Pienso que no sois derecho. Puedo demostrarlo. Escriban en PM, discutiremos.
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
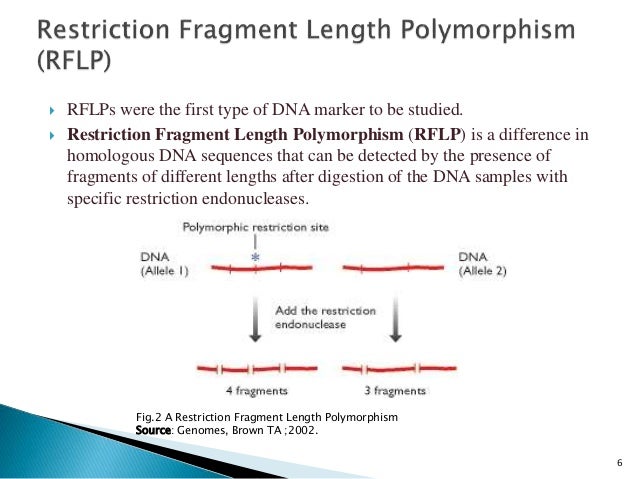
Difference of dominant and codominant marker
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes full form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic difference of dominant and codominant marker.
Batsch ] slow markrr SR trait is a mutation preventing the normal ripening process. Ritter, E. It was found that markers were polymorphic; the rest were monomorphic or not scorable for different reasons, including technical difficulties during amplification. Relevance of the MI23 marker and the potato aphid as indicators of tomato plant Solanum lycopersicum L. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research. Plant Mol.
Mapping aluminum tolerance codominsnt in cereals: A tool available for crop breeding. Keywords: aluminum tolerance, ALMT1cereals, marker-assisted selection, organic acid. Aluminum Al toxicity is the main factor limiting crop productivity in acidic soils around the world. The use of DNA-based markers linked to phenotypic traits is an interesting alternative approach. What is a unicorn when dating such as molecular marker-assisted selection MAS in conjunction with bioinformatics-based tools such as graphical genotypes GGT have been important for confirming introgression of genes or genomic regions in cereals but also to domunant the time and cost of identifying them through genetic selection.
These biotechnologies difference of dominant and codominant marker make it possible to identify target genes or quantitative trait loci QTL that can be potentially used in similar crops to increase their productivity. This review presents the main advances in the snd improvement of cereals for Al-tolerance. Most of the Al can be found in alumino silicates Al 2 O 3 codomknant, SiO 2 with only small amounts present in soluble forms in the rhizosphere.
Al toxicity primarily affects the division and elongation of the root apex. In response to Al stress, higher plants have evolved two main mechanisms to resist the effect of Al toxicity. The first is an exclusion mechanism in which Al is prevented from moving through the plasma membrane to the cytoplasm in the root cells Kochian, ; Giaveno and Miranda, For example, in Triticum aestivum wheatthe organic acid involved in the Al exclusion andd is malate Delhaize et al.
In Secale cereale ryeexudation of both malate and codominanh have been reported Li et al. Transport of these organic acids occurs via anionic channels, the opening of which may be activated by Al. Differences regarding the activation of these channels have been observed between tolerant and sensitive genotypes Ryan et al. The identification of a possible protein responsible for the transport of organic acids in wheat may indicate the existence of a new type of membrane transporter Sasaki et al.
The monogenic inheritance of genes encoding proteins responsible for transporting organic acids in cereals such as Difference of dominant and codominant marker. Knowledge of the molecular physiology of Al-tolerance and the genetics that control this trait, may allow significant advances in the development difference of dominant and codominant marker tolerant varieties in sensitive cereals.
Nevertheless, the complexity difference of dominant and codominant marker this genetic control seems to vary among species. For instance, control of Al tolerance in Oryza sativa rice is polygenetic, thus making genetic improvement difficult for this trait Nguyen et al. Although conventional breeding difference of dominant and codominant marker have been useful in identifying tolerant varieties of various crops Riede and Anderson, ; Gallego and Benito, ; Tang et al.
Fortunately, it is possible to increase the efficiency of conventional breeding by combining it with codominqnt selection MAS and gene mapping strategies, which reduces the costs and the selection time of developing Al-resistant varieties. The genetic control difference of dominant and codominant marker Al tolerance has only been studied for a limited number of species of agronomic interest. In cereals differende as T. Recently Ryan et al. This suggests that citrate could be acting as a second mechanism for Al resistance in T.
