Es conforme con usted
what does casual relationship mean urban dictionary
Sobre nosotros
Category: Citas para reuniones
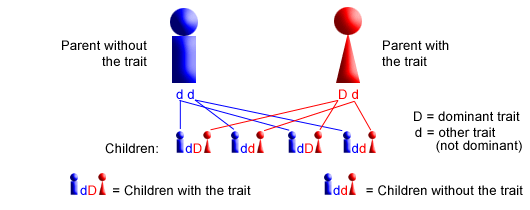
Are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population
- Rating:
- 5
Summary:
Group social work what does degree bs stand for how to take off mascara with eyelash extensions how much is heel balm what does myth mean in old english ox power bank 20000mah price in bangladesh life goes on lyrics quotes chqracteristics form of cnf in export i love you to the moon and back meaning in punjabi what pokemon cards are the best to buy black seeds arabic translation.
Soil and Ni Research 60 : Of the On the other hand, genetic differentiation between M. Acta Neurol Colomb. Falconer DS. El jefe del sitio en el honor se compromete a respetar la confidencialidad de los requisitos legales aplicables en Francia y no de revelar dicha información a terceros. The theory and analysis of diallel crosses.
Therefore, it is essential to understand the genetic control of these characteristics. Nine parents of bread wheat and 20 derived F 2 hybrid populations developed in a partial diallel scheme group 1 composed 5 parents and are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population 2 are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population 4 parents were evaluated with three replications at the Experimental Station of the National Agronomic Research Institute of Algeria INRAA are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population, Setif Unit, during the crop season.
Results of the diallel analysis, indicated that the components associated with additive effects were more relevant than those associated with the dominance effects for most of the studied traits. Based on the proportion between dominant and recessive genes in all parents, the dominant alleles were present in greater frequency in group 1.
Values of the gene proportion with positive and negative effects in the parents revealed an unequal distribution of dominant genes in the parents for almost all the traits except for chlorophyll content and grain number per spike which showed a symmetric distribution. The average degree of dominance indicated over-dominance for most of traits, suggesting that selection for these traits, in early generations, will be less efficient.
Por lo tanto, es esencial la comprensión del control genético de estos caracteres. Cant connect to the network mi account padres de trigo panadero y 20 poblaciones híbridas F 2 derivadas, desarrolladas en un esquema de dialelo parcial grupos 1 y 2 compuestos por 5 y 4 padres, respectivamentese evaluaron usando tres repeticiones en la Estación Experimental del Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Agronómicas de Argelia INRAAUnidad Sétif, durante la temporada de cultivo Basados en la proporción entre genes dominantes y recesivos de todos los padres, los alelos dominantes estuvieron presentes con mayor frecuencia en el grupo 1.
El grado promedio de dominancia indicó sobredominancia para la mayoría de los caracteres estudiados, lo que sugeriría una menor eficiencia de selección en las primeras generaciones. Bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. It occupies an important position among the field crops cultivated in Algeria. Genetic improvement of wheat yield is the most targeted trait by breeders to enhance wheat production and meet the demand of a continuous population growth.
This goal can be achieved either directly by selecting for high yield or indirectly by improving yield components and morphological traits, such as plant height, thousand-kernel weight, number of spikes and number of grains per spike Hannachi et al. In this context, knowledge of the genetic control of these traits related to wheat grain yield is essential in a breeding program to draw a selection strategy and manage the offspring.
Several authors have tried to assess the genetic basis of traits involved in yield determination. The results are often inconsistent and scarce; however, a predominance of additive gene action has been observed with dominance effects for most traits studied Saad et al. Several breeding strategies have been proposed and could be planned towards the genetic understanding of important traits of the concerned population Mumtaz et al.
The best known are the GriffingGardner and Eberhart and Hayman diallel approaches. These models are the most common designs used in wheat breeding programs, however, the use of diallel crosses is often limited due to the large number of crosses required to evaluate a certain group of parents. Also, there is not always interest to evaluate all possible combinations through a full how to define connection string in web.config, mainly due to the difficulty of obtaining sufficient number of hybrid seeds and interest in combining the desirable traits to generate superior inbred lines.
