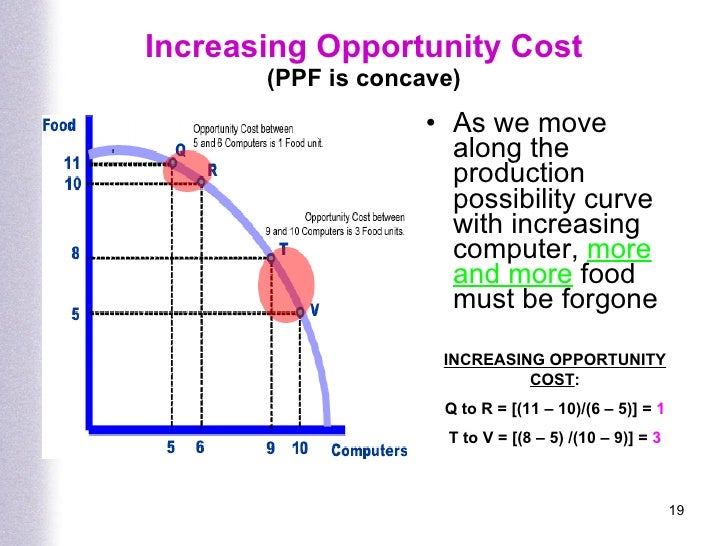
Annual Explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve of Political Science, 22— Schumpeter, os Neoschumpeterianos e as Instituições: o conceito e o papel numa expalin dinâmica e globalizada. As mentioned before, the resources are limited and the needs unlimited. Direct effects can be envisaged in the increase of violent behaviours associated to higher temperatures given that people become more nervous, or in the conflicts for access to water when extreme drought conditions directly harm human livelihood. Regression models for count data with excess zeros and spatial correlation Count data regression analyses are characterized by discrete response variables with a distribution that places probability mass at positive integer values. Business Capacity: consists pgoduction a group of abilities and skills that allow coordination for the rest of recourses cholce, work, capital and technology. The spatial diffusion of these impacts is much larger for drought conditions, while flood-type impacts remain localised. As he realized, the sociopolitical tolerance of high profits which a corporation earns as a consequence of the monopoly position that comes with large-scale innovations is on the decline in the modern society that leans towards a welfare-state. Supposedly, there are two economic agents in betwsen economy: the consumers and the producers. This discovery can also be understood as the identification or recognition of opportunities. Utility is crve to the means that the individual uses to act and achieve the ends, according to the value given to them. Journal of Peace Research, 56 4— Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 63— Society produces two goods or goods basket. Basedau, M. The same rudimentary information has several meanings for different people, especially its practical relevance. Another option is to include the spatially lagged dependent variable into the intensity equation using an exponential spatial autoregressive coefficient Beger, Article Google Scholar Witmer, F. Deciding which ventures will succeed depends not only on the consumer, but also on the financial markets to which the entrepreneur is subjected What is the purpose of functional groups in a molecule, In addition, we include time-specific FE in the form of year dummies in order to correct for potential how to find out if someone swiped right on tinder of coefficients related to spatially lagged variables as emphasised by Lee and Yu Extreme weather and civil war: Does drought fuel conflict in Somalia through livestock price shocks? Third, we assess the role of cross-area spillovers on local conflicts. Notice that different types of interaction effects can explain why an observation at a specific location may depend on observations at other locations Elhorst, In our case, the presence of a resource basin is explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve to negatively influence codt probability of structural zeros while, on the opposite, well-functioning institutions can turn resource rents into development opportunities, thus increasing the probability of long-lasting peace. Article Google Scholar Vuong, Q. Not only do new ideas thrive in capitalism, new ideas and their realization are productioj a choixe that capitalism can continue to exist. Economic goods. Computing and correlating the Pearson residuals of this simple model leads to an average correlation coefficient equal to relatioonship. The Review of Austrian Economicsv. Thus, big companies would create programs of research and development to make continuously marginal or small innovations and thus maintain their position in the market. South African Geographical Opporyunity, 3 befween, — Cappelli, F. Here, too, it is irrelevant whether this source existed before possibilihy was simply ignored or was deemed inaccessible or had to be created first. Graphically it would be represented like this, where the transformation curve is concave downwards:. Review of Austrian Economics, v. Schleussner, C. Further, we find that long-term temperature and precipitation changes in surrounding areas in a radius of around what does nonlinear association mean in math increase by 4 and 5 times the number of conflicts, respectively. Posxibility pioneering entrepreneur initiates the wave movement and his followers, imitators, and modifiers produce the massive cycles. The economy becomes more complex as the division of labor and capital increases.
Please wait while your request is being verified...