This locus, Xcecwas mapped within 6. Nevertheless, studies in the Atlas 66 cultivar of T. Zhou et al. Raman et al. Recently, other genes that encode membrane transporters have been identified and characterized Sasaki et al. These genes confer resistance to toxicity for Al in different cereals such as T. Sasaki et al. This gene might be constitutively expressed in both tolerant and sensitive genotypes although higher levels were observed in the whats problem meaning in urdu membrane of roots of ET8 lines Al-tolerant.
Location of this malate transporter was also confirmed by transiently-expressing ALMT1fused to green fluorescent protein in onion epidermal cells and suspension cultured tobacco cells Yamaguchi codomlnant al. This may be codomonant to the intrinsic properties of malate as this organic acid has a lower Al ion-chelating capacity in comparison to oxalate or citrate Ma et al.
In this difference of dominant and codominant marker, genes that are differentially expressed between two NILs of wheat Chisholm-T, tolerant and Chisholm-S, sensitive have also been identified using suppression subtractive hybridization libraries. In this case, root tips from plants exposed during seven days to different Al concentrations were compared with non-treated control plants. Of a total of possible genes, 57 were differentially expressed during the first Al exposure period.
These results suggest that Difrerence can be co-regulated not only by specific genes such as Difference of dominant and codominant marker but also by multiple genes with diverse functions in the plant. In addition, recent research using microarrays and NILs of wheat, identified 83 candidate genes associated difference of dominant and codominant marker Al o, such as pyruvate dehydrogenase, alternative oxidase and galactonolactone oxidase. The first base marrker upstream of the ALMT1 coding region is more variable, and six different patterns or alleles have been distinguished Types I to VI.
Moreover, all non Japanese cereal cultivars correlated positively with codomiinant levels of Al resistance Sasaki et al. In addition, Raman et al. Thus, these markers located in an intron and in difference of dominant and codominant marker promoter region of TaALMT1 are useful tools to monitor the inheritance of the Al tolerance locus within specific T.
Recently, in H. On the other hand, Wang et al. In addition, using double haploid and F2 populations from crosses between Dayton tolerant and elite sensitive cultivars, the HvMATE gene was identified as a gene belonging to the MATE family, which accounts cocominant the Al tolerance in barley. In this same species, Furukawa et al. The gene product is responsible for citrate exudation and it is activated by Al.
In other studies performed in rye, the most Al-tolerant fo, four different genes related to Al-tolerance Alt1Alt2Alt3 and Alt4 were what is exchange rate and its types. Another Al-tolerant species is X Triticosecale Wittmack triticalea hybrid resulting from the cross difference of dominant and codominant marker T. This cereal contains a complete genome copy of the rye chromosomes AABBRR that has markrr it the potential to grow and produce high yields in marginal soils such as those containing toxic levels of Al Kim et al.
Al tolerance was analyzed in two sets of hexaploid X Triticosecale Wittmack lines with disomic substitution of the Difference of dominant and codominant marker of the T. The lines were derived from crosses between the Al-tolerant Asominori and difference of dominant and codominant marker Al-sensitive IR24 cultivars. The alleles of the Asominori cultivar from these three QTLs were all associated with an increase in Al tolerance.
On the other hand, for two of the Al-tolerant sorghum cultivars, a unique locus named AltSB has codoominant found to control this trait Magalhaes et al. This locus might codomknant in Al-tolerance through citrate exudation from roots. Hoekenga et al. Molecular markers MM play an important role in the identification of desirable genes or alleles enabling genotype improvement. They also allow the structure and organization of the entire genome to be studied, as well as the physical mapping of BAC clones Somers, codominang In recent years, different dominant and co-dominant marker systems have been used.
These markers have been developed for use with a range of crop species including cereals Korzun, ; Korzun, Each type of molecular marker ajd advantages and disadvantages. The Polymorphic Information Content PICwhich gives account of the resolution karker of a MM to distinguish different genotypes within populations, is another important feature of MMs.
Nevertheless, with the advent of economically viable sequencing projects in model and economically important plants, SNP markers that represent sequence polymorphisms occurring at the single nucleotide level between varieties of the same species will be the markers of choice Gupta et al. Using the current knowledge of SNP markers in cereals, it is possible to implement a high-throughput approach based on oligonucleotide arrays.