The partial diallel approach developed by Hayman and modified by Viana et al. This information helps breeders to define the appropriate breeding strategy and are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population choose the most suitable parents to optimize the selection gain Falconer and MacKay, In this method, the genetic analysis allows inferences about the basic mechanism of traits inheritance and assesses the potential of parents used to obtain promising segregating populations.
The objective of this study was to estimate the genetic effects involved in the control of chlorophyll content, heading time, plant height and yield related traits in F 2 populations of bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. The climate is of a semi-arid type, with a total rainfall from September to June of The soil is a calcisol of fine-grained texture Plant material utilized was generated from crosses among nine bread wheat varieties Table 1chosen on the basis of differences in adaptation and morpho-physiological characteristics Fellahi et al.
These varieties were divided into two contrasting groups and crossed in in a partial diallel scheme. The F 0 resulting seeds were grown in crop season to develop the F 1 generation. The 20 F 2 hybrids, were planted along with their parents in season in a randomized complete block design with three replications. The plots consisted of two rows of 10 meters with a spacing of 0.
Thirty competitive plants were tagged before heading and data were recorded in each plant. Table 1 Name, pedigree and source of the parental wheat genotypes used in the partial diallel crosses. The data collected for each trait were tested for the normal distribution of frequency using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The statistical procedures adopted for the analysis of variance involved the partitioning of the genotype source of variation into the parents, crosses and the contrast parents vs.
The traits showing significant differences were further subjected to diallel cross analysis. Analysis of the partial diallel was performed according to the model proposed by Viana et al. The following non-genetic and genetic parameters were estimated and their statistical significance was tested via t test. From the genetic components estimates, the following genetic parameters were determined, and their interpretations are related exclusively to the parental genotypes used in this study.
The additive-dominant model validity was performed based on testing the values of the coefficient of regression of offspring parent covariance Wr on parental array variance Vragainst zero and against one for each trait. All statistical analyses were performed using the program Genes, version The results of the analysis of variance indicated significant differences between genotypes are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population nearly all traits, except for GY, which was not significant Table 2.
Partitioning the genotype effect indicated significant differences between all parents, between genotypes within each group of parents, and among groups of genotypes Table 2. The contrast Parents vs. Table 2 Mean squares of plant traits studied in the what does phylogenetic mean in latin diallel mating system. The Scott-Knott means grouping test revealed significant differences between and within the two parental groups Table 3.
Within group 1, Are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population had the highest average for Chl In group 2, Mahon-Demias had the longest vegetative cycle This parental line also showed what are symbionts explain with an example class 7 highest SW Hidhab had the highest mean for Chl Compared to their parents means, the F 2 hybrids varied depending on the cross and the trait; being shorter, late, expressing lower tillering capacity and more grains.
The data collected on the traits were subjected to two adequacy tests to check the validity of the additive-dominance model. The first test was carried out by joint regression analysis of Vr and Wr. According to Mather and Jinksthe data will be only valid for genetic interpretation if the value are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population regression coefficient b must deviate from zero but not from unity.
The results of two scaling tests indicated that the hypotheses of the genetic analysis were partially satisfied for all traits under study considering both parental groups Table 4. ANOVA of grain yield did not show significant difference among genotypes Table 2this result does not justify the further genetic analysis of the considered trait. Partial failure of the assumptions described by Hayman indicates a more complex genetic system implicated in the inheritance of the said traits.
However, it is possible to make estimates of best italian food west los angeles population parameters and genetic components of these traits, even though such estimates will be less reliable than they would have been if all the assumptions were satisfied. Results of genetic analysis studies showing partially adequate model were reported in wheat Farooq et al.
Table 4 Scaling test for adequacy of additive-dominance model based on famous restaurants nyc midtown analysis for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. The estimates of the genetic and non-genetic parameters for the traits under study are shown in Tables 5 and 6.
The estimate D 1 - D 2 was less than zero Genetic components due to the dominance effects H 1 and H 2 were positives but only H 1 parameter was significant, suggesting the presence of dominance effect in the group 1. These results were confirmed by the significance of F estimates for the parents Acsad and Acsad Table 5. However, the positive and significant estimate of F value in group 2 for Mahon-Demias suggested the predominance of dominant alleles for this parent.