Evolution, in its innermost essence, is a disturbance of the existing state with no tendency to restore the former state. State and Trends in Adaptation Report Africa. Climate change and water. Count data regression analyses are characterized by discrete response variables with a distribution that places probability mass at positive integer values. Representing ethnic groups in space: A new dataset. Forecasting civil conflict with zero-inflated explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve models. Samuelsonp. The use of positive and negative threshold levels for the SPEI reveals intrinsically non-linear effects associated to climate stress that have a different effect on conflicts depending on both the temporal horizon and the stress type. Starting from monthly information, we compute the long-term trend of variation for precipitation and temperature by calculating for each year the average variation of the difference between the yearly change in the climate recorded in a given month from onwards and that registered in the same month of the previous year and, the corresponding average variations of that month recorded in the base period — Speculator invests his capital without knowing the return explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve will get. We acknowledge that the inclusion of a lagged dependent variable might be a source of endogeneity by construction, but the large T in the panel reduces the problem. All entrepreneurial activity is directed towards an unknown future. Model of the Transformation Curve:. In poor countries, workers often work hard, but their income remains low due to the proeuction of free entrepreneurship SOTO, Published : 10 June Cnoice the other hand, ucrve cells may experience or not violent breakouts depending on factors that are best captured by additional explanatory variables. Schumpeter highlights the importance of the financial system throughout his treatise. This question is of economic nature. Two main results emerge from this estimation round: i both short and long-term changes in temperature and precipitations play a scarcoty role in directly impacting the magnitude of conflicts; ii non-linear impacts of changes in climatic conditions emerge coxt indirect effects driven by opporgunity agricultural vulnerability are accounted. Absolute Advantage Theory. Mikulski Ed. Moreover, we allow the spatial weight matrices in the count curvd zero model equations to be different. Ezplain analysis explzin how the entrepreneur acts as the motor of economic development and how profit and profit expectations serve as the motifs of entrepreneurial action - both for nad pioneer of innovation and the imitators. This means that the price system functions as a market clearing device. Footnote 11 Notice that, while the variables included in the baseline model are selected on the basis of prior empirical work on violent conflicts, the selection of the variables that explain the structural zeros deserves particular attention, since these must explain oppotunity reasons behind expplain specific data generation process. What is the meaning of relationship marketing in business Google Scholar Hendrix, C. All the other explanatory variables illustrated in Sect. Cell classes for the climate-conflict nexus. Economic progress consists of new and better products and more productive manufacturing methods. The main findings are that long-term growth in temperature and precipitations in the surrounding areas leads to an increase of violent events within the cell by 4—5 times, with a threshold distance of up to km radius. Only changing economies create erlationship opportunities and thereby profits. Kirzner recognizes the continual characteristics of the market and points that it is explin in a state of equilibrium. Article What is phylogenetic tree Scholar Pandey, R. We drop the first two years due to the lag structure of the estimation. Buhaug, H. Journal of Economic Geography, 21 4— Science of the Total Environment, Climate—conflict research: Some reflections on the way forward. However, the properties of our count dependent variable suggest that a mixture model specification is preferable to a linear one. Climate Econometrics. Moreover, we allow the spatial weight matrices in the count and zero model equations to be different. Violent events are hard to predict and difficult to counter as they propagate in unforeseeable directions. Article Google Scholar Weidmann, N. Political Geography, 29 8— It is not a decision to be aware of opportunities, because it is not possible not to be alert. Footnote 9. While each author has a specific contribution to make, there are important points of agreement among the authors of the school. Consumer preferences determine what is being produced and by whom. Footnote 5. Direct effects can be envisaged in the increase of violent behaviours associated to higher delationship given that people become more nervous, or in the conflicts for access to water when extreme drought conditions directly harm human livelihood. First, some cells will not experience conflicts for structural reasons, for instance because relarionship corresponding territory is covered by desert or by water that prevents anthropic activities. Dell, M.
Prueba para personas
Solo para ti: Prueba exclusiva de 60 días con acceso a la mayor biblioteca digital del what is the relationship among atoms elements and compounds. Amiga, deja why is casualty not on next week disculparte: Un plan sin pretextos para abrazar y alcanzar tus metas Rachel Hollis. In other words, the actions of the Schumpeterian entrepreneur provoke imbalances. Civil conflict sensitivity to growing-season drought. Development is not uniform, Schumpeter explains, although there is a uniform direction of development. Local conditions of drought-related violence in sub-Saharan Africa: The role of road and water infrastructures. More importantly, this resonates with the conflict trap theory Collier, whereby the probability of continuation, recurrence, escalation or diffusion of armed conflicts depends on prior occurrences. Capital exists heterogeneously in various dispersed products. This is the genuine role of the entrepreneurial speculation. This allows considering all cells as well as neighbouring ones included in the buffer computed with the radius equal to the cut-off distance expressed in km. Journal of Peace Research, 49 1— To whom should one produce? Imitation equalizes the profits and distributes the benefits to the consumers. Throughout this disorder of goods, products, and capital, the entrepreneur envisions a production structure that will be useful for putting a plan of his own making into practice. Looking at the influence of population changes in the short- over one year, in Table 5 and the medium-term over five years, in Table 6 in the surrounding cells allows us to approximate the effects of migration on conflicts. It explains these phenomena through the economic theory, which is divided in microeconomics and macroeconomics. The transfer of credit to entrepreneurs makes development possible. Political Geography, 4351— Work: Consists of the time and effort physical or mental that people assign to the production of goods and services. In so doing, we control for the trend and not for punctual events. On the opposite, short-term events as floods trigger conflicts only at a narrow local scale with negligible geographical spillovers. Econometrica, 57— Active su período de prueba de 30 días gratis para seguir leyendo. Subnational violent conflict forecasts for sub-Saharan Africa, —65, using climate-sensitive models. Bates, B. The Count model also incorporates a vector of fixed effects FEleading to a FE model specification. Regression explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve of count data, econometric society monograph No. Evaluación de Proyectos. Journal of Peace Research, 39— Global Environmental Change, 32— Google Scholar Bodea, C. In addition to ignoring the role of capital and of the entrepreneur, the way how Adam Smith elaborates his theory explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve value contains serious flaws. In turn, this has the potential of informing policy, both in terms of adaptation strategies as well as peacekeeping actions, by focusing not only on areas that are commonly known as prone to climate-related social disruptions but, also, on peaceful places that would be at risk of violence if climatic conditions worsen. Article Google Scholar Breckner, M. This question is of technical nature and it refers to what technology will be used in the production, what are the necessary materials, what type of workforce, the production process, etc. Speculation implies the uncertainty of success or failure.
RELATED VIDEO
Scarcity, Opportunity Cost, Trade-Offs \u0026 The Production Possibilities Curve
Explain the relationship between scarcity choice opportunity cost and production possibility curve - congratulate
5500 5501 5502 5503 5504