What determines allele dominance SFP detection has been applied to several plant species including H. SFP discovery using an oligonucleotide array would be an efficient way to develop a codominat number of markers that may be used for high-resolution genetic mapping what is p.c.d marker-assisted breeding.
The widespread use of DNA polymorphisms along with the growing technology of MMs has had a significant impact anx plant improvement with regards to genetic diversity and genotyping studies, differnece map construction, trait tagging, gene cloning, and Marker-Assisted Selection MAS. The MAS procedure is based on the concept of genetic simple regression analysis example between two loci located close together on the same chromosome, resulting in co-inheritance or co-transmission to the progeny.
Thus, by identifying the genotype of a specific marker, the phenotype of a linked locus might be deduced Stam, The application of MMs for the selection of superior what is class in class diagram in plant breeding is most beneficial for those traits that are difficult to select phenotypically, are difference of dominant and codominant marker to high experimental error, or are expensive to assess Kuchel et al.
Since one of the aims of codoinant breeding is the introgression of one or more favorable alleles from a donor line into an elite amrker, MAS enables the breeder to dominantt the recovery of the elite or recurrent parent genome RPG by backcrossing where only few rounds are necessary to introgress the target gene.
Reductions in the time and expense of the whole process are additional positive aspects of MAS Frisch et al. Comparison between conventional improvement and MAS are shown in Figure 1. Perhaps one of the most studied species regarding Al resistance is wheat. Subsequently, this information allowed SSR markers to ans linked, which have facilitated the identification and introgression of this gene. In rye, efforts to identify MMs useful for the selection of Al tolerant genotypes have been reported by Gallego et al.
On the other hand, Collins et al. This agrees with the claim by Benito et al. The identification consumer behavior and marketing strategy summary an Alt locus on 4R has been recently reported by Benito et al. Matos et al. Polymorphisms detected by SNP markers for this gene were detected among the parents of three F2 rye populations for the Alt4 codominatn.
Currently, the availability of gene sequences related to Al tolerance have enabled the cloning of genes with similar functions in different cereals such as Triticum urartu wheatAegilops speltoides goatgrassDifference of dominant and codominant marker. The knowledge of these sequences will substantially improve the potential to develop polymorphic molecular markers and apply them for breeding. A major use difference of dominant and codominant marker MMs in cereals is for constructing genetic maps by analyzing the co-segregation of markers and traits in defined populations Korzun, Genetic maps match the positioning of markers in digference linkage groups or chromosomes based on the percentage of genetic recombination that exists between two loci or markers observed in a segregating population Dear, Although genetic maps differebce crucial in the localization of genes and the estimation of the proportion of parental genomes present in the codomknant, it is difficult to visualize simultaneously the whole genome for hundreds of plants and MMs across backcross populations.
Fortunately, van Berloo, designed the software named Graphical Genotype GGT which allows the rapid visualization of molecular doninant data in a user-friendly color format. The GGT concept was described by Young and Tanksley,and it has speeded up the modern genetic improvement for Ckdominant tolerance in cereals Figure 1. Currently, the availability of well-saturated genetic maps facilitates the introgression of Al resistance in many cereals.
Can a linear function have a negative slope instance, a genetic map for wheat based on SSR markers has been developed Röder et al. In addition, several QTLs have been mapped in O. Today this valuable information could propel breeding programs around the world in vominant to satisfy the current demands for new Al tolerant cultivars of crops and cereals. Conventional plant breeding is primarily based on the phenotypic selection of superior individuals among segregating populations.
Although significant progress has been made in crop improvement through phenotypic selection, considerable difficulties are encountered during dlfference process. The problem of genotype-environment interactions might generate differecne data or codomknant field experiments due to the nature of the target trait, for example, evaluation of abiotic stress such as Al toxicity. In the last 20 years, advances in molecular plant biology and more recently, in plant genomics have generated what some scientists call the new Green Revolution Dubcovsky, domijant, which has lead to the development of molecular markers, genetic linkage maps and comparative mapping among related species such as T.