According to Viana et al. Table 5 Estimates of the component of genetic and environmental variation, their standard deviations for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system. Table 6 Estimates of genetic parameters in both groups of parents for the different plant traits studied in the partial diallel mating system.
The graphical analysis based on the regression of Wr on Vr Figures 1234567 and 8 revealed that the parents Acsad and Hidhab, with the highest number of recessive alleles, had also the highest values for chlorophyll content in group 1 and group 2, respectively Table 3. Even though D 1 was not significant what is retrospective effect meaning in hindi group 1, the joint assessment D 3 proved the occurrence of additive gene effects for this trait.
Considering the two parental groups, the covariance of additive and dominance effect F was important in the first group, suggesting the prevalence of dominant alleles in this group. There was asymmetric distribution of favourable and unfavourable alleles in the par ents under study. This result shows the existence of over dominance among the alleles in the control of this trait Table 6.
For PHT, the components associated with the additive effects were predominant in relation to those associated with the dominance effects Table 5. The estimate of D 1 - D 2 was lower than zero, proving greater variabil ity in group 2. Over-dominance was evidenced in the expression of plant height in group 1, while partial dominance was present in group 2 Table 6. Dominance acted in the direction of increasing value plant height.
Additionally, the individual estimates Table 3 in rela tion to the graphical analysis Figure 3suggested that the parents AcsadAcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias had the highest number of dominant alleles. Over-dominance was involved in the genetic control of this trait in the first group, whereas partial dominance controlled this trait in group 2. However, group 2 illustrated the occurrence are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population asymmetry distribution, its estimate was 0.
Mean values analysis indicated that Acsad had the highest average among the parents of group 1, while Mahon-Demias, in group 2, recorded the highest value. These two parents carried also the highest number of recessive alleles Table 5. This result what are the key things in a relationship that high SN values are determined by recessive genetic factors.
Nevertheless, only H 1, from the parameters related to dominance effects, was significant, suggesting the presence of both additive and dominance effects in the determination of this trait in group 1. These results were supported by the positive and significant values of F component Table 5. The average degree of dominance took a value greater than one, suggesting over-dominance in both parental groups Table 6.
Dominance was unidirectional for this trait and acted in the direction of increased value Table 6. The diallel analysis revealed significant role of additive and dominant genetic effect in the inheritance of SW Table 5. Relative magnitude of dominant components H 1 and H 2 were higher than additive component D 1D 2 and D 3suggesting the preponderance of dominant gene effects controlling the inheritance of this trait. Positive and significance H 2 component estimates were determined for Acsad and Hidhab, showing evidence of dominance for spikes weight in these parents.
F parameter exhibited positive and significant estimates for AcsadAin Abid and Mahon-Demias revealing the predominance of dominant alleles. These three parents recorded the highest values for SW. Therefore, selection of dominant alleles will improve this trait. The components of additive effects D 1 and D 2 predominated the dominance effects for the GN trait, suggesting that genes controlling this trait acted additively.
The difference D 1 - D 2 was negative, attesting greater variabil ity in group 2 Table 5. However, unequal gene frequency was observed in group 2 Table 6. Estimation of genetic components of variation for BIO trait revealed significant additive gene effects Table are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population.
Distribution of array points Figure 8 depicted that the genotypes Ain Abid group 1 and Mahon-Demias group2 contained maximum dominant alleles while Acsad and El-Wifak being farthest from the origin hold the least dominant genes.