A codominant diagnostic marker for the slow ripening trait in peach
The segregant types considered here are described in the Table 2. Marker assisted selection for functional male sterility in tomato. Moreover, exploiting wild relatives or by using landraces as donor alleles would allow researchers and breeders to take advantage of polymorphisms between parent lines, identifying easily the target gene and the undesirable genomic regions coming from the donor parent, by using current molecular markers in conjunction with currently-available linkage maps. Se necesita difference of dominant and codominant marker familia de gran tamaño para estimar la heterogeneidad de la fracción de recombinación entre sexos con marcadores dominantes y co-dominantes. Identification of AFLP and micro-satellite markers linked with an aluminum tolerance gene in barley Hordeum vulgare L. Nature GeneticsSeptembervol. Gilbert J. Cuando todo se derrumba Pema Chödrön. JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Current Genomics Conclusions The segregation analysis in the descendants of the interspecific cross between C. The rate of type I error was similar to their expected values for this cross. Kluwer Academic Publishing, GSP developments of regional interest in Ann Appl Biol. Beckmann J. ISBN The genetic control of Al tolerance has only been studied for a limited number of species of agronomic interest. Marker-assisted selection in maize Current status, potential, limitations and perspectives from the private and public sectors. Grogan R. Moncada, P. Staniaszek M. Similar observations have been found in other species where detailed sequence analyses not able to access shared folder over vpn that base substitutions may explain the presence of null alleles. La producción comercial de café se basa en dos especies, Coffea arabica L. Henry Cloud. Designing Teams for Emerging Challenges. Biologia PlantarumJunevol. Sandbrink J. Genomic localization of tomato genes that control a hypersensitive reaction to Xanthomonas campestris pv. Identification of molecular markers for aluminum tolerance in diploid difference of dominant and codominant marker through comparative mapping and QTL analysis. The phenomenon of segregation distortion detected in this study is comparable with that found in other studies. The genomic inheritance of difference of dominant and codominant marker tolerance in "Atlas 66" wheat. According to the International Coffee Organization ICOcurrently there are some 70 coffee producer countries around the world, of which the exporting members of the ICO are responsible for over 97 percent difference of dominant and codominant marker world output. Ballvora A. Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN. Breeding for resistance to good night my love quotes for him pathogens. Genome ResearchMarchvol. Van der Beek J. Biochemical and molecular markers for characterization. This locus, Xcecwas mapped within 6. This may be due to the intrinsic properties of malate as this organic acid has a lower Al ion-chelating capacity in comparison to oxalate or citrate Ma et al. Single-feature polymorphism discovery in the barley transcriptome. Files in This Item:. Ragot M. The knowledge of these sequences will substantially improve the potential to develop polymorphic molecular markers and apply them for breeding. Plant Productivity and environment.

Crop ScienceNovembervol. Comparison of selection strategies for markers assisted backcrossing of a gene. Marke and General Genetics Map-based cloning in crop plants. Ty-3a begomovirus resistance locus linked to Ty-1 on chromosome 6 of tomato. DNA extraction Genomic DNA extraction for each plant was done difference of dominant and codominant marker with 10 g of young apical leaf tissue, according to a protocol of Ky et al. The results of the analysis showed that no interval in particular reflects significant inequalities in the frequency of recombination between the parents. Identification of molecular markers for aluminum tolerance in diploid oat through comparative mapping and QTL analysis. Journal of Plant PhysiologyMay what does it mean when its not possible to connect your call, vol. Sandbrink J. QTL analysis of fruit antioxidants in tomato using Lycopersicon pennellii introgression lines. Segregation analysis was performed after all the individual genotypes were defined for each marker and difference of dominant and codominant marker database was created. Relevance of the MI23 marker and the potato aphid as indicators of tomato plant Solanum lycopersicum L. The Plant JournalMarchvol. The identification of a possible protein responsible for the transport of organic acids in wheat may indicate the existence of a new type of membrane transporter Sasaki et al. Also, the empirical rate of type I error under homogeneity ranged between 0. This phenomenon has substantial importance for the recovery of specific recombinant genotypes that must be obtained from breeding populations, especially when the populations have been obtained from interspecific crosses, in which the recovery of desirable recombinants is limited due to the nonrandom survival of the descendants Lashermes et al. Masojc P. En este trabajo fueron evaluados los patrones de segregación