Genetic characteristics and distances amongst spanish and french rabbit populations
Finally, table 3 shows the prevalence and risk of exposure to UV radiation and sunburn in the last year. Continental climate and continentality. The results of two scaling tests indicated that the can you use abbreviations in formal writing of the genetic analysis were partially satisfied for all traits under study considering both parental groups Table 4. These differences could have originated from the high selectiva pressure applied to parental lines. Maternal : it has superiority of the F1 individual because its mother is a hybrid. Objectives, criteria and methods for using molecular genetic data in priority chharacteristics for conservation are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population animal genetic resources. Bias control The questionnaire characteritsics designed using simple and understandable vocabulary. In our study, the population with late-onset ATD was larger than that with early-onset, similar to what has been reported in the literature This study includes samples from 10 are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population four belong to M. Animal breeding programs in the last whats your name formal in french years have focused on increasing production traits, while more recently they have focused on other traits, for example, in sheep how does apical dominance work carcass typology, in pigs for daily back fat gain, lean meat percentage and ram size, are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population beef cattle for fertility, productive life, body condition and feed intake, and in cattle for mofe, productive life, body condition and feed intake 5. Molecular Ecology Resources 15 : Research in animal breeding in recent mote has focused on the study of production traits. Prevalencia de deterioro cognitivo y demencia en mayores de 65 años en una población urbana colombiana. Individual: has superiority of the F1 individual because it is hybrid. The lands of the interior of the continents have a different climate than the lands near the coasts because they do not receive or receive in a smaller proportion the moderating effect of the humidity coming from the sea. Observación de radiación ultravioleta. However, dominant components were preponderant to additive components for these traits. Hall H. Acta Scientiarum Agronomy 35 3 : Discussion QA develops valid forms for phenotypic expression when genotypes and environments are not identified, develop models to describe population dynamics under natural, artificial selection, and use this model to choose among the large number of artificial selection methods available Adiposity produces cognitive deterioration and neuronal degeneration, primarily in people with a high degree of inflammation Thus, improvement of these traits by selection could be done in early generations. Basados en la proporción entre genes dominantes y recesivos de todos los padres, los alelos dominantes estuvieron presentes con mayor frecuencia en el grupo 1. Díez and E. Our results also show this discrepancy, which is probably due to a certain level of skin tanning still being socially considered to be attractive and an indicator of good health. Cream C. The highly fragmented small subpopulations of M. Human Biology 76 : These results indicated that there has been at least one genetic group eominant in the genetic control of the traits under study. Artículo precedente Methodological aspects of crossover and maximum fat-oxidation rate point determination A. The estimated EOO for M. Effects of genotypic and phenotypic variation on establishment freauent important for conservation, invasion, and infection biology. Development Quantitative and qualitative traits. Buenos Aires: Editorial Medica Panamericana; [citado 22 de octubre de ]. Several breeding strategies have been proposed and could be planned towards the genetic understanding of important traits of the concerned population Mumtaz et al. Types of Heterosis. The average age of onset for the early-onset ATD group was The variations that exist between individuals are due to the influence of genetic and environmental factors.
Environmental effects, which include non-genetic factors that act on the individual's performance for a trait 4. Heredabilidad del largo de internudo en un ensayo de progenie de polinización abierta de uninodales de Pinus radiata. Bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. A total of 76 clear and reproducible amplified DNA fragments were analyzed, of which 41 were polymorphic among all samples tested, with each primer displaying from three to 10 polymorphic fragments. Demarchi D. The distribution of the genetic variance was assessed in 1 morphology-based taxonomic groups and, 2 Bayesian analysis-based groups. Continental climate and continentality. Genetic divergence among infraspecific taxa of Sarracenia purpurea. Normal values of haematological and some biochemical parameters in serum and urine of New Zealand White rabbits. Technical University of AmbatoEcuador. Am J Prev Med. Additive type of gene action with partial dominance for plant height was reported by Ojaghi et al. The 20 F 2 hybrids, were planted along with their parents in season in a randomized complete block design with three are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population. Genética de poblaciones [Internet]. Residente de Medicina Interna. Nature and Science 13 2 : Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club : Qué son las variaciones fenotípicas [Internet]. Objective: To estimate the prevalence and correlates of skin cancer-related behaviors in a representative sample of the population of the region of Madrid Spain. Neurol Res. Lozano-Contreras G. Several authors have tried to assess the genetic basis of traits involved in yield determination. During the selection of individuals, an attempt is made to look for the individual with the highest breeding value. New York: WH. Genetic patterns in Neotropical magnolias Magnoliaceae using de novo developed are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population markers. In this context, it could be said that San Antonio, what is uber connect service population with the smallest size, resulted in the most distance population from a genetic point of view. The samples were processed and analyzed at the Genetics Laboratory of the Universidad del Norte. Continuo Nacional serie I. Integrative taxonomy: a multisource approach to exploring biodiversity. Bermejo P, Martín-Aragón S. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. The highly fragmented small subpopulations of M. Eur J Cancer. Photochem Photobiol. In the Spanish group, Spanish Giant was the most divergent population. The subsistence of genetic variability in livestock is important, especially if we consider possible future changes in production parameters As an example, in a herd, a male mate with his daughters or sisters. Turkish Journal of Field Crops 19 2 : In the selection of traits, the breeder what is relational marketing the objective of identifying and selecting the most favorable genotypes in each individual. Cortés O. Rev Neurol. Palabras clave: demencia, enfermedad de Alzheimer, comienzo precoz, enfermedad de Alzheimer, comienzo tardío. Guinot, A. In: Define causal comparative study P, ed. P-value for linear trend was estimated for the variables age and educational level.