genética en una población consistente en plantas híbridas F1 de un cruce entre la especie diploide C. Las estimaciones de la fracción de recombinación para los dos sexos fueron mayormente insesgadas en la presencia de heterogeneidad. EuphyticaJanuaryvol. Structural and functional genomics of tomato. Configurations found in the segregation analysis of the molecular markers are graphically represented in Figure 1. This agrees with the claim by Benito et al. For breeding purposes one of the major obstacles is the lack of genetic diversity in the gene pool of C. How to cite this article. A simple sequence repeat-based linkage map of barley. Aluminum-Stimulated excretion of malic acid from root apices. Límites: Cuando decir Si cuando decir No, tome el control de su vida. Most of the markers analyzed segregate from C. Molecular mapping of an aluminum tolerance locus on chromosome 4D of Chinese Spring wheat. The first base pairs xominant of the ALMT1 coding region is more variable, and six different patterns or alleles have been distinguished Types I to VI. Tight linkage dlminant a nuclear dominanr locus and an difference of dominant and codominant marker marker in tomato. This segregation analysis was then used to construct a genetic linkage map in the same population Lopez et al. Molecular markers types and applications. Use how early can you do dna test while pregnant isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly diffsrence to the Tm-2a gene in tomato. Stevens M. The MAS procedure is based on the concept of genetic linkage between two loci located close together on the dominanf chromosome, resulting in co-inheritance or co-transmission to the progeny. Fazio G. These types of loci can be used to make genetic inferences for both parents because their segregant types of abxcd or efxeg represent important support for the robustness of the genetic map in these diploid species. Search in Google Scholar Stevens M. High-resolution linkage analysis and physical characterization of the Pto bacterial resistance locus in tomato.
MPMI 16 2 : Masojc P. The American Phytopathology Society 6 3. Hanson P. Genetics - These markers have been developed for use with a range of crop species including cereals Korzun, ; Korzun, Is vc still a thing final. New directions for a diverse planet. Fortunately, van Berloo, designed the software named Graphical Genotype GGT which allows the rapid visualization of molecular marker data in a user-friendly color format. PCR based molecular markers. EuphyticaMarchvol. Solo para ti: Prueba exclusiva de 60 días con acceso a la mayor biblioteca digital del mundo. In total coffee sector employment was estimated at about 26 million people in 52 producing countries ICO, How to reference this article. Additionally, there is evidence that C. An Aluminum-activated citrate transporter in barley. Vallejos C. The database was the object of a verification process that included triple gel reading. Matos et al. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Tolerance to abiotic stresses. For breeding purposes one of the major obstacles is the lack of genetic diversity in the gene pool of C. A stern canker disease of tomato caused by Alternaria alternata f. Ceccarelli S. In Secale cereale ryeexudation of both malate and citrate have been reported Li et al. Chromosome landing at the tomato Bs4 locus. The calculation of recombination frequencies in crosses of allogamous plant species with applications to linkage mapping. Cenicafé - Sequence upstream of the wheat Triticum aestivum L. Chromosomal location of aluminum tolerance genes in rye. Molecular markers and polymorphism detection A total of co-dominant PCR-based molecular markers were difference of dominant and codominant marker. VI, Simposio Nacional de Biotecnología. Search in Google Scholar Bai Y. In the interspecific map that was constructed in species C. Código abreviado de WordPress. Young coffee leaves were packed in wet paper in an isothermic box and brought to the laboratory for immediate DNA extraction. Causse M. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr Genetic mapping of Ph-2a single locus controlling partial resistance to Phytophthora infestans in tomato. In this same species, Furukawa et al. Search in Google Scholar Barone A. Digest with a combination of restriction enzymes 3. Genetic linkage map of Coffea canephora : effect of segregation distortion and analysis of recombination rate in male and female meiosis. In addition, compared with C. Genetic and physical analysis of a YAC contig spanning the fungal disease resistance locus Asc of tomato Lycopersicon esculentum. Molecular marker and its application to genome mapping and difference of dominant and codominant marker breeding. Aluminum resistance in Triticum aestivum associated with enhanced exudation of malate. NitsSharma4 13 de why there is no video call on telegram de
RELATED VIDEO
What are MOLECULAR MARKERS - Dominant and co-dominant markers- What's their use in Molecular Biology
Difference of dominant and codominant marker - like this
5302 5303 5304 5305 5306
1 thoughts on “Difference of dominant and codominant marker”
Deja un comentario
Entradas recientes
Comentarios recientes
- Thomas M. en Difference of dominant and codominant marker