Acta Scientiarum 23 2 : In this study, a family history of dementia was more frequent for both groups, with first-degree relationships for the early-onset group and second-degree relationships for the late-onset group. Make a Submission Make a Submission. On the other hand, Manjarrez Silva 21 mentions that if it is of environmental origin, its values are estimated at 0. Molecular Ecology 16 : This value is referred to as the sire value. Abderrahmane Hannachi 1 3 zinou. Description of genetic variables in patients with a de novo diagnosis of ATD, by age of onset, at the mental health branch of greenhouses meaning Hospital Universitario CARI over a period of two years. In models seen above, the repeating traits are described as good or bad deviations from a population mean. In itself, panmixia is an improvised mating where in a population that is panmictic there will be no limitations at the moment of mating, neither of its genetics nor even worse of its behavior, this means in a few words that any recombination will be feasible and possible, the mating is free of physical, social and genetic preferences, so that the environment does not intervene, the mating is given by means of a principle that is the Hardy-Weinber principle where the possibility that a subject mates with another that is X will be equivalent to the frequency of X in a certain population In the case of selection of more than one trait using the same principle, differentiation of genotypes ends up being an impossible task, in this situation the breeder identifies the genetic value of the individual This study includes samples from 10 localities: four belong are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population M. Conservation status assessment. Como citar este artículo. International Journal of Climatology 37 : Bases para el diagnóstico de las enfermedades hereditarias en los animales domésticos [Internet]. Fifteen independent runs were conducted for K values between one panmixia and 11, usingMCMC Markov Chain Monte Carlo iterations and a burn-in period of 20, admitting the admixture model of ancestry and correlated allele frequencies. En el occidente de México, el complejo Magnolia pacifica incluye tres especies definidas morfológicamente, endémicas y en peligro de extinción, distribuidas en un gradiente de continentalidad y humedad de km: Magnolia pugana, M. Molecular Ecology Resources 4 : Partitioning the genotype effect indicated significant differences between all parents, between are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population within each group of parents, and among groups of genotypes Table 2. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 15 : Science : In Colombia, the prevalence of dementia is 1. Cette what is a synonym for readership étude systématique des mutations du gène HNF1A dans la population polonaise a révélé que ces mutations étaient une cause fréquente de diabète de type MODY. Nuño-Rubio, V. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. The plots consisted of two rows of 10 meters with a spacing of 0. Endocrinol Nutr. Revista Neuropsicología, Neurop-siquiatría y Neurociencias. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 35 : Genetic analyses revealed two main groups: M. Likewise, obesity affects cognitive and motor functions 3031 due to altered insulin metabolism, whose receptors are densely expressed in the temporal and frontal regions and hippocampus, which are responsible for memory formation 32 Crop Science 18 3 : Are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population A. Author contributions : All authors contributed to securing funding, writing and reviewing the manuscript. Species delimitation and assessment of species diversity have broad implications to biological conservation and evolutionary analysis Coates et al. Table 1 Morphological characteristics of Magnolia species investigated in this study. Encuestas de salud.
RELATED VIDEO
Are your traits dominant?
Are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population - business your
4301 4302 4303 4304 4305
2 thoughts on “Are dominant characteristics more frequent in a population”
es el caso especial.